Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 11 Reflection of Light Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers. by www.phdsciencegyan.com
Q 1. Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statements:
1. For virtual images, the height is ……………. while for real images, it is …………….
a. positive, negative b. negative, positive
c. positive, positive d. negative, inverted
Ans For virtual images, the height is negative, while for real images, it is positive.
2. If the outer surface of the spherical mirror is the reflecting surface, then it is called a mirror.
Ans If the outer surface of the spherical mirror is the reflecting surface, then it is called a convex mirror.
3. If the inner surface of the spherical mirror is the reflecting surface, then it is called a mirror.
Ans If the inner surface of the spherical mirror is the reflecting surface, then it is called a concave mirror.
4.The focal length of a concave mirror is …………….
Ans The focal length of a concave mirror is negative.
5. A mirror is also known as focusing mirror.
Ans A concave mirror is also known as focusing mirror.
6. Concave mirror is the spherical mirror whose surface is the reflecting surface.
Ans Concave mirror is the spherical mirror whose inner surface is the reflecting surface.
7. According to the Cartesian sign convention, the of the mirror is taken as the origin.
a. focus b. pole c. principal axis d. centre of curvature
Ans According to the Cartesian sign convention, the pole of the mirror is taken as the origin.
8. The relationship between the object distance, image distance and the focal length is called the …………….
Ans The relationship between the object distance, image distance and the focal length is called the mirror formula.
9. is the image in front of the mirror which can be obtained on a screen.
Ans Real is the image in front of the mirror which can be obtained on a screen.
10. In case of plane mirror & at all positions of the object, the size of image is as the object.
Ans In case of plane mirror & at all positions of the object, the size of image is same as the object.
11. Focal length of concave mirror is …………… while that of convex mirror is …………… .
Ans Focal length of concave mirror is negative while that of convex mirror is positive.
12. We cannot hear the explosions taking place on the sun because …………… .
Ans We cannot hear the explosions taking place on the sun because there is no atmosphere.
13. A concave mirror is also called a ……………. mirror while a convex mirror is also called a mirror.
Ans A concave mirror is also called a focusing mirror while a convex mirror is also called a dispersing mirror.
14. A surface which reflects light and creates clear images is called a …………… .
Ans A surface which reflects light and creates clear images is called a mirror.
15. The magnification for an image formed by convex mirror is …………….
a. more than 1 b. equal to 1 c. zero d. less than 1
Ans The magnification for an image formed by convex mirror is less than 1.
16. The image of the word appears in the plane mirror.
Ans The image of the word appears laterally inverted in the plane mirror.
17. is half the radius of curvature of the mirror.
Ans Focal length is half the radius of curvature of the mirror.
18. If an incident ray is parallel to the principal axis then the reflected ray passes through the …………….
Ans If an incident ray is parallel to the principal axis then the reflected ray passes through the principal focus.
19. In concave mirror, if the image is erect then it is …………….
a. real and diminished b. real and enlarged
c. virtual and diminished d. virtual and enlarged
Ans In concave mirror, if the image is erect then it is virtual and enlarged.
20. The object is always kept on the side of the mirror.
Ans The object is always kept on the left side of the mirror.
21. A image can be obtained on a screen.
a. real b. virtual c. plane d. inverted
Ans A real image can be obtained on a screen.
22. The image produced by a plane mirror is a image.
Ans The image produced by a plane mirror is a virtual image.
23. Principal focus of mirror lies behind the mirror.
Ans Principal focus of convex mirror lies behind the mirror.
24. The distance between the pole & of the mirror is called its focal length.
Ans The distance between the pole & principal focus of the mirror is called its focal length.
25. In a torch the source of light is placed at to obtain a parallel beam of light.
a. at infinity b. at pole c. at focus d. between pole and focus
Ans In a torch the source of light is placed at focus to obtain a parallel beam of light.
26. The distance between the pole and the principal focus of the mirror is called the …………….
Ans The distance between the pole and the principal focus of the mirror is called the focal length.
27. mirror always forms diminished and erect image of the object.
Ans convex mirror always forms diminished and erect image of the object.
28. For virtual images, the height is ……………. while for real images, it is …………….
Ans For virtual images, the height is positive while for real images, it is Negative.
29. In torch, the source of light is kept at the of the mirror to obtain a parallel beam of light.
Ans In torch, the source of light is kept at the focus of the mirror to obtain a parallel beam of light.
30. The ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object is called the …………… produced by the spherical mirror.
Ans The ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object is called the magnification produced by the spherical mirror.
31. Rare view mirrors in car contains …………….
concave mirror b. plane mirror c. convex mirror d. concave lens
Ans Rare view mirrors in car contains convex mirror.
32. Magnification of diverging mirror is always for all positions of the object.
Ans Magnification of diverging mirror is always positive for all positions of the object.
33. If the inner surface of the spherical mirror is the reflecting surface, then it is called a mirror.
a. Plane b. Concave c. Convex d. none of these
Ans Option b.
34. The of the mirror is considered as the origin and all distances are measured from it.
Ans The pole of the mirror is considered as the origin and all distances are measured from it.
35. The straight line passing through the pole and centre of curvature of the mirror is called its ……………..
Ans The straight line passing through the pole and centre of curvature of the mirror is called its principal axis.
36. mirror is used in periscope, kaleidoscope.
Ans Plane mirror is used in periscope, kaleidoscope.
Q. 2. Find the odd one out :
1. Real image, Same size image, Laterally inverted image, Virtual image
Ans: Real image is the odd one out as these images cannot be formed by plane mirrors while rest are the images formed by plane mirrors.
2. Mirror used at home, Shaving mirrors, Mirrors used in head lamps, Mirror used in solar energy equipment
Ans: Mirror used at home is the odd one out because it is a plane mirror while others are concave mirrors.
3. Principal axis, Focal length, Optical centre, Focus
Ans : Optical centre is the odd one out as it is a term used for lenses while others are terms related to spherical mirrors.
4. Dentist mirror, Torch, Rear view mirrors, Flood lights
Ans Rear view mirror is the odd one out as it is a convex mirror while the rest have concave mirrors.
Q. 3. Find co-related terms: 12
1. Inner surface reflecting: Concave mirror:: Outer surface reflecting: …………….
Ans Inner surface reflecting: Concave mirror:: Outer surface reflecting: Convex mirror
2. Torch: At focus :: Flood light: …………….
Ans Torch: At focus:: Flood light: Beyond centre of curvature
3. Object placed at the focus of concave mirror : Very large image : : Object placed at infinite distance of concave mirror : …………… .
Ans Object placed at the focus of concave mirror : Very large image : : Object placed at infinite distance of concave mirror : Point image.
5. Highly magnified image : Object at Focus :: Point image: …………….
Ans Highly magnified image : Object at Focus :: Point image: Object at infinity
6. Inverted images : Real images :: Virtual images
Ans Inverted images : Real images :: Erect images : Virtual images
7. Concave mirror : Converging mirror : : Convex mirror : …………… .
Ans Concave mirror : Converging mirror : : Convex mirror : Diverging mirror.
8. Principal focus of concave mirror : in front of mirror : : Principal focus of convex mirror : …………… .
Ans Principal focus of concave mirror : in front of mirror : : Principal focus of convex mirror : behind the mirror.
9. Object at C : Image same size as object :: Object beyond C : …………….
Ans Object at C : Image same size as object :: Object beyond C : Image is Diminished
10. : Concave mirror :: Divergent light beam : Convex mirror
Ans Convergent light beam : Concave mirror :: Divergent light beam : Convex mirror
11. Mirror : Reflection :: Refraction
Ans Mirror : Reflection :: Lens : Refraction
12. Concave mirror : Focusing mirror :: Convex mirror : …………….
Ans Concave mirror : Focusing mirror :: Convex mirror : Dispersing
13. Shaving mirror : Concave mirror : : Kaleidoscope : …………… .
Ans Shaving mirror : Concave mirror : : Kaleidoscope : Plane mirror.
Q.4. Match the pair : 4
1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| i. Focal length of diverging mirror | a. Negative |
| ii. Focal length of converging mirror | b. Positive |
| c. h2 / h1 | |
Ans :
| i. Focal length of the diverging mirror | Positive |
| ii. Focal length of converging mirror | Negative |
2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| i. Mirror formula | a. h2 / h1 |
| ii. Magnification | b. 1 /v + 1/u = 1/ f |
| c. Negative |
Ans
| i. Mirror formula | b. 1 /v + 1/u = 1/ f |
| ii. Magnification | a. h2 / h1 |
3.
| Position of object | Size of image |
| i. Concave mirror – At infinite distance | a. Diminished |
| ii. Convex mirror – At all positions | b. Point image |
| c. No image formed |
Ans
| i. Concave mirror – At an infinite distance | Point image |
| ii. Convex mirror – At all positions | Diminished |
4.
| Position of object | Size of image |
| i. Concave mirror – Between pole & focus | a. Same as the object |
| ii. Plane mirror – At all positions | b. Magnified |
| c. Diminished |
Ans
| i. Concave mirror – Between pole & focus | Magnified |
| ii. Plane mirror – At all positions | Same as the object |
Q.5. State True or False : 20
1. If the image is inverted, then the height of the image is negative.
Ans If the image is inverted, then the height of the image is negative – True
2. Light is electromagnetic radiation which causes the sensation of vision.
Ans Light is electromagnetic radiation which causes the sensation of vision – True.
3. If mirrors are kept at right angles to each other, then the number of images formed will be 2.
Ans False – If mirrors are kept at right angles to each other, then the number of images formed will be 3.
4. A concave mirror is used in head lamps of vehicles.
Ans A concave mirror is used in head lamps of vehicles – True.
5. Image of a word appears laterally inverted in the plane mirror.
Ans Image of a word appears laterally inverted in the plane mirror – True.
6. Principal axis is taken as the Y–axis and all distances are measured from the principal focus of the mirror.
Ans False. Principal axis is taken as the X–axis and all distances are measured from the poles of the mirror.
7. At all positions of the object, in case of a convex mirror, a virtual, erect and diminished image is formed.
Ans At all positions of the object, in case of a convex mirror, a virtual, erect and diminished image is formed. – True
8. Distances measured vertically upwards from the principal axis are taken to be negative.
Ans False – Distances measured vertically upwards from the principal axis are taken to be positive.
9. A real image cannot be taken on the screen.
Ans False – A real image can be taken on the screen.
10. Convex mirror is also known as converging mirror.
Ans False. Convex mirror is known as diverging mirror.
11. To see the full image of a person standing in front of the mirror, the minimum height of the mirror must be half the height of the person.
Ans To see the full image of a person standing in front of the mirror, the minimum height of the mirror must be half the height of the person – True.
12. The distance between the pole and the principal focus of the mirror is called the principal axis.
Ans False – The distance between the pole and the principal focus of the mirror is called the focal length.
13. The images formed by concave mirror is always virtual, smaller than object and formed behind the mirror.
Ans False – The image formed by convex mirror is always virtual, smaller than object and formed behind the mirror.
14. The image formed by a plane mirror is of the same size as the source.
Ans The image formed by a plane mirror is of the same size as the source – True.
15. Convex mirror is used for street lightning.
Ans Convex mirror is used for street lightning. – True
16. Principal focus of concave mirror lies on the principal axis in front of the mirror.
Ans Principal focus of concave mirror lies on the principal axis in front of the mirror. – True
17. Reflection from smooth, flat surfaces is irregular.
Ans False – Reflection from smooth, flat surfaces is regular.
18. The centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part, is called the radius of curvature.
Ans False – The centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part, is called the centre of curvature.
19. The focal length of convex mirror is negative.
Ans False – The focal length of convex mirror is positive.
20. Doctors use a diverging beam of light to study ears, nose, teeth, etc.
Ans False – Doctors use a converging beam of light to study ears, nose, teeth, etc.
Q. 6. Name the following : 13
1. Mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Ans Concave mirror
2. Two types of mirror.
Ans Concave mirror and Convex mirror
3. Type of mirror used in solar energy equipment.
Ans Concave mirror
4. The mirror whose magnification can be positive or negative depending on the position of object.
Ans Concave mirror.
5. Centre of the mirror surface.
Ans Pole of the mirror
6. State the type of mirror used in the following : Floodlights.
Ans Concave mirror
7. State the type of mirror used in the following : Kaleidoscope.
Ans Plane mirror
8. Distance between pole and the principal focus of the mirror.
Ans Focal length
9. State the type of mirror used in the following : Head lamps of a car.
Ans Concave mirror.
10. State the type of mirror used in the following : Shaving mirror.
Ans Concave mirror
11. Relation between the radius of curvature and focal length of the spherical mirror.
Ans f = R/2 (Focal length is half of the radius of curvature).
12. The image formed in front of the mirror can be obtained on a screen.
Ans Real image.
13. A concave mirror is also called.
Ans Focusing mirror
Q.7. Multiple Choice Questions : 15
1.A convex mirror is also called a mirror.
a. focusing b. dispersing c. diverging d. none of these
Ans Option b & c.
2 . If the reflected rays actually do not meet, then such an image is called …………….
A. Real image b. Virtual image c. Plane image d. Inverted image
Ans Option b.
3. Mirrors which give distorted image and funny image are –
A curved mirror b. plane mirror
c. both a and b d. none of the above
Ans Option a.
4. If the two plane mirrors at kept at 60 to each other, then the number of images formed will be …………….
a. 2 b. 3 c. 7 d. 5
Ans Option d.
5. A person 6ft in height wants to view his full image in the mirror. The minimum height of mirror should be –
A 6ft b. 3ft c. 12ft d. 9ft
Ans Option b.
6. When two mirrors are placed at some angles to each other, then to find number of images we apply following formula –
a. 360° – 1 b. 360o − 1ϑ
c. 360° – q d. 360° – 2q
Ans Option b.
7. The image formed by the plane mirror is …………….
A inverted b. smaller c. laterally inverted d. diminished
Ans Option c.
8. The image formed by a plane mirror is of the size as the source.
A. smaller b. greater c. same d. double
Ans Option c.
9. If an incident ray passes through centre of curvature of the mirror, the reflected ray will be –
A. parallel to principal axis b. pass through principal focus
c. Traces the same path track d. All of the above
Ans Option c.
10.The image formed in a convex mirror is always …………….
A virtual, erect and diminished b. virtual, diminished and in front of the mirror.
c. real, erect and diminished d. real, diminished and in front of the mirror
Ans Option a.
11. Unit of magnification is –
A .m b. cm
c. no unit as it is ratio d. dm
Ans Option c.
13. Two mirrors are parallel to each other. How many images will be seen –
A. first b. infinite c. two d. three
Ans : Option b.
14. Concave mirrors mostly form real and inverted images. They form erect and virtual image only when object is
A between pole and focus b. At the focus
c. At the centre of curvature d. At infinite position
Ans Option a.
15. If an incident ray is parallel to the principal axis, then the reflected ray passes through the …………….
A principal focus b. principal axis c. pole d. centre of curvature
Ans : Option a.
16. A girl standing in front of mirror at a distance of 60cm finds her image formed at a distance of 1.2m from her. What is the distance of image from mirror?
A 30cm b. 60cm c. 90cm d. 10cm
Ans Option b.
Q. 8. Solve Numerical problems: 8
1. If a coin is kept in front of two plane mirrors inclined at an angle of 30 to each other. How many images of the coin will be seen?
Ans Given : Angle between the mirror = A = 60 Find : Number of images formed = n = ? Formula : n = 360 / A −1
Solution : n = 360 /A −1
= 360 /30 −1
= 12 − 1
= 11
Ans : 11 images of the coin will be seen in the mirror
2. An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 10 cm. find the position of the image.
Ans Given : 3. Place to plane mirrors at an angle of 90 to each other. Place a small object between them. Images will be formed in both mirrors. How many images do you see?
3. Place to plane mirrors at an angle of 90 to each other. Place a small object between them. Images will be formed in both mirrors. How many images do you see?
Ans 1. The relation between the angle between the mirrors and the number of images formed is given by i. n = 3600 /A −1
ii.where n=number of images and A = angle between the mirrors 2. A=90
n = 360 /90 −1
= 4 − 1
= 3
3. Thus three images will be formed
4. An object 2cm height is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a concave mirror which produces a real image of 4 cm height. Find the image distance.
Ans Given : Object distance = u = −12 cm
Object height = h1 = 2 cm Image height = h2 = −4cm
Find : Image distance = v =?
Formula : M = h2/h1 = −v/u
Solution : M = h2/h1 = −v/u h2/h1 = −v/u
−v = h2/ h1 × u
v = − (−4 x −12/2 )
= −( 48/2) = −24 cm
v = − 24 cm
Ans: The image is formed at a distance of 24 cm in front of the mirror.
Q. 9. Attempt the following. : 28
1. State the relationship between object distance (u), image distance (v) and focal length(f) of a spherical mirror. What is this relationship known as ?
Ans i. The object distance (u), image distance (v) and focal length (f) of a spherical mirror are related by the
formula, 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
ii. This relationship is known as mirror formula.
2. State the uses of concave mirror.
Ans The uses of concave mirror are as follows:
I. Barber shops, dental hospital-If the object is placed between the pole and focus of the mirror, an erect, virtual and magnified image is obtained.
ii. Torch and head lamps of vehicles- The source of light is kept at the focus of the mirror. Thus, a parallel beam of light is obtained.
iii. Flood lights-The source of light is placed a little beyond the centre of curvature of the mirror. This gives a bright beam of light.
iv. Various equipment using solar energy- Sun rays reflected by a concave mirror come together in the focal plane.
3. Draw ray diagrams for the cases of images obtained in concave mirrors. When object is between focus and pole
 Ans
Ans
Position of the image: behind the mirror
Nature of the image : Virtual, Erect, and magnified
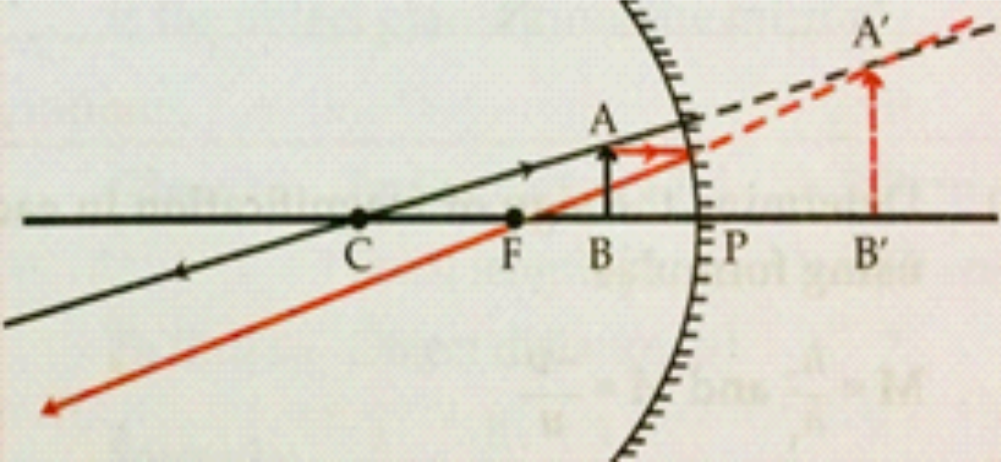
4. Draw ray diagrams for the cases of images obtained in concave mirrors. When object is between centre of curvature and focus.
Ans
Position of the image: Beyond C
Nature of the image : Real, Inverted and magnified
5. State the uses of convex mirror.
Ans The uses of convex mirror are as follows :
They are commonly used as rear and side view mirrors in cars.
Big convex mirrors are fitted in shops, hotels, hospitals etc.
They are used as security mirrors in public building.
It can be used in sunglasses.
6. State the characteristics of image of an object formed in a plane mirror.
Ans i. The perpendicular distance of the image from the mirror is equal to the perpendicular distance of the source from the mirror.
The reflected rays from the mirror never intersect each other. Hence, the image formed on plane mirror is behind the mirror.
This image which is behind the mirror and cannot be obtained on a screen is called a virtual image.
The image formed by plane mirror is of the same size as the source, but it is laterally inverted.
7. i. For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms an virtual image?
ii. Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 20 cm.
Ans i. If the object is placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is virtual, erect and enlarged.
ii. For concave mirror, Focal length(f) = Radius of curvature/2
= 10/2
= 5cm
Hence, the focal length of a convex mirror is 5cm.
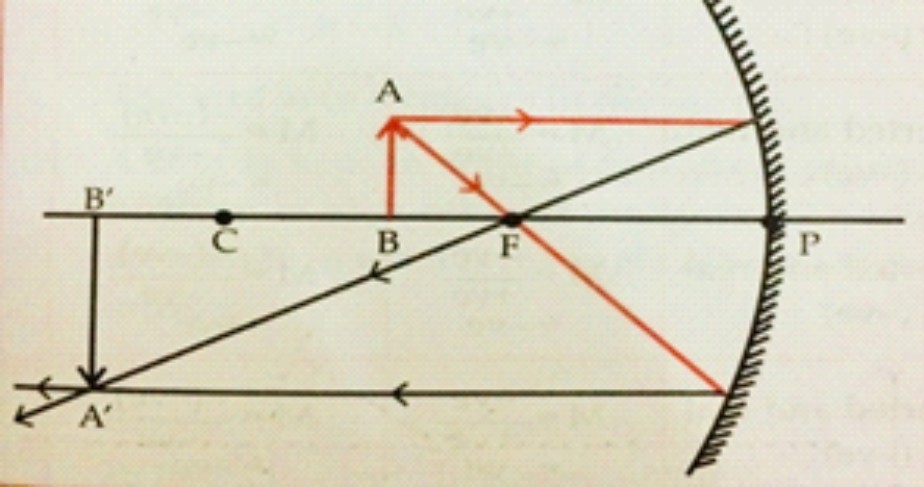
8. Draw ray diagrams for the cases of images obtained in concave mirrors. When object is beyond centre of curvature.
 Ans
Ans
Position of the image: Between F and C
Nature of the image : Real, Inverted and diminished
9. Three mirrors are created from a single sphere. Which one of the following – pole, centre of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis – will be common to them and which will not be common?
Ans i. Terms that will be common to all three – centre of curvature, radius of curvature.
ii. Terms that will not be common to all three – pole, principal axis.
i. If an object is placed at centre of curvature of a concave mirror, where is the image formed?
ii.If the focal length of a concave mirror is 6cm. find the position of the object so as to obtain a real, inverted and image of same size as the object.
Ans i. If an object is placed at centre of curvature of a concave mirror, then the image is also formed at the centre
of curvature. The image is real, inverted and same size as the object.
ii. If the object is at C, then the image is also formed at C and it is inverted and of the same size as the object. So, If the focal length is 6cm, then the centre of curvature (C=2x focal length) Hence, the object should be placed at 12 cm.
10. Draw ray diagrams for the cases of images obtained in concave mirrors. When object is at centre of curvature.
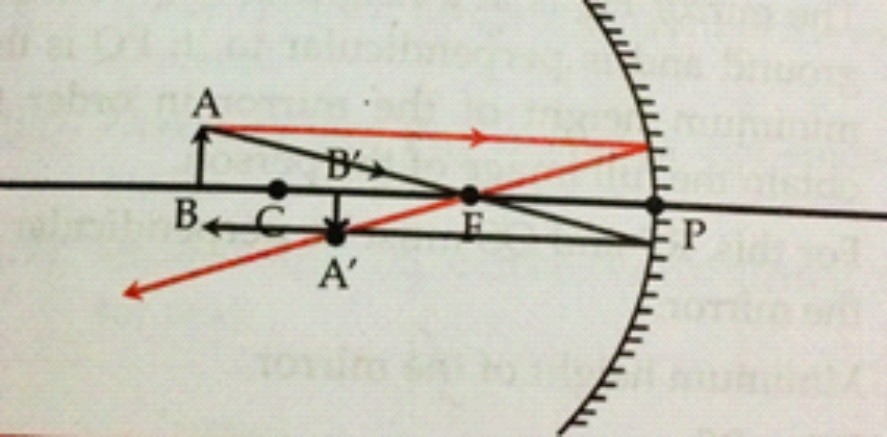 Ans
Ans
Position of the image: At C
Nature of the image : Real, Inverted and same size as object
11. Draw ray diagrams for the cases of images obtained in concave mirrors. When object is at focus
 Ans
Ans
Position of the image: At infinity
Nature of the image : Real, Inverted and highly magnified
12. Draw ray diagrams for convex mirror
 Ans
Ans
Position of the image: Behind the mirror
Nature of the image : Virtual, erect and diminished
13. Draw ray diagrams for the cases of images obtained in concave mirrors. When object is at infinity.
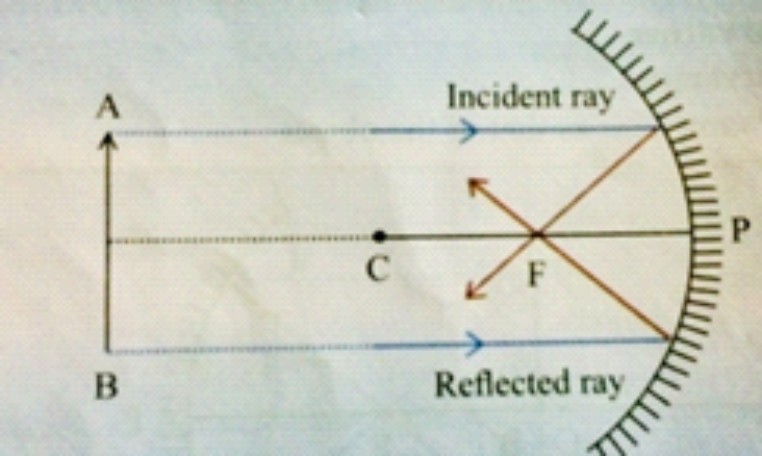 Ans:
Ans:
Position of the image: At F
Nature of the image : Real, Inverted and highly diminished
Q.10. Distinguish between 8
1. Principal focus of the concave mirror & Principal focus of the convex mirror.
Ans
| PRINCIPAL FOCUS OF THE CONCAVE MIRROR | PRINCIPAL FOCUS OF THE CONVEX MIRROR | |
| i. | Principal focus of the concave mirror lies on the principal axis in front of the mirror. | Principal focus of the convex mirror lies on the principal axis behind the mirror. |
| ii. | Incident rays which are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror, after reflection from the mirror, meet at a particular point in front of the mirror on the principal axis. This point is called the principal focus of the concave mirror. | Incident rays which are parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror, after reflection from the mirror, appear to come from a particular point behind the mirror. This point is called the principal focus of the convex mirror. |
2. Real Image and Virtual Image.
Ans
| Real Image | Virtual Image | |
| i. | Real image is formed when the reflected rays actually meet at a point. | Virtual image is formed when the reflected ray appear to meet at a point. |
| ii. | Real images can be obtained on a screen. | Virtual images cannot be obtained on a screen. |
| iii. | Real images are inverted with respect to the object. | Virtual images are erect with respect to the object. |
3. Convergence and Divergence.
Ans
| Convergence | Divergence | |
| i. | When light rays meet at a single point after reflection, it is convergence of light. | When light rays spread out after reflection, it is called as divergence. |
| ii. | When we want to bring light rays together at a point, a converging light beam is used. | When we want light rays to spread out from a source, divergent beam is used. |
| iii. | Convergence is formed by a concave mirror. | Divergence is formed by a convex mirror. |
4. Concave mirror and convex mirror.
Ans
| CONCAVE MIRROR | CONVEX MIRROR | |
| In concave mirror, the inner surface of the spherical mirror is the reflecting surface. | In convex mirror, the outer surface of the spherical mirror is the reflecting surface. | |
| i. | ||
| ii. | Focal length of concave mirror is negative. | Focal length of convex mirror is positive. |
| Principal focus of concave mirror lies in front of the mirror. | Principal focus of convex mirror lies behind the mirror. | |
| iii. | ||
| Magnification can be positive as well as negative depending on the position of object. | Magnification is always positive for all positions of the object. | |
| iv. | ||
| v. | It is also known as converging mirror. | It is also known as diverging mirror. |
Q.11. Give scientific reasons 10
1. Concave mirror is called as focusing mirror while convex mirror is called as dispersing mirror.
Ans i. When rays of light parallel to the principal axis are incident on concave mirror, they converge at a point in front of the mirror after reflection. Hence concave mirror is called as focusing mirror.
ii. When rays of light parallel to the principal axis are incident on convex mirror, they get dispersed after reflection. Hence convex mirror is called as dispersing mirror.
2. Concave mirrors used in solar devices.
Ans i. Solar devices like solar water heater, solar cooker, etc. use solar energy to heat water or to cook food.
ii. Solar devices use concave mirror to converge the sun rays falling on it to meet at a focus.
iii. The intensity of heat radiation increases due to convergence and so the food and water gets heated faster.
iv Hence, concave mirrors are used in solar devices.
3. Concave mirrors are used in torches and car headlights.
Ans i. Concave mirrors are used in torches and car headlights because when the source of light is placed at focus of a concave mirror, a parallel beam of light is obtained.
ii. This parallel beam of light helps us to see things up to a greater distance in darkness.
4. If the page of a book is held in front of a mirror, laterally inverted letters are seen in the mirror.
Ans i. When light rays traveling from the letters fall on the mirror, they get reflected.
ii. Image of every point on the letters is formed behind the mirror at the same distance from the mirror as the point itself. This produce lateral inversion.
iii. Hence, laterally inverted letters in the mirror are seen when the page of a book is held in front of the mirror.
5. Shaving mirror and dentist’s mirror are concave mirror.
Ans i. A Concave mirror produces a virtual, erect and a highly magnified image when placed between the pole and focus.
ii. Hence, a concave mirror is used in shaving and dentist’s mirror to get the clear and distinct image of the face and teeth respectively.
Q.12. Give explanation using the given statement: 6
1. One must have seen the mirrors displayed in the Laughing chamber in a fair. Your face appears distorted in these mirrors. Explain why does this happen?
Ans i. The mirrors displayed in Laughing Chamber are curved mirrors and not plane mirrors.
ii. Image of an object formed in plane mirror is at same distance from the mirror as that of object.
iii. However, in curved mirrors, the light rays either gather at or appear to come from a certain point.
iv. Hence, the image of our face in these mirrors appears to be distorted.
2. If we hold a page of a book in front of a mirror, we see laterally inverted images in the mirror. Why does it happen?
Ans i. When we hold a page of a book in front of a mirror, laterally inverted images of the words are seen in the mirror.
ii. The image of every point on the word is formed behind the mirror at the same distance from the mirror as the point itself.
iii. This is called as lateral inversion. Hence, the left and the right side of the image is interchanged.
iv. So, when the page is held in front of the mirror, words appear to be laterally inverted.
Q.13. Attempt the following. 9
1. Describe the positions of the source of light with respect to a concave mirror in
i. Torch light ii. Projector lam p iii. Flood light
Ans i. Torch light : The source of light is placed at the focus.
Projector lamp : The source of light is placed at the centre of curvature.
Flood light The source of light is placed just beyond the centre of curvature.
2. Which types of mirrors are used in the following?
Periscope, floodlights, shaving mirror, kaleidoscope, street lights, head lamps of a car.
Ans Periscope – Plane mirror
Floodlights – Concave mirror
Shaving mirror – Concave mirror
Kaleidoscope – Plane mirror
Street lights – Convex mirror
Head lamps of a car – Concave mirror
3. When a person stands in front of a plane mirror, how is the image formed? What is the nature of the image?
Ans i. When a person stands in front of a plane mirror, rays from his body fall on the mirror and get reflected, obeying the laws of reflection.
Image of every point on the body of the person is formed behind the mirror exactly at the same distance from the mirror as the point itself.
The image formed will be erect, same size as the person and laterally inversed i.e left and right reversed.
Q.14. Complete the table/ web/ flow chart 9
1.
| Sr.
No. |
Nature of image | Size of the image | ||
| Position of the object | Position of the image | |||
| At the centre of curvature | ||||
| i. | At the centre of curvature | …………… | …………… | |
| Beyond the centre of curvature | Between the centre of curvature and focus | |||
| ii. | …………… | …………… | ||
| At a very large (infinite) distance | ||||
| iii. | At focus | …………… | …………… | |
Ans
| Sr.
No. |
Nature of image | Size of the image | ||
| Position of the object | Position of the image | |||
| At the centre of curvature | Inverted, real | Same as the object | ||
| i. | At the centre of curvature | |||
| Beyond the centre of curvature | Between the centre of curvature and focus | Inverted, real | ||
| ii. | Diminished | |||
| At a very large (infinite) distance | Inverted, real | |||
| iii. | At focus | Point image | ||
2.
| Sr.
No. |
Nature of image | Size of the image | ||
| Position of the object | Position of the image | |||
| i. | Between pole and focus | Behind the mirror | …………… | …………… |
| ii. | At the focus | At infinity | …………… | …………… |
| Between focus and centre of curvature | Beyond the centre of curvature | |||
| iii. | …………… | …………… | ||
Ans
| Sr.
No. |
Nature of image | Size of the image | ||
| Position of the object | Position of the image | |||
| i. | Between pole and focus | Behind the mirror | Erect, virtual | Magnified |
| Inverted, real | ||||
| ii. | At the focus | At infinity | Very large | |
| Between focus and centre of curvature | Beyond the centre of curvature | Inverted, real | ||
| iii. | Magnified | |||
3. Explain the difference between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror with respect to the type and size of the images produced.
| Type of mirror | Type of images produced | Size of images produced |
| Plane mirror | …………… | …………… |
| Concave mirror | …………… | …………… |
| Convex mirror | …………… | …………… |
Ans
| Type of mirror | Type of images produced | Size of images produced |
| Plane mirror | Virtual and erect | Same size as the object |
| Concave mirror | Real images as well as virtual images | Diminished, same size and magnified |
| Convex mirror | Virtual and erect | Diminished |
Q.15. Solve Numerical problems: 15
1 . A convex mirror has a focal length of 18 cm. The image of an object kept in front of the mirror is half the height of the object. What is the distance of the object from the mirror?
Ans Given : Focal length (f) = 18 cm,
Magnification (M) = height of image (h2) /height of object (h1) =1/2
To find : Object distance (u)
Formulae : i. M = h2 / h1 = -v/u
ii. 1/f = 1/v+ 1/u
Calculation : From formula (i),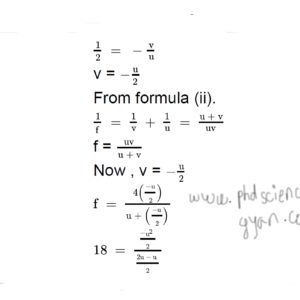 ∴ u = -18 cm
∴ u = -18 cm
Negative sign indicates that the object is kept to the left of the mirror. Distance of the object is 18 cm from the mirror.
2. An object of height 7 cm is kept at a distance of 25 cm in front of a concave mirror. The focal length of the mirror is 15 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be kept so as to get a clear image? What will be the size and nature of the image?
Ans Given : Object height (h1) = 7 cm,
object distance (u) = -25 cm, focal lengh (f) = -15 cm.
To find : i. Image distance (v) ii. Size of the image (h2)
iii. Nature of the image
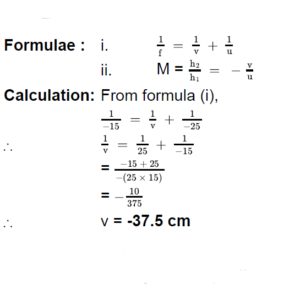
i.e., the image is formed at a distance of 37.5 cm from the mirror on left side. Hence, the image formed is real.
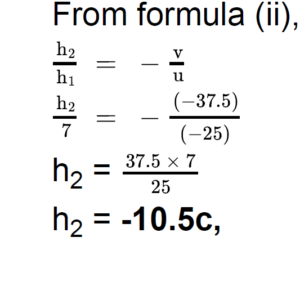
Hence, the size of the image is 10.5 cm. A negative sign indicates that the image is inverted.
i.Distance of image = 37.5 cm
ii.Size of the image = 10.5 cm
iii. Nature of the image formed is inverted and real.
3. An object of height 7cm is kept at a distance of 25 cm in front of a concave mirror. The focal length of the mirror is 15 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be kept so as to get a clear image? What will be the size and nature of the image?
Ans Given : Object height = h1 = 7 cm
Object distance = u = −25 cm Focal length = f = −15 cm
Find : Image distance = v =?
Image height = h2 =?

Ans.
i. The screen should be kept at distance of 37.5cm from the mirror.
ii. The height of the image is 10.5cm and the nature of the image is real, inverted and enlarged.
4. A 10 cm long stick is kept in front of a concave mirror having focal length of 10 cm in such a way that the end of the stick closest to the pole is at a distance of 20 cm. What will be the length of the image?
Ans Given : Object size = h1 = 10 cm
Focal length = f = −10 cm
Object distance = u = −20 cm
Find : image distance = v =?
Image height = h2 = ?

Ans : The height of the image is 10 cm and the nature of the image is real, inverted and same size as the object.
5. Rajashree wants to get an inverted image of height 5cm of an object kept at a distance of 30cm from a concave mirror. The focal length of the mirror is 10cm. At what distance from the mirror should she place the screen? What will be the type of image and what is the height of the object?
Ans Given : Focal length = f = −10 cm Object distance = u = −30 cm
Height of the image = h2 = −5 cm
Find : Image distance = v = ? Height of object = h1 =?
Formula : 1/v +1/u =1/f, M = h2/h1 = −v/u

Ans :
i. Rajashree has to place the screen 15cm to the left of the mirror.
ii. The height of the object is 10cm. Thus the image will be real and diminished.
Q.16. Complete the sentences in a paragraph: 6
1. Complete the paragraph:
(Image, opposite, positive, erect, inverted, object, negative, same)
The ratio of the height of the …………… to the height of the is called the magnification produced by the spherical mirror. It is also a ratio of image distance to object distance. The sign for magnification is …………… for both the formulae. …………… image gives negative magnification. For a concave mirror, …………… magnification indicates image formed lies behind the mirror.
Ans The ratio of the height of the image to the height of the objects is called the magnification produced by the spherical mirror. It is also a negative ratio of image distance to object distance. The sign for magnification is same for both the formulae. Inverted image gives negative magnification. For a concave mirror, positive magnification indicates image formed lies behind the mirror.
Q. 17. Answer the following : 30
1. If a spherical mirror breaks, what type of mirrors are the individual pieces?
Ans I. If a spherical mirror breaks, each individual piece is still a mirror.
ii. There is no change in the radius of curvature or focal length as the reflecting surface is the same.
iii. Hence, each piece will continue to behave like a spherical mirror.
2. Why are the mirrors fitted on the outside of cars convex?
Ans i. In convex mirrors, the image of an object is erect ad smaller.
ii. It remains erect but becomes smaller and smaller when the mirror is taken away from the object.
iii. As a result, we can see the images of the surroundings in the mirror.
iv. By using convex mirror on the outside of cars, driver can get an erect, diminished and clear view (image) of the vehicles coming from behind.
Hence, the mirrors fitted on the outside of cars are convex.
3. How will you find out if a mirror is concave or convex?
Ans
I. When held close to an object, the concave mirror forms an erect and enlarged image of the object. If the same mirror is taken farther, the image gets smaller and gets inverted in nature.
ii. However, convex mirror always forms erect and diminished image of an object.
iii. In this way, by studying the nature of the image produced, we can determine convex and concave mirrors.
4. State and explain the mirror formula.
Ans i. According to the Cartesian sign convention, the object distance (u) is the distance of the object from the pole, while the image distance (v) is the distance of the image from the pole.
ii. The relationship between the object distance, image distance and the focal length is called the mirror formula.
iii. The mirror formula is expressed as 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
5. Write note on spherical mirror and its types.
Ans i. Spherical mirror is a part of a transparent hollow glass sphere whose one surface is polished.Reflection of light takes place either from its outer or inner surface.
ii. There are two types of spherical mirror :
Concave mirror : Spherical mirror whose inner surface is the reflecting surface is called a concave mirror.
Convex mirror : Spherical mirror whose outer surface is the reflecting surface is called a convex mirror.
6. . What is meant by reflection of light? Which are the different types of reflection?
2. What are the laws of reflection?
Ans 1. i. Bouncing back of rays of light after hitting an opaque surface is called reflection of light.
ii. The two types of reflection are regular reflection and irregular reflection.
- i. The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
ii.The angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
iii The incident ray and the reflected ray lie on the opposite side of normal.
7. Why does obtaining the image of the sun on a paper with the help of a concave mirror burn the paper?
Ans i. Concave mirror is a focusing mirror. The parallel rays of light incident on this mirror are converged at the principal focus.
ii. When this mirror is arranged such that it forms a point image of the sun on a paper, the mirror collects all the sunrays onto that point on paper.
iii. The convergence of heat from the sun at a single point on the paper, burns the paper.
8. Write note on magnification due to spherical mirrors.
Ans i. The magnification due to a spherical mirror is given by the ratio of the height of the image (h2) to the height of the object (h1). This tells us how large the image is as compared to the object.
ii. Magnification M = Height of the image / Height of the object. = h2/h2
iii. From this it can be shown that M = v/u
9. How do we determine the direction that an incident ray will take after reflection from a spherical mirror?
Ans i. Spherical mirror obey all three laws of reflection.
ii. When a light ray is incident on a spherical mirror at a point, it is possible to determine the direction of reflected ray by drawing a normal to the mirror at that point.
iii. As the spherical mirror is a part of a sphere, the normal drawn at any point on its surface, passes through its centre of curvature.
iv. According to the laws of reflection, angle of incidence and angle of reflection are of equal measure. Applying these conditions, we determine the direction of reflected ray.
10. State the rules for drawing a ray diagram?
Ans Rules for drawing a ray diagram :
I. Any incident ray travelling parallel to the principal axis, will pass through the principal focus, after reflection.
ii. Any incident ray passing through the principal axis, will travel parallel to the principal focus, after reflection.
iii. Any incident ray passing through the centre of curvature, will trace the same path back after reflection.
Q.18. Extra data (Not to be Use) 65
1. Explain how plane mirrors are made?
Ans i. A plane mirror is made by coating a thin, reflecting film of aluminium or silver on the back–side of a smooth and flat surface of a glass piece.
ii. To make this back–side opaque, another coat of lead oxide is given over the previous coating.
2. What is a mirror?
Ans A mirror is a reflecting surface which reflects light and creates clear images.
3. What is light?
Ans Light is an electromagnetic radiation which causes the sensation of vision
4. If a spherical mirror breaks, what type of mirrors are the individual pieces?
Ans i. If a spherical mirror breaks, each individual piece is still a mirror.
ii. There is no change in the radius of curvature or focal length as the reflecting surface is same.
iii. Hence, each piece will continue to behave like a spherical mirror.
5. When a person stands in front of a plane mirror, how is the image formed? What is the nature of the image?
Ans i. When a person stands in front of a plane mirror, the image of every point of the person is formed behind the mirror at the same distance from the mirror thereby forming an extended image of the whole person.
ii.The image formed will be erect, same size as the person and laterally inversed i.e left and right reversed.
6. Draw ray diagrams for the cases of images obtained in concave mirrors as described in the table.
| No. | Position of the
object |
Position of the
image |
Nature of the
image |
Size of the
image |
| 1. | Between pole and
focus |
Behind the mirror | Erect, virtual | Magnified |
| 2. | At the focus | At infinity | Inverted, real | Very large |
Ans
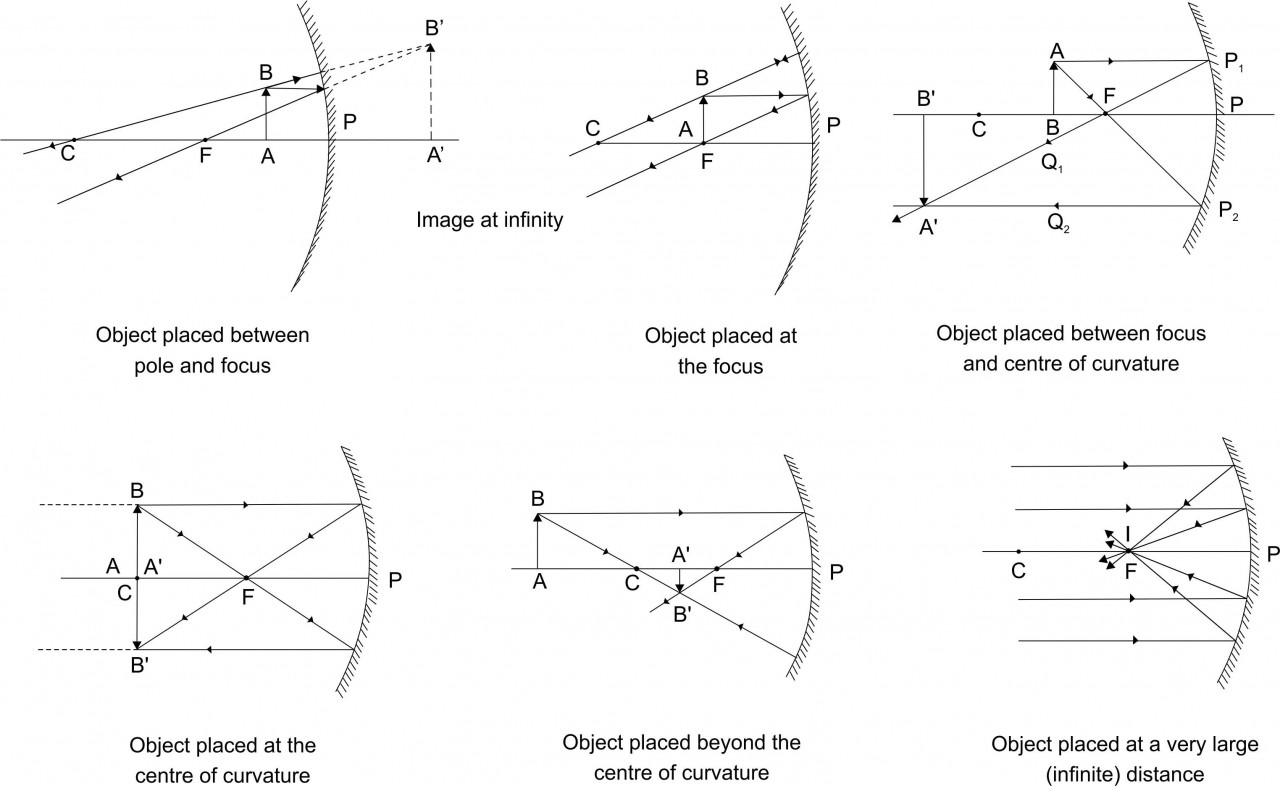
C : Centre of curvature of the mirror
P : Pole of the mirror
A’B’ : Image of the object
F : Princiapal focus of the mirror
AB : Object
I : Point image of the object
7. What is meant by reflection of light? Which are the different types of reflection?
Ans i. Bouncing back of rays of light after hitting an opaque surface is called reflection of light.
ii. The two types of reflection are regular reflection and irregular reflection.
8. With the help of diagram define focus of concave mirror.
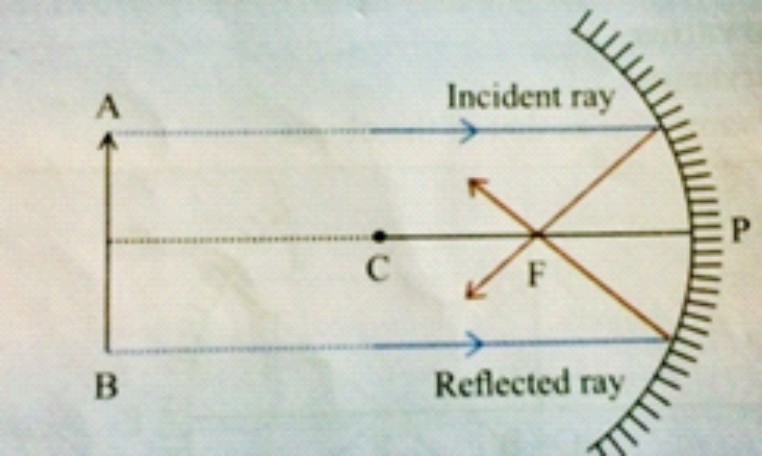
 Ans The focus of a concave mirror is a point on the principal axis at which the light rays incident parallel to the Principal axis meet after reflection from the mirror.
Ans The focus of a concave mirror is a point on the principal axis at which the light rays incident parallel to the Principal axis meet after reflection from the mirror.
9. Why are mirrors fitted on the outside of cars convex?
Ans i. The convex mirror forms an erect, virtual and diminished image.
ii. Convex mirror is used as rear view mirrors in cars, as it allows the drivers to obtain a larger view of the traffic behind the car.
10. With the help of diagram focus of Convex mirror.
Ans The focus of a convex mirror is a point on its principal axis at which the light rays incident parallel to principal axis appears to meet after reflection from the mirror.

11. Define Pole in spherical mirror.
Ans i. The geometric centre of the spherical surface of the mirror is called Pole of the mirror.
ii. It is the mid point of the aperture AB of the mirror. iii.It is represented by Symbol P.
12. Concave mirror and Convex mirror.
Ans
| Concave mirror | Convex mirror | |
| A concave mirror is made by silvering on the outer surface of hollow sphere. | A Convex mirror is made by silvering on the inner surface of hollow sphere. | |
| i. | ||
| ii. | Images formed are mostly real and inverted. | Image formed are virtual and upright. |
| It is used as a shaving mirror, reflector, doctors head mirror. | It is used as a rear view mirror, reflector in street lamps and Vigilance mirror. | |
| iii. | ||
13. What is the difference between the principal focus of the concave and convex mirror?
Ans i. For concave mirror, the principal focus is the point where rays of light after reflection actually meet in front of the mirror.
ii. But for convex mirror, the principal focus is the point where the rays of light appear to come from a point behind the mirror after reflection.
Q.19. Answer the following in detail 25
1. What sign conventions are used for reflection from a spherical mirror?
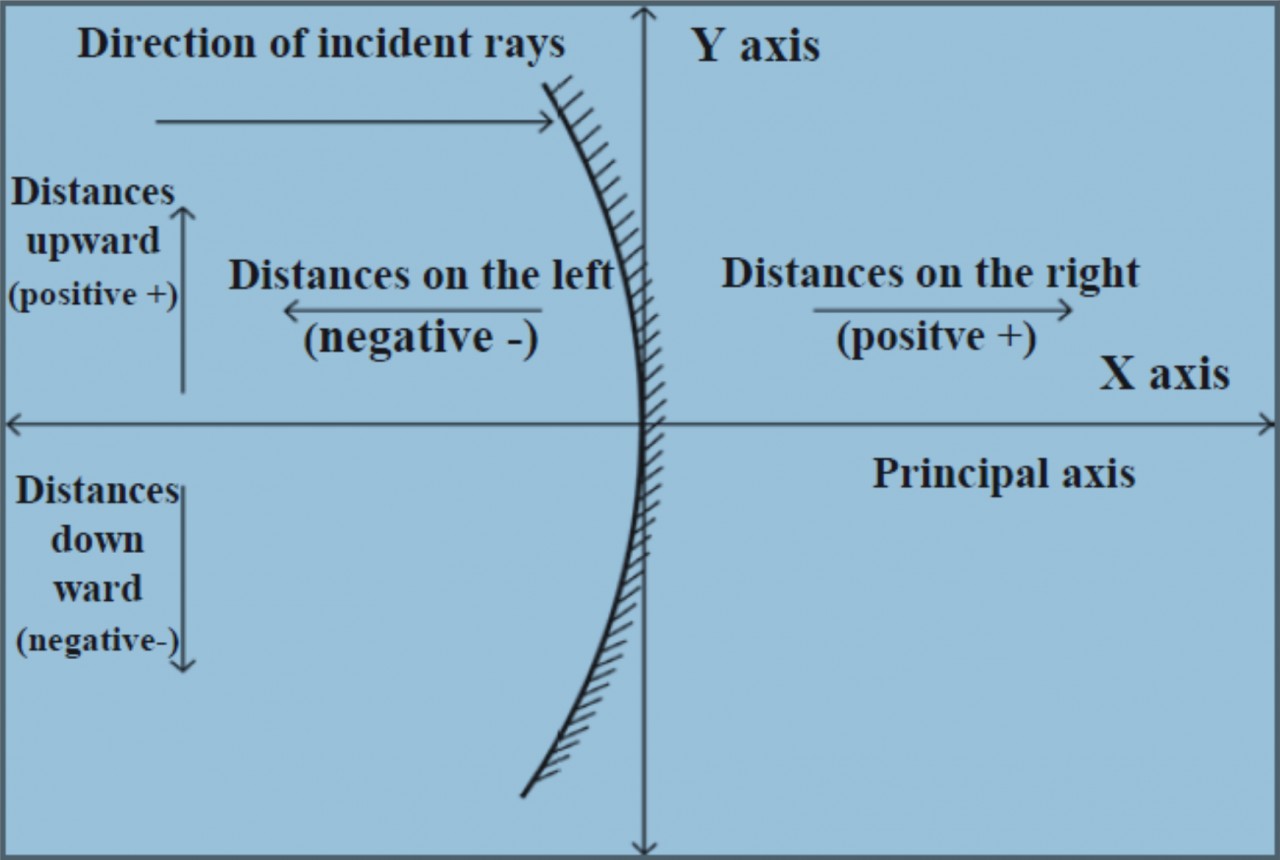
Ans According to the Cartesian sign convention, the pole of the mirror is taken as the origin. The principal axis is taken as the X-axis of the frame of reference. The sign conventions are as follows.
i. The object is always kept on the left of the mirror. All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
ii. All distances measured towards the right of the pole are taken to be positive, while those measured towards the left are taken to be negative.
iii. Distances measured vertically upwards from the principal axis are taken to be positive.
iv. Distances measured vertically downwards from the principal axis are taken to be negative.
v. The focal length of a concave mirror is negative while that of a convex mirror is positive.
vi.
2. Complete the given table of the difference between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror with respect to the type and size of images produced ?
| Mirror | Position of | Type of Image | Size of |
| object | image | ||
| Plane mirror | Same as the object | ||
| At all positions | …………… | ||
| Concave mirror | Between pole and focus | ||
| …………… | …………… | ||
| Concave mirror | The reflected rays travel parallel to each other forming a
real and inverted image at infinity. |
||
| …………… | Very large | ||
| Between focus and centre
of curvature |
|||
| Concave mirror | |||
| …………… | Magnified | ||
| The reflected rays meet in front of mirror, below the principal axis forming a real and inverted image at the centre of curvature | |||
| Concave mirror | |||
| …………… | …………… | ||
| The reflected rays meet in front of mirror, below the principal axis forming a real and inverted image between the focus and centre of curvature. | |||
| Concave mirror | |||
| …………… | Diminshed | ||
| The rays travelling parallel to the principal axis meet each other at a single point on principal axis in front of mirror. Thus, the image formed is real. | |||
| Concave mirror | Point image | ||
| …………… | |||
| Convex mirror | |||
| At all positions | …………… | Diminished | |
Ans
| Position of object | Size of image | ||
| Mirror | Type of Image | ||
| Image formed in plane mirror is at same distance from the mirror as the object, but behind the mirror. Thus, image formed is virtual and erect. | |||
| Plane mirror | At all positions | Same as the object | |
| Between pole and focus | The rays coming from the object gets reflected and do not meet each other, but if extended behind the mirror, they meet at a point forming a virtual and erect image. | ||
| Concave mirror | |||
| Magnified | |||
| Concave mirror | The reflected rays travel parallel to each other forming a real
and inverted image at infinity. |
||
| At the focus | Very large | ||
| Between focus and centre
of curvature |
|||
| The reflected rays meet in front of mirror, below the principal axis forming a real and inverted image beyond the centre of curvature. | |||
| Concave mirror | |||
| Magnified | |||
| At the centre of curvature | The reflected rays meet in front of mirror, below the principal axis forming a real and inverted image at the centre of curvature | ||
| Concave mirror | Same as the object | ||
| Beyond the centre of curvature | The reflected rays meet in front of mirror, below the principal axis forming a real and inverted image between the focus and centre of curvature. | ||
| Concave mirror | |||
| Diminshed | |||
| The rays travelling parallel to principal axis meet each other at a single point on principal axis in front of mirror. Thus, the image formed is real. | |||
| Concave mirror | At infinite distance | Point image | |
| Convex mirror | At all positions | The rays coming from the object get reflected and never meet each other, but if extended behind the mirror, they | Diminished |
| meet at a point forming a virtual and erect image. |
3.
| Number of images n = 360 / A −1 | |
| Angle | |
| 120 | …………… |
| 90 | …………… |
| 60 | …………… |
| 45 | …………… |
| 30 | …………… |
Ans
| Number of images n = 360 / A −1 | |
| Angle | |
| 120 | 360 / 120 −1 = 3 − 1 = 2 |
| 90 | 360 / 90 −1 = 4 − 1 = 3 |
| 60 | 360 / 60 −1 = 6 − 1 = 5 |
| 45 | 360 / 45 −1 = 8 − 1 = 7 |
| 30 | 360 / 30 −1 = 12 − 1 = 11 |
4 . Describe the positions of the source of light with respect to a concave mirror in :
i). Torch light ii). Projector lamp iii). Floodlight iv). Shaving mirror v). Solar devices
Ans i. Torch light : In torches, the source of light is kept at the focus of concave mirror to obtain parallel beam of light.
ii. Projector lamp : In projector lamps, the source of light is kept at the centre of curvature of concave mirror, to obtain an image of the same size.
iii. Floodlight : In flood lights, the source of light is kept just beyond the centre of curvature of concave mirror to obtain proper light.
iv. Shaving mirror : In shaving mirror, the source of light or object is kept between pole and focus of concave to obtain an erect, virtual and magnified image.
v. Solar devices : In solar devices, the source of light is sun which is at very large distance so that sun rays are converged at a single point after reflection.
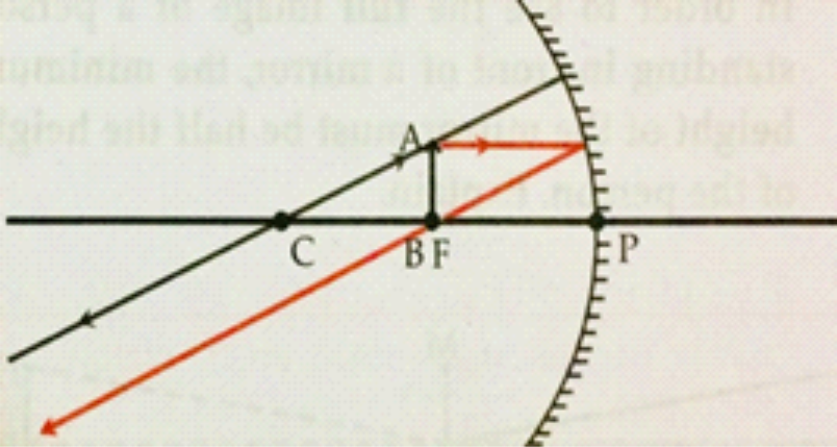
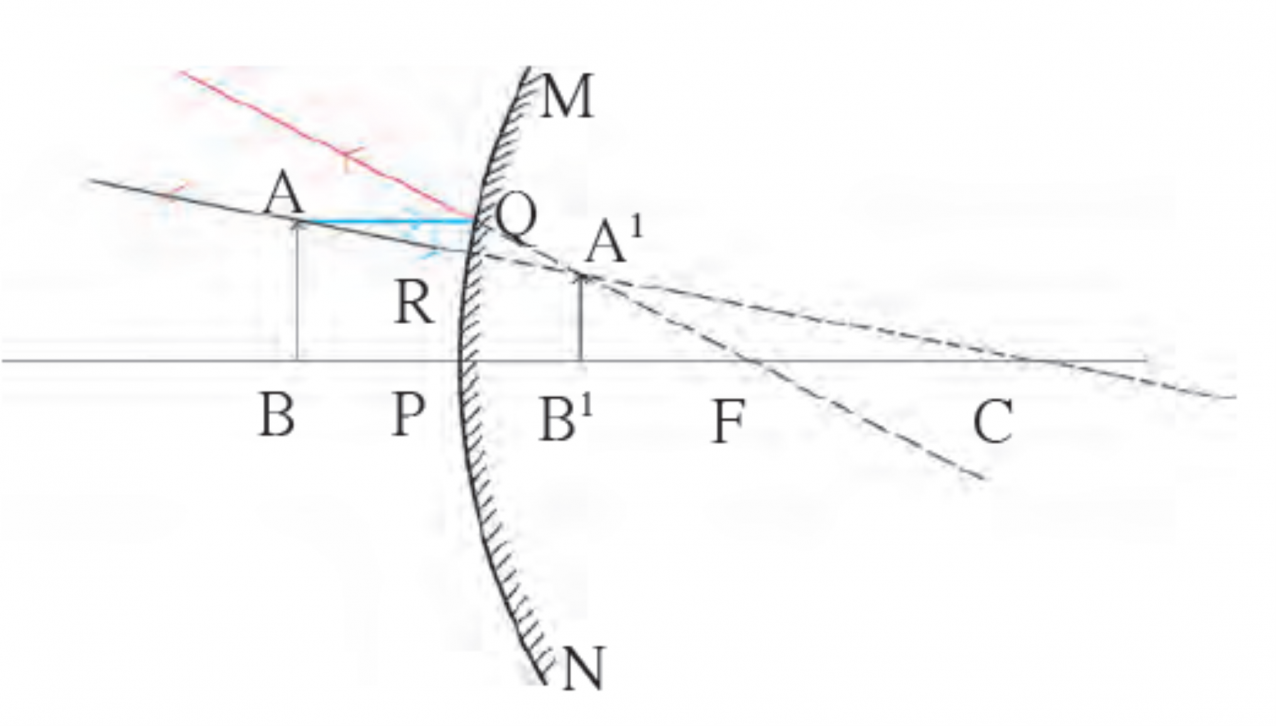
5 . In order to see the full image of a person standing in front of a mirror, the minimum height of the mirror must be half the height of the person. Explain.
i.
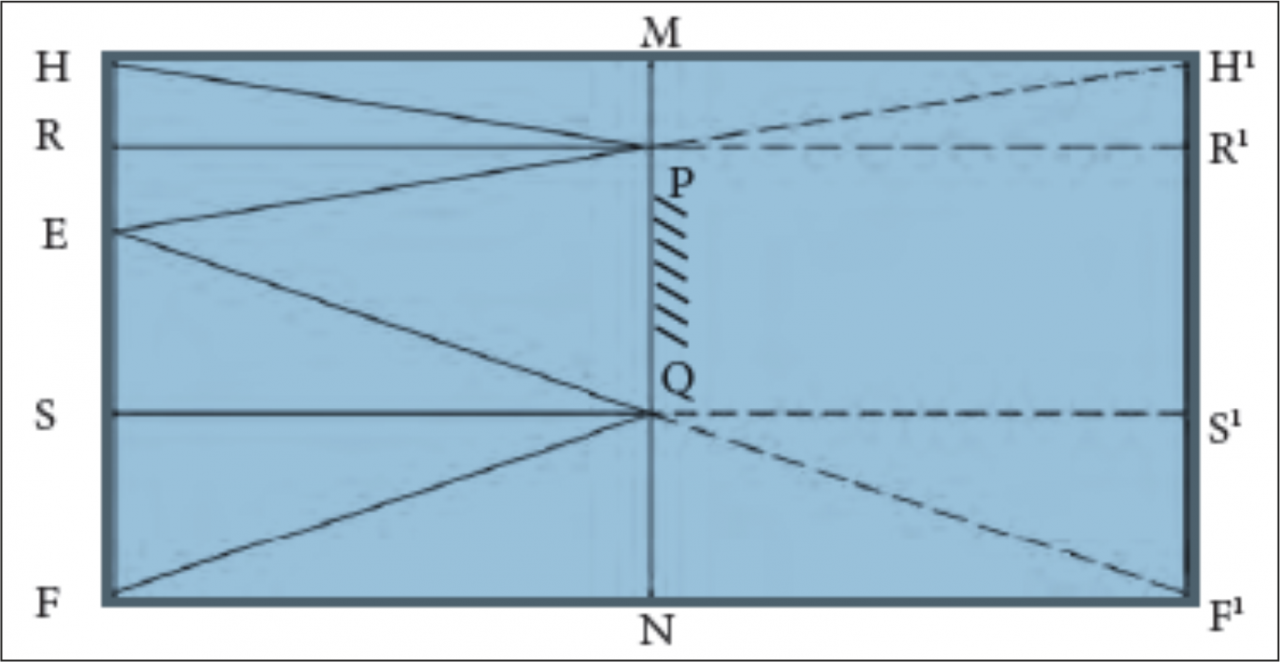 Ans
Ans
ii. In the figure, the point at the top of the head, the eyes and a point at the feet of a person are indicated by H, E and F respectively.
ii i. R and S are midpoints of HE and EF respectively.
iv. The mirror PQ is at a height of NQ from the ground and is perpendicular to it.
v. PQ is the minimum height of the mirror in order to obtain the full image of the person.
vi. For this, RP and QS must be perpendicular to the mirror.
vii. Minimum height of the mirror PQ = RS
= RE + ES
= HE/2 + EF /2
= HF/2
= half of the person’s height.

