Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 11 Human Body and Organ System Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Q.1. Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statements:
1. Lungs are present on either side of the heart in cavity.
Ans Lungs are present on either side of the heart in thoracic cavity.
2. A muscular partition is present at the base of thoracic cage which is called as ……………
Ans A muscular partition is present at the base of thoracic cage which is called as diaphragm.
3. Blood pressure is measured by ………….. .
Ans Blood pressure is measured by sphygmomanometer.
4. protect the body from microbes and other harmful particles.
Ans Antibodies protect the body from microbes and other harmful particles.
5. carry the blood away from the heart.
Ans Arteries carry the blood away from the heart.
6. Person who donates the blood is referred as …………..
Ans Person who donates the blood is referred as blood donor.
7. Blood Pressure is measured with the help of …………..
Ans Blood Pressure is measured with the help of sphygmomanometer.
8. system performs the function of transport of various substances through blood.
Ans Circulatory system performs the function of transport of various substances through blood.
9. carries the CO2 from various parts of body towards lungs.
Ans Blood carries the CO2 from various parts of body towards lungs.
10. is essential to operate all the life processes in human body.
Ans Energy is essential to operate all the life processes in human body.
Q.2. Find the odd one out
1.Neutrophils, globulins, albumins, prothrombin.
Ans Neutrophils – They are a type of WBCs while remaining are the components of blood plasma.
2. A, O, K, AB, B.
Ans K – All others are types of blood group while K is not a blood group.
3. Trachea, alveoli, diaphragm, capillaries.
Ans Capillaries – They are part of circulatory system while others are parts of respiratory system.
4. A, B, AB, Na
Ans Na – It is not an blood group but an inorganic ion found in plasma of blood while others are the human blood groups.
5. Blood plasma, platelets, blood transfusion, blood corpuscles.
Ans Blood transfusion – It is a process of blood transfer while remaining are the components of blood.
6. RBCs, WBCs, Platelet, Pharynx
Ans Pharynx – It is an part of respiratory system rest all are the components of blood.
Q.3. Find co-related terms :
1. Upper chambers of heart: Atria :: Lower chambers of heart :
Ans Ventricles : The upper chambers of heart are called atria and the lower chambers of heart are called ventricles.
2. Enucleated blood cells : RBCS :: Nucleated blood cells:
Ans WBCs
3. The enucleated blood cells are RBCs and nucleated blood cells are WBCs.
Inhalation : oxygen gas :: Exhalation : ?
Ans Inhalation : oxygen gas :: Exhalation : Carbon dioxide or CO2 gas
4. Universal donor : blood group ‘O’ :: Universal acceptor : ?
Ans Universal donor : blood group ‘O’ :: Universal acceptor : Blood group ‘AB’.
5. Blood away from heart : Arteries :: Blood towards heart : ?
Ans Blood away from heart : Arteries :: Blood towards heart : Veins.
6. ABO bloods groups : :: AB blood group : Decastello and Sturli.
Ans 60 – 79 mm Hg
The normal systolic B.P (blood pressure) is 90 – 119 mm Hg and normal diastolic B.P (blood pressure) is 60- 79 mm Hg.
Q. 4. Extra data:
1. Fill blanks in paragraph
Process of pumping the blood towards various parts of the body and bringing it back towards the heart is called as …………………. circulation. So as to maintain the continuity in circulation, heart alternately and ……………………. Consecutive single contraction and relaxation of heart constitutes a single ………………….
Ans Process of pumping the blood towards various parts of the body and bringing it back towards the heart is called as Blood circulation. So as to maintain the continuity in circulation, heart alternately Contracts and Relaxes Consecutive single contraction and relaxation of heart constitutes a single Heart beat.
2. Blood donor & blood recipient and Blood transfusion and Circulation.
Ans
| Blood donor & blood recipient | Blood transfusion and Circulation. |
| i. Person who donates the blood is referred as blood donor where as Person who receives the blood is referred as recipient. | i. Circulation is process where blood transports various substances throughout the body where as Blood transfusion is the process in which blood from one person is carried out to compensate the blood shortage in body of another person. |
Q. 5. Match the pair :
1.
| Column – A | Column – B |
| i. Contraction | a. Clotting |
| ii.Universal recipient | b. Systolic pressure |
| c. AB |
Ans
| i. | Contraction | Systolic pressure |
| ii. | Universal recipient | AB |
2.
| Column – A | Column – B | ||
| 1. | WBCs | a. | Protection |
| 2. | Fibrinogen | b. | 5000-10000 per mm3 |
| c. | Clotting | ||
Ans
| i. | WBCs | 5000-10000 per mm3 Protection |
| ii. | Fibrinogen | Clotting |
3.
| Column – A | Column – B |
| i. Heart beats | a. 62 mm of Hg |
| ii. Blood donation | b. 700ml |
| c. 72 | |
| d. 350ml |
Ans
| i. Heart beats | 72 |
| ii. Blood donation | 350 ml |
4.
| Column – A | Column – B | ||
| i. | Universal donor | a. | 50 – 60 lakh/ mm3 |
| ii. | RBCs | b. | Protection |
| c. | O | ||
Ans
| i. | Universal donor | O |
| ii. | RBCs | 50 – 60 lakh RBCs |
5.
Column – B
Column – A
| i. Normal body temperature | a. 6.75 |
| ii. pH of oxygenated blood | b. 7.4 |
| c. 25° C | |
| d. 37° C |
Ans
| i. Normal body temperature | 37° C |
| ii. pH of oxygenated blood | 7.4 |
6.
| Column – A | Column – B |
| i. RBC | a. 5000-6000 per blood mm3 |
| ii. Blood donation | b. 2.5 – 4 lakh per mm3 |
| c. 90 -92 % water | |
| d. 50 – 60 lakh/mm3 |
Ans
| i. RBC | 50 – 60 lakh/mm3 |
| ii. Blood donation | 5000-6000 per blood mm3 |
7.
| Column – A | Column – B | ||
| i. | Globulins | a. | 5000-10000 per mm3 |
| 2. | Contraction | b. | Protection |
| c. | Systolic pressure | ||
Ans
| i. | Globulins | Protection |
| ii. | Contraction | Systolic pressure |
Q. 6. Name the following :
1. Today, her child became one and half year old. However, that child does not seem to be healthy and happy. It was continuously crying and gradually becoming weak. It has shortness of breath. Its nails have become blue.
Ans Asthma
2. Name the two gases involved in respiration process.
Ans Oxygen and carbon dioxide.
3. Name any two human blood group. types (Any two).
Ans i. AB iii. B
A iv. O
4. Name any two parts of the respiratory system (write any two).
Ans i. Nose iii. Wind pipe
ii. Lungs iv. Pharynx
5. Name any two types of blood vessels.
Ans Arteries, veins and capillaries.
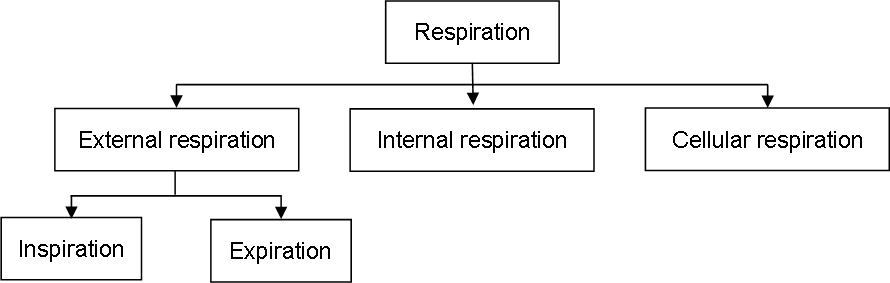
6. Name the two steps of external respiration.
Ans Inspiration / Inhalation and Expiration / Exhalation.
7. Name the four main groups of human blood.
Ans A, B, AB and O.
8. Name any two types of WBCs.
Ans basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils, monocytes & lymphocytes.
9. How many ml of blood is collected from a person during donation ?
Ans 350 ml
10. Name the partition between the thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity.
Ans Diaphragm
11. High blood pressure than the normal is referred as ?
Ans Hypertension
Q.7. Answer in one sentence
1.What are produced in red bone marrow ?
Ans WBCs are produced in red bone marrow.
2.What is the role of albumin in blood plasma ?
Ans It distributes the water all over the body.
3.State property of nose.
Ans Respiratory system and respiration begins with nose. Air is filtered with the help of hair and mucus present in the nose.
4.Which mechanism was explained by William Harvey ?
Ans He proposed a theory that our heart is a muscular pump by which blood is circulated in the body.
5. What is called as beating of heart ?
Ans The contraction and relaxation of involuntary cardiac muscle with a definite rhythm is called as beating of heart.
6. Blood donor :
Ans Person who donates the blood is referred as blood donor.
Q.8. Multiple Choice Questions (Activity) :
1. 37o C is maintained by blood through which of the following ?
Blood transfusion
Vasodilation and vasoconstriction
Generating heat in the capillaries
Producing heat controlling hormones
Ans Option b.
2. Pulse generated is the body is due to ……………
a. Blood pressure b. Oxygenation of blood
c. Deoxygenation of blood d. Beating of heart
Ans Option d.
3. Circulatory system does not include which of the following part?
a. Heart b. Blood vessels c. Capillaries d. Pleura
Ans Option d.
4. Food pipe and wind pipe both originate at ……………
a. Larynx b. Alveolus c. Pharynx d. Trachea
Ans Option c.
5. Systolic blood pressure of a healthy person should have a pressure around ……………
a. 120 mm to 139 mm of Hg b. 80 mm to 139 mm of Hg
c. 120 mm to 89 mm of Hg d. 80 mm to 89 mm of Hg
Ans Option a.
6. Human heart in total is divided into how many chambers? a.2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 6
Ans Option c.
Q.9. Multiple Choice Questions (Experiment) :
1. What happens to systolic and diastolic pressure in hypertension ?
Decreases b. increases c. normal d. no change
Ans Option b.
2. As pressure due to diaphragm on lungs decreases,
the air moves out of the lungs b. the air move into lungs.
c. the air exchange takes place d. no change is observed.
Ans Option b.
3. Amount of energy generated during cellular respiration is ……………
36 ATP b. 38 ATP c. 32 GTP d. 38 GTP
Ans Option b.
4. Which of the following cells ensure protection of body against pathogens and microbial bodies?
RBCs b. Platelets c. Fibrinogen d. WBCs
Ans Option d.
5. Heart is present almost at centre in ?
Atria b. ventricle c. Thoracic cage d. Valve
Ans Option c.
6. Blood group of a person depends upon ……………
Genes inherited from parents.
Number of RBCs present in the body.
The proteins present in the blood plasma.
Thickness of the blood.
Ans Option a.
7. ph. of oxygenated blood is ?
a. 7.5 b. 7.0 c. 7.4 d. 8
Ans Option c. 7.4
8. All veins carry deoxygenated blood except for the one which ……………
carries blood from heart to lungs
carries blood from lungs to heart
carries blood from heart to the body
carries blood from heart to brain
Ans Option b.
9. How much ml of blood is pump during each heart beat?
70ml b. 75ml c. 80ml d. 72ml
Ans Option b.
Q.10. Write Short Notes :
1. Diaphragm
Ans i. A muscular partition is present at the base of thoracic cage. This partition is called as diaphragm. It is present between the thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Simultaneous rising up of ribs and lowering of diaphragm causes the decrease in pressure on lungs. Due to this, air moves into the lungs through nose. When ribs return to their original position and diaphragm rises up, pressure on the lungs increases. Due to this, air moves out from it through nose. Continuous upward and downward movement of diaphragm is necessary to bring about the breathing.
2. Hematology
Ans Branch of medical science that deals with the study of blood, hematopoietic organs and blood diseases is called as hematology. Research of diagnosis and remedies of blood diseases is also performed in this branch.
3. Blood Pressure
Ans i. Blood is continuously kept flowing through blood vessels due to contraction and relaxation of the heart. Due to contraction of the heart, pressure is exerted on the wall of arteries and it is called as blood pressure. Proper blood pressure is necessary to supply the blood in all parts of the body.
The pressure recorded during the contraction of the heart is called as ‘systolic pressure’ and that one recorded during relaxation is called ‘diastolic pressure’.
The blood pressure of a healthy person is about 120/80 mm to 139/89 mm of Hg. It is measured with the help of sphygmomanometer’.
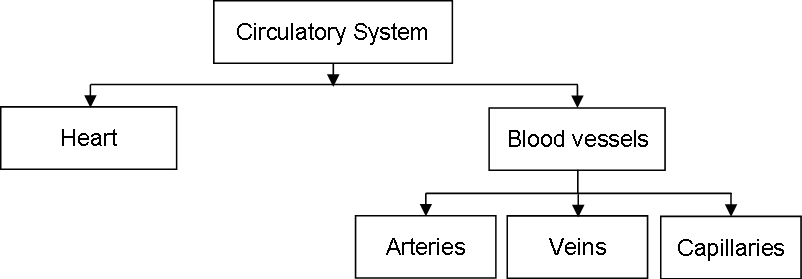
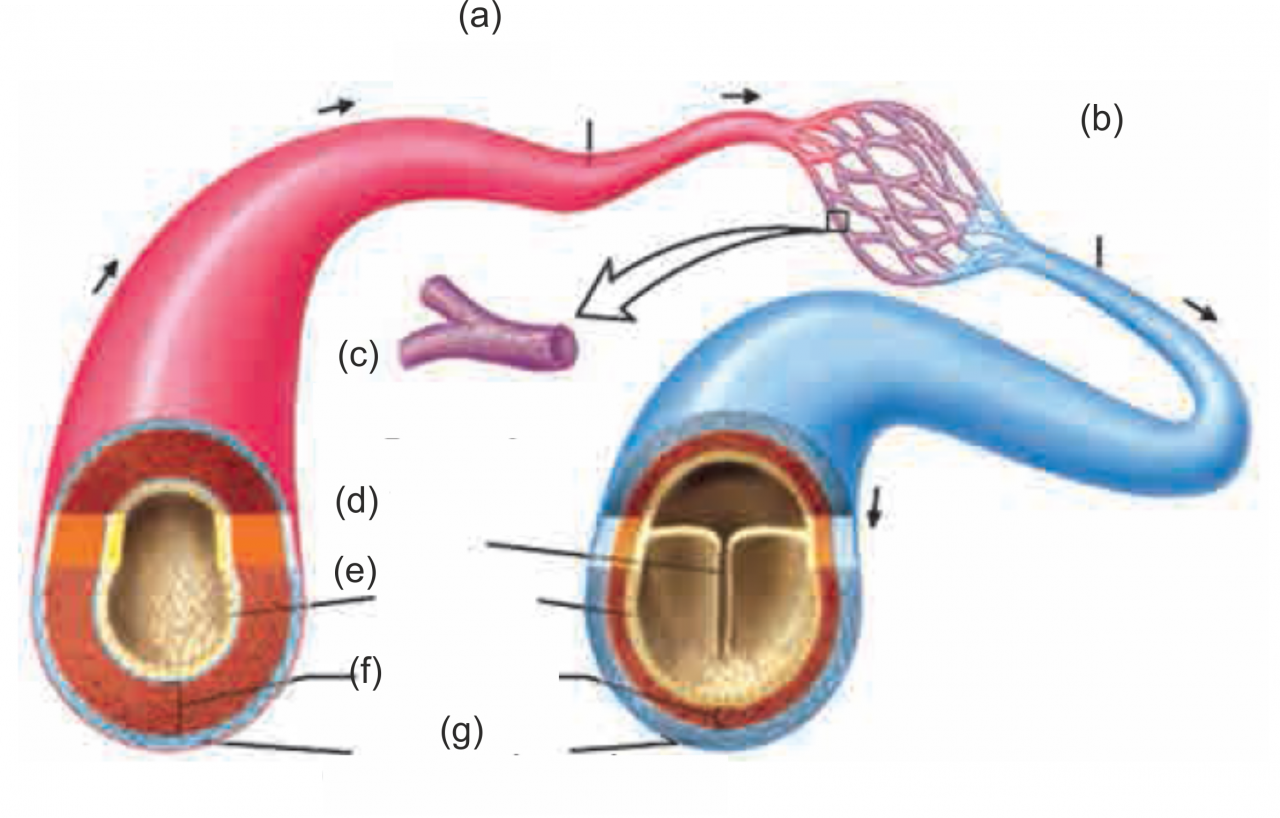
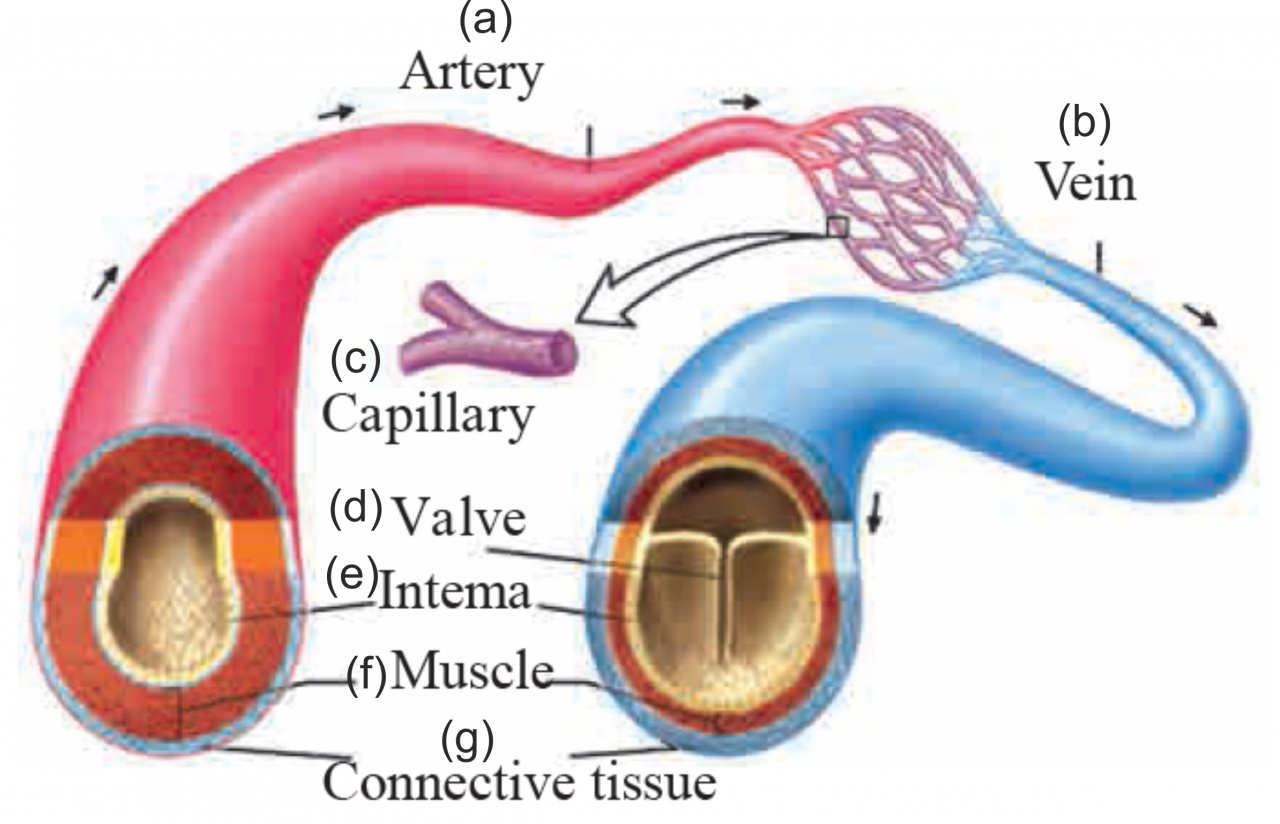
4. Structure of Artery and Vein
Ans i. Blood vessels that carry the blood away from the heart are called arteries. Except for the one carrying blood toward lungs, all carry oxygenated blood.
These are deeply located in the body and their walls are thick. These vessels do not have valves.
Vessels carrying the blood towards the heart from various parts of body are called as veins. All veins except the one carrying blood from lungs transport deoxygenated blood.
Most of the veins are superficially located in the body. Their walls are thin and these are provided with valves.
5. Hypertension
Ans High blood pressure than the normal is referred as hypertension. In arteries of the person with hypertension, unnecessary tension develops. Heart needs to perform more function than the normal condition in case of hypertension. Both, systolic and diastolic pressures are high in hypertension
Q.11. Complete the given flow chart/table / diagram
1 Complete the table by filling the components present in blood plasma based on their function given.
| Function | Component of blood plasma |
| Distributes the water all over the body. | …………… |
| Protection (immune system) | …………… |
| Help in blood clotting process. | …………… |
| Control the function of muscles and nerves. | …………… |
Ans
| Function | Component of blood plasma |
| Distributes the water all over the body. | Albumin |
| Protection (immune system) | Globulins |
| Help in blood clotting process. | Fibrinogen & prothrombin |
| Control the function of muscles and nerves. | Inorganic ions – Ca, Na, K |
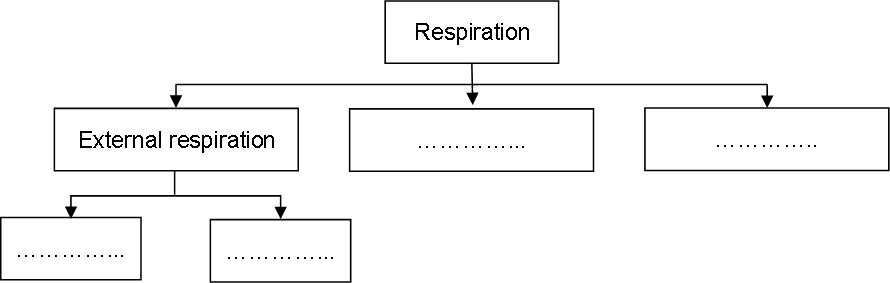 2
2
 Ans
Ans
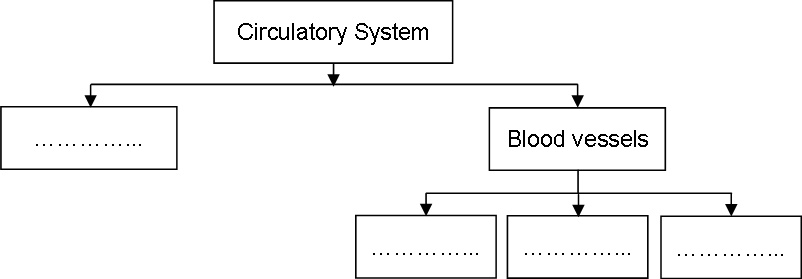 3
3
 Ans
Ans
Q.12. Distinguish between :
1. Arteries and veins
Ans
| Arteries | Veins |
| i. Blood vessels which carry the blood away from heart are called as arteries. | i. Vessels carrying the blood towards the heart from various parts of body are called as veins. |
| ii. Their walls are thick. | ii. Their walls are thin. |
| iii. Most of the veins are superficially located in the body. | |
| iii. These are deeply located in the body.. | |
| iv. These vessels do not have valves. | iv. These vessels are provided with valves. |
2. Arteries & Veins
Ans
| Arteries | Veins |
| i. Blood is carried away from heart. | i. Blood is carried towards the heart. |
| ii. It carries oxygenated blood . | ii. It carries deoxygenated blood. |
| iii. Valves are absent. | iii. Valves are present. |
| iv. Deeply located. | iv. Superficially located. |
3. External and internal respiration
Ans
| External | Internal respiration |
| i. External respiration occurs through two steps- Inspiration and Expiration. | i. Internal respiration occurs only in single step in the Lungs. |
| ii. It occurs collectively with help of lungs, through nose. | ii. It occurs only in the lungs. |
| iii. Air is only taken in and blown out in the process. | iii. Exchange of gases between cells and tissue fluid takes place in this process. |
| iv. This process is not specific towards the gases. | iv. This process is specific to Oxygen which moves from blood into tissue fluid and carbon dioxide which moves from tissue fluid into blood. |
Q.13. Laws/define/principles :
1. Haematology:
Ans i. Branch of medical science that deals with the study of blood, hematopoietic organs and blood diseases is called as haematology.
Research of diagnosis and remedies of blood diseases is also performed in this branch.
2. Blood circulation:
Ans Process of pumping the blood towards various parts of the body and bringing it back towards the heart is called as blood circulation
3. Blood Pressure:
Ans i. Blood is continuously kept flowing through blood vessels due to contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Due to contraction of the heart, pressure is exerted on the wall of arteries and it is called as blood pressure.
4. Hypertension.:
Ans i. High blood pressure than the normal is referred as hypertension. In arteries of the person with hypertension, unnecessary tension develops.
Heart needs to perform more function than the normal condition in case of hypertension.
5. Internal Respiration:
Ans i. Exchange of gases between cells and tissue fluid is called as internal respiration.
Oxygen moves from blood into tissue fluid and carbon dioxide moves from tissue fluid into blood.
6. Thermoregulation:
Ans i. Human Body temperature is maintained constant at 370 C by vasodilation and vasoconstriction.
This process is known as Thermoregulation.
Q.14. Write properties, uses, inferences, important factors, examples :
1. Give the properties of human blood.
Ans i. Blood is a red coloured fluid material.
It is fluid connective tissue.
The oxygenated blood is deep red coloured, salty in taste and its pH is 7.4.
Blood is composed of mainly two components- plasma and blood corpuscles or cells.
Q.15. Give scientific reasons :
1. Upward and downward movement of diaphragm occurs consecutively.
Ans i. Diaphragm is a muscular partition is present at the base of thoracic cage. It is present between the thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity.
Simultaneous rising up of ribs and lowering of diaphragm causes the decrease in pressure on lungs. Due to this, air moves into the lungs through nose.
When ribs return to their original position and diaphragm rises up, pressure on the lungs increases. Due to this, air moves out from it through nose.
Therefore, Continuous upward and downward movement of diaphragm is necessary to bring about the breathing.
2. Food must have limited amount of salts.
Ans i. Blood plasma contains inorganic ions such as Na, K and Ca.
These ions are obtained from the salts which are taken through the diet on regular basis. These ions are mainly used to control the function of muscles and nerves.
Excess of the salts can increase the concentration of these ions which increases concentration of blood plasma and thickens the blood.
As the blood becomes dense, it can lead to increase in blood pressure and can rupture the arteries due to high blood pressure.
3. Person with blood group ‘AB’ is called as universal recipient.
Ans i. Person who received blood is a recipient.
ii. Person with blood group ‘AB’ can receive blood from person with any other blood group i.e O, A, B and AB.
Thus, a person with blood group ‘AB’ is called as universal recipient.
4. Blood donation is considered to be superior of all donations.
Ans i. Loss of blood can occur due to number of reasons. Blood is required in various situations like accidents, bleeding, parturition, surgical operations, etc.
Blood transfusion is performed only after the blood group matching. If it is done without matching, it may prove fatal for the patient.
Person who donates the blood may be recipient in future. Blood donation without any expectation is always life saving.
Blood donated by healthy person is used to save the life of needful person. Hence, blood donation is considered as the best donation.
5. Human blood is red coloured.
Ans i. Human blood consists of 45% of Blood corpuscles in which Red Blood Corpuscles (RBCs) are very high in number, around 50 – 60 lakh RBCs in each cubic milimetre of blood.
RBCs are red due presence of an iron compound which is red in colour, Haemoglobin which is necessary for oxygen transport.
The remaining components of blood do not show any bright colour due to which only the colour RBCs can be observed clearly.
And therefore, due to presence of RBCs in high amount, the colour of the blood appears as red.
Q.16. Activity based question (3 mks) :
1
| Name of the process | |
| Definition of Process | |
| …………… | Internal Respiration |
| Pumping the blood towards various parts of the body and bringing it back towards the heart | |
| ………….. | |
| …………… | Thermoregulation |
| Air is taken in through nose and sent towards the lungs through trachea | …………… |
| Blood from one person is transferred into the body of another | …………… |
| …………… | Heart beat |
Ans
| Name of the process | |
| Definition of Process | |
| Exchange of gases between cells and tissue fluid | Internal Respiration |
| Pumping the blood towards various parts of the body and bringing it back towards the heart | |
| Blood circulation | |
| Body temperature is maintained constant | Thermoregulation |
| Inspiration / Inhalation | |
| Air is taken in through nose and sent towards the lungs through trachea | |
| Blood from one person is transferred into the body of another | Blood transfusion |
| Contraction and relaxation of heart with a definite rhythm. | Heart beat |
Q.17. Activity based questions. (2 mks) :
1. Classify the parts of (a) Human respiratory system and (b) Blood circulatory system.
[Larynx, systemic aorta, Lungs, inferior vena cava, tricuspid valve, alveoli, wind pipe, ventricle]
Ans Respiratory system : [Larynx, lungs, wind pipe, alveoli]
Blood circulatory system : [ Ventricle, inferior vena cava, tricuspid valve, systemic aorta]
2. Classify the parts of Human respiratory system and Blood circulatory system.
[Larynx, systemic aorta, Lungs , inferior vena cava , tricuspid valve , alveoli ,wind pipe , ventricle]
Ans Respiratory system – Larynx, lungs, wind pipe, alveoli.
Blood circulatory system – Ventricle, inferior vena cava, tricuspid valve, systemic aorta.
 3. Structure of artery and vein
3. Structure of artery and vein
Ans
 4. Human Respiratory System and Alveoli.
4. Human Respiratory System and Alveoli.
Ans
Q.18. Explain the statement. :
1. Explain the functional correlation of circulatory system with respiratory, digestive and excretory system.
Ans i. Circulatory system performs the function of transport of various substances like water, hormones, oxygen, soluble nutrients, and waste materials through different organs. It consists of heart, blood vessels and capillaries.
Circulation is co-related with all other system in the body as it forms a connective link throughout the body.
Respiration helps in intake of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide. The exchanges of gases occur directly into the blood in the lungs.
Also, cellular respiration occurs in the cells after the gases are transported by circulation.
Digestive system provides nutrients by digestion of the food which are absorbed by the blood and transported to all the tissues in the body.
Excretory products are transported all by means of blood into excretory organs like kidney and blood is purified.
Thus, circulatory system is correlated to all other organ systems such as respiratory, digestive and excretory system.
2. Explain the importance and need of blood donation.
Ans i. Blood transfusion is needed in various situations like when a person meets with an accident, that results in heavy blood loss; during surgeries; in case of patients of anaemia, thalassemia, cancer and also after parturition (childbirth)
ii. Also, there is a constant need for regular blood supply as blood can only be stored for a limited time before use.
iii. Regular blood donations will ensure the availability of safe blood wherever and whenever needed.
iv. A person who donates blood may be a recipient in the future. Thus, blood donation must be done without
any expectations.
v. Blood donated by a healthy person can save the life of a needful person. Hence, it is considered as the best donation.
3. Blood transfusion can be done to compensate the loss of blood in any person.
Ans i. Loss of blood can occur due to many reasons in a person. Many times, blood transfusion is necessary during the surgical operation. Similarly, blood is transfused in case of patients of anemia, thalassaemia, cancer too.
Blood transfusion is carried out to compensate the blood shortage in body. This is called as blood transfusion.
Blood is collected in blood banks by specific method from the healthy persons and supplied to the needful persons. If the collected blood is not to be used immediately, it can be stored for some days in refrigerator.
Person who donates the blood is referred as blood donor. Person who receives the blood is referred as recipient.
Person of the blood group ‘O’ can donate the blood to the person having any other blood group whereas the person with ‘AB’ blood group can receive the blood from the person with any other blood group.
Hence, person of blood group ‘O’ is called as universal donor and the person with blood group ‘AB’ is called as universal recipient.
4. All the vital processes which are essential properties of living beings, are collectively called as life processes.
Ans i. Different organs in our body are working in group so as to smoothly carry out various life processes.
These life processes take place in various steps. Specific organs carry out the specific steps. Group of organs working together to perform a specific function is called as organ system.
Various organ systems like digestive, respiratory, circulatory, nervous, excretory, reproductive, skeletal, muscular, etc. are functioning in our body.
Energy is essential to operate all the life processes in human body. Energy production occurs within the cells.
Cells need the supply of soluble nutrients and oxygen for this purpose. This supply takes place with the help of respiratory and circulatory systems.
Hence, all the processes in the human body are interdependent on each other and function together.
Q.19. Explain the diagram :
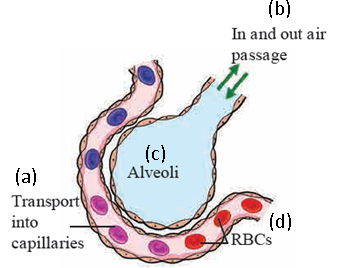
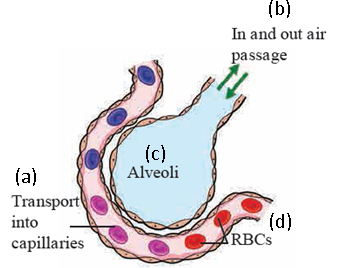 1. Explain the given diagram Human Respiratory System and Alveoli.
1. Explain the given diagram Human Respiratory System and Alveoli.
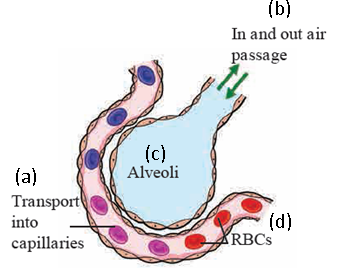
Ans i. The given diagram shows the alveoli with its surface covered with capillaries, where exchange of gases take place.
Rich network of capillaries is present around each alveolus. Walls of alveoli and capillaries are extremely thin.
Gaseous exchange can easily take place across these thin walls. As large number of alveoli is present in lungs, larger surface is available for gaseous exchange. Gaseous exchange occurs continuously while blood is circulating around the alveoli.
An iron containing protein- haemoglobin is present in the RBCs of blood. Haemoglobin absorbs the oxygen from air within alveoli.
Simultaneously, CO2 and water vapours move from blood into the alveoli.
Thus, oxygen is taken into the blood and CO2 and water vapours are removed from the blood and given out by exhalation.
Q. 20 .Complete the sentences in a paragraph :
1. Complete the paragraph:
(internal, cellular, Oxygen, ATP, carbon dioxide, cells, muscles)
Exchange of gases between ………………… and tissue fluid is called as respiration.
………………….. moves from blood into tissue fluid and moves from tissue fluid into blood. In
………………… respiration, dissolved nutrients like glucose are slowly burnt with the help of oxygen and energy is released in the form of Waste materials like CO2 and water vapours are produced during
this process.
Ans Exchange of gases between cells and tissue fluid is called as internal respiration. Oxygen moves from blood into tissue fluid and carbon dioxide moves from tissue fluid into blood. In cellular respiration, dissolved nutrients like glucose are slowly burnt with the help of oxygen and energy is released in the form of ATP. Waste materials like CO2 and water vapours are produced during this process.
2. Fill in the blanks using appropriate words given in the bracket.
(hemoglobin, alkaline, diaphragm, red bone marrow, acidic, voluntary, involuntary,)
RBCs of the blood contain , an iron compound. is present between thoracic and abdominal cavity.
Cardiac muscles are …………… . pH of oxygenated blood is …………… . Production of RBCs occurs in …………… .
Ans i. RBCs of the blood contain hemoglobin, an iron compound. Diaphragm present between thoracic and abdominal cavity.
Cardiac muscles are involuntary pH of oxygenated blood is alkaline. Production of RBCs occurs in red bone marrow.
3. Complete the paragraph:
(pharynx, entry, open, food pipe, air, lid, close, water )
Food pipe and wind pipe originate in the ……….. Wind pipe is present in front of the There is a ………. at the beginning of wind pipe. This lid closes the wind pipe during passing of food into food pipe and thereby normally prevents the ………. of food particles into wind pipe. Otherwise, wind pipe remains ……….. Hence passes through pharynx into wind pipe.
Ans Food pipe and wind pipe originate in the pharynx. Wind pipe is present in front of the food pipe. There is a lid at the beginning of wind pipe. This lid closes the wind pipe during passing of food into food pipe and thereby normally prevents the entry of food particles into wind pipe. Otherwise, wind pipe remains open. Hence air passes through pharynx into wind pipe.
4. Complete the paragraph:
( sphygmomanometer, 120/80 mm, Systolic pressure, Diastolic pressure, 129/89 mm, Arteries, 139/89 mm)
Blood is continuously kept flowing through blood vessels due to Contraction and relaxation of the heart. Due to contraction of the heart, pressure is exerted on the wall of and it is called as blood pressure. Proper blood pressure is necessary to supply the blood in all parts of the body. Pressure recorded during the contraction of heart is called as ………………… and that one recorded during relaxation is called as …………………… Blood pressure of a healthy person is about ………………. to of Hg. It is measured with the help of ………………………
Ans Blood is continuously kept flowing through blood vessels due to Contraction and relaxation of the heart. Due to contraction of the heart, pressure is exerted on the wall of Arteries and it is called as blood pressure. Proper blood pressure is necessary to supply the blood in all parts of the body. Pressure recorded during the contraction of heart is called as Systolic pressure and that one recorded during relaxation is called as Diastolic pressure Blood pressure of a healthy person is about 120/80mm to 139/89mm of Hg. It is measured with the help of sphygmomanometer.
Q. 21. Answer the following based on the paragraphs:
- A lung is present on either side of heart in thoracic cavity. Maximum area of thoracic cavity is occupied by lungs and they cover the maximum part of heart. Each lung has double layered covering. It is called as pleura. Lungs are elastic like a sponge. Lungs are made up of many small compartments, called as alveoli. Rich network of capillaries is present around each alveolus. Walls of alveoli and capillaries are extremely thin. Gaseous exchange can easily take place across these thin walls. As large number of alveoli is present in lungs, larger surface is available for gaseous exchange. Gaseous exchange occurs continuously while blood is circulating around the alveoli. An iron containing protein- haemoglobin is present in the RBCs of blood. Haemoglobin absorbs the oxygen from air within alveoli. Simultaneously, CO2 and water vapours move from blood into the alveoli. Thus, oxygen is taken into the blood and CO2 and water vapours are removed from the blood and given out by exhalation.
i. Which component in blood cells is important for transport of oxygen?
ii. Why are walls of alveoli and capillaries extremely thin?
iii. Lungs are present in which cavity of the body?
Ans i. An iron containing protein- haemoglobin is present in the RBCs of blood which is important for oxygen transport.
Walls of alveoli and capillaries are extremely thin due to which gaseous exchange can easily take place across these thin walls.
Lungs are present in the thoracic cavity of the body.
2. Blood vessels which carry the blood away from heart are called as arteries. Except the one carrying blood towards lungs, all carry oxygenated blood. Vessels carrying the blood towards the heart from various parts of body are called as veins. All veins except the one carrying blood from lungs transport deoxygenated blood. Arteries gradually branch out with decrease in their diameter as they spread in the body and finally form fine hair-like vessels called as capillaries. Walls of capillaries are extremely thin and made up of single layer of cells. Due to this, exchange of materials between capillaries and cells becomes easy. During the exchange, the oxygen, nutrients, hormones, vitamins, etc. are sent towards the cells and waste materials of the cells move into blood. Capillaries unite together to form the vessels of more diameter, called as veins. Capillary network is present in each organ.
i. Which artery carries deoxygenated blood?
ii. How are capillaries formed?
iii. Why do capillaries have thin walls?
Ans i. Artery which carries blood towards lungs is the only one which carries deoxygenated blood.
Arteries gradually branch out with decrease in their diameter as they spread in the body and finally form fine hair-like vessels called as capillaries.
Capillaries have thin walls due to which exchange of materials between capillaries and cells becomes easy.
3. Depending upon the proteins like antigens and antibodies, different blood groups are formed. There are four main groups of human blood as A, B, AB and O. Besides, there are two types as ‘Rh’ negative and ‘Rh’ positive of each of those four groups. Thus, in all eight blood groups are formed. Person of the blood group ‘O’ can donate the blood to the person having any other blood group where as the person with ‘AB’ blood group can receive the blood from the person with any other blood group. Hence, person of blood group ‘O’ is called as universal donor and the person with blood group ‘AB’ is called as universal recipient.
Including positive and negative groups, how many total types of blood groups are found?
Person of which blood group can accept blood from any person?
Ans i. Including positive and negative group types, in all, eight blood groups are formed.
ii. Person of blood group AB can accept blood from any person.
Gaseous exchange occurs continuously while blood is circulating around the alveoli. An iron containing protein- haemoglobin is present in the RBCs of blood. Haemoglobin absorbs the oxygen from air within alveoli. Simultaneously, CO2 and water vapours move from blood into the alveoli. Thus, is taken
into the blood and CO2 and water vapours are removed from the blood and given out by …………… .
When does gaseous exchange occurs ?
What is presents in the RBCs of blood ?
Ans Gaseous exchange occurs continuously while blood is circulating around the alveoli. An iron containing protein- haemoglobin is present in the RBCs of blood. Haemoglobin absorbs the oxygen from air within alveoli. Simultaneously, CO2 and water vapours move from blood into the alveoli. Thus, Oxygen is taken into the blood and CO2 and water vapours are removed from the blood and given out by Exhalation.
It occurs continuously while blood is circulating around the alveoli.
Iron containing protein – haemoglobin.
Q. 22.Answer the following :
1. Your neighboring uncle has been diagnosed with hypertension. What should he do to keep his blood pressure
within normal range?
Ans i. Hight blood pressure increases the risk of heart attack. Making lifestyle adjustments is a key to maintain normal blood pressure.
Blood pressure can be controlled in the following ways:
Eating a healthy diet: In order to manage blood pressure, one should limit the amount of salt in the diet and consume less fat containing food.
Regular exercise: Regular exercise can help in maintaining weight and lower the blood pressure. Also, brisk walking is beneficial.
Managing stress: Learning to manage stress can improve mental and physical health. It will help in controlling high blood pressure. Techniques like meditation, listening to music, etc., can help in managing the stress.
Avoiding alcohol and smoking: Both these habits can increase blood presure and the risk heart attack and stoke. Thus, they should be avoided.
2. One should not talk while eating. Why is it so?
Ans i. Food pipe and wind pipe originate in the pharynx. Wind pipe is present in front of the food pipe.
There is a lid at the beginning of wind pipe. This lid closes the wind pipe during passing of food into food pipe and thereby normally prevents the entry of food particles into wind pipe.
Otherwise, wind pipe remains open. Hence air passes through pharynx into wind pipe.
While eating, if the person is taking the air passing out tends to open the lid of the wind pipe.
This can cause the entry of food particles into the wind pipe leading to choking of the person, making the person unable to breathe.
Therefore, one must avoid taking while eating to avoid choking of the food in the wind pipe.
3. Which health parameters of blood donor should be checked?
Ans The different parameters of blood donor that need to be checked are as follows:
Illness: The donor should not be suffering from any communicable disease.
Age: The donor’s age must be between 16 – 70 years.
Weight: The donor’s weight should be minimum 45kg.
Pulse: The pulse rate should be 60-100 beats/min.
Blood pressure: The blood pressure of an individual should be near normal i.e., 120/80 mm Hg indicating that the donor is healthy.
Body temperature: The body temperature should not exceed above 37.5°C.
4. Why do you think arteries have thick walls and no valves?
Ans i. Blood is continuously kept flowing through blood vessels due to contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Due to contraction of the heart, pressure is exerted on the wall of arteries and it is called as blood pressure. Proper blood pressure is necessary to supply the blood in all parts of the body.
This blood pressure is generally observed on arteries as they carry the oxygenated blood from the heart to all other parts of the body.
The blood pressure increases and decreases as the blood requirement of the body.
Thus, the walls of arteries are thick so that they do not rupture easily during high blood pressures.
As the arteries carry oxygenated blood through blood pressure, there is no chance of back flowing of blood and so, they do not have any valves.
Q. 23 . Draw a well labeled diagram and explain. :
1. Write a note on heart with a neat labelled diagram Structure of heart and blood circulation.
Ans
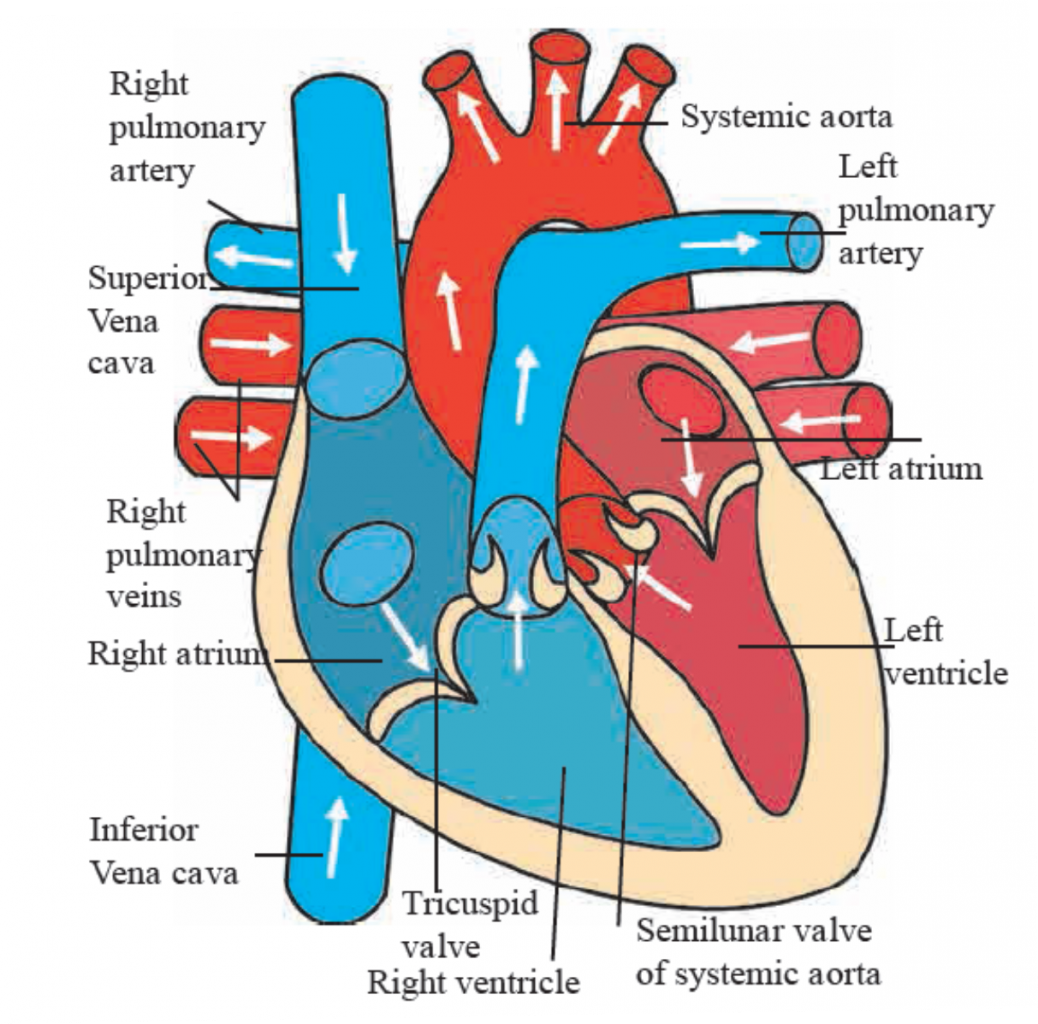
Heart is present almost at centre in thoracic cage. It is present behind the ribs, between two lungs and slightly inclined on left side.
Size of our heart is equal to one’s own fist and its weight is about 360 grams. It is covered by a double layered peritoneal membrane.
A fluid is present between two membranes due to which heart is protected from friction and mechanical shocks.
Human heart is a muscular organ. It is made up of involuntary cardiac muscles. They contract and relax with a definite rhythm. This is called as beating of heart.
Internally, heart is divided into left and right compartments by a vertical partition. Each of those compartments is again divided into two chambers.
Thus, in all, heart consists of four chambers. Upper chambers are called as atria (singular – atrium) and lower chambers as ventricles.
2. Explain the human respiratory system with a neat labelled diagram.
 Ans
Ans
Nose :
Respiratory system and respiration begins with nose. Air is filtered with the help of hair and mucus present in the nose.
Pharynx :
Food pipe and wind pipe originate in the pharynx. Wind pipe is present in front of the food pipe.
There is a lid at the beginning of wind pipe. This lid closes the wind pipe during passing of food into food pipe and thereby normally prevents the entry of food particles into wind pipe.
Otherwise, wind pipe remains open. Hence air passes through pharynx into wind pipe.
Wind pipe :
Wind pipe is swollen at the beginning due to sound box. Wind pipe bifurcates in the thorax.
One branch enters the right lung and the other into left lung.
Lungs :
A lung is present on either sides of heart in thoracic cavity. Maximum area of thoracic cavity is occupied by lungs and they cover the maximum part of heart.
Each lung has double layered covering. It is called as pleura. Lungs are elastic like a sponge.
Lungs are made up of many small compartments, called as alveoli. Rich network of capillaries is present around each alveolus.
iv Walls of alveoli and capillaries are extremely thin. Gaseous exchange can easily take place across these thin walls. As large number of alveoli is present in lungs, larger surface is available for gaseous exchange.
Diaphragm :
A muscular partition is present at the base of thoracic cage. This partition is called as diaphragm. It is present between the thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity.
Simultaneous rising up of ribs and lowering of diaphragm causes the decrease in pressure on lungs. Due to this, air moves into the lungs through nose.
When ribs return to their original position and diaphragm rises up, pressure on the lungs increases. Due to this, air moves out from it through nose.
Continuous upward and downward movement of diaphragm is necessary to bring about the breathing.
Q. 24 Answer the following in detail :
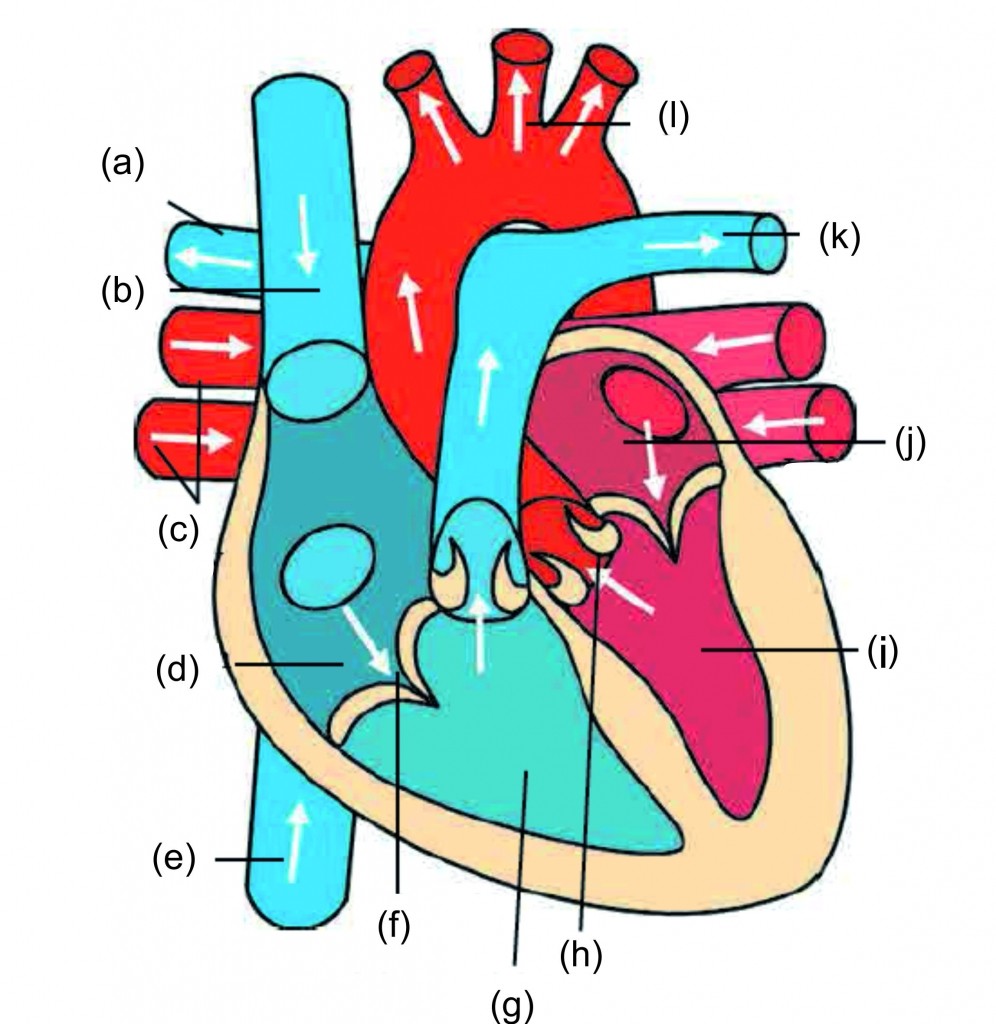
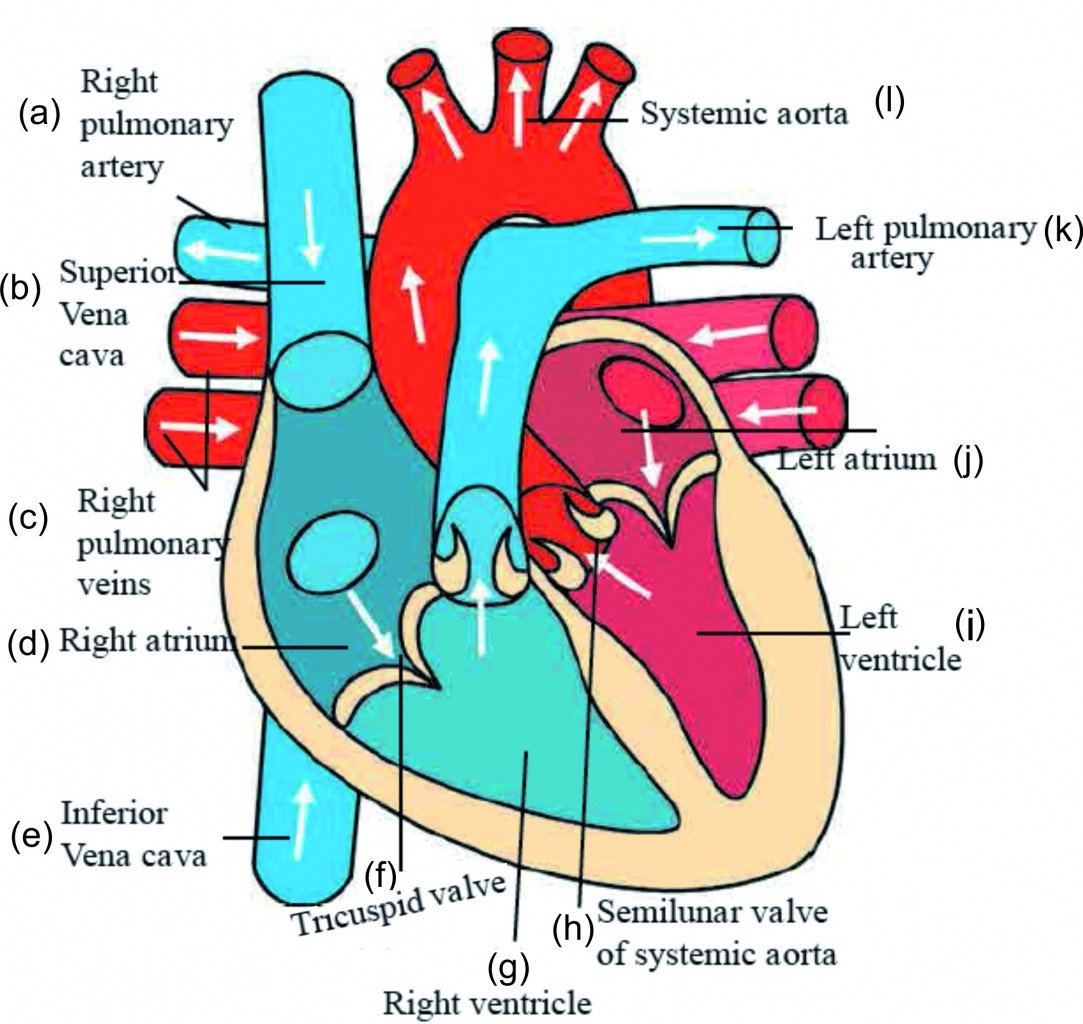 1. Label the diagram of structure of heart and blood circulation.
1. Label the diagram of structure of heart and blood circulation.
Ans
2. Explain the structure and function of human blood.
Ans: Structure of blood:
Blood is a red coloured fuid connective tissue.
The oxygenated blood is deep red coloured, salty to taste.
The pH of bloods is 7.4 (slightly alkaline).
Blood is composed of mainly two components- plasma and blood cells.
Plasma: Plasma is pale yellow coloured, clear and slightly alkaline fluid. It contains 90 – 92% water, 6 – 8%
proteins and 1 – 2% inorganic salts and few other components.
Albumin is the most abundant protein in plasma. Albumins help in maintaining osmotic balance.
Globulins perform a very important role in fighting infections (protection)
Fibrinogen and prothrombin help in blood clotting process.
Inorganic ions like Ca, Na and K regulate the fuction of muscles and nerves.
Blood cells: The major types of blood cells are:
Red Blood Corpuscles (RBCs) /Erythrocytes: Thery are circular, small and enucleated cells (nucleus is absent). RBCs appear red coloured due to the presence of hemoglobin, an iron containing protein. Hemoglobin carries oxygen to the body tissues. There are around 50 to 60 lakh RBCs per mm3 of blood. They are produced in the red bone marrow. The life span of RBCs on an average is 120 days.
White Blood Cells (WBCs) / Leucocytes: WBC are large, nucleated and colourless cells. 5000 – 10000
WBCs are present per mm3
of blood. There are five types of WBCs present in blood – basophils,
3.
Ans
| Organ systems | Organs | Functions | |
| Respiratory system | |||
| i. | Nose | Filters air with the help of hair and mucus | |
| Pharynx | It conducts air to the wind pipe | ||
| Wind pipe | Allows passage of air into lungs | ||
| Lungs | Carries out exchange of gases | ||
| It lowers and rises up helping in inhalation and exhalation of air | |||
| Diaphragm | |||
| Circulatory system | |||
| ii. | Heart | It pumps blood throughout the body | |
| Blood vessels | |||
| It transports blood throughout the body | |||
eosinophils, neutrophils, monocytes and lymphocytes. WBCs are formed the in red bone marrow. They serve a specific role in the human immune system. WBCs attack pathogens, fight infections and protect human body from various diseases.
Platelets/Thrombocytes: Platelets are extremely small and disc-shaped. About 2.5 – 4 lakh platelets are present per mm3 of blood. They are involved in formation of blood clots in case of injury.
Function of blood:
Transport of gases: Oxygen is transported via blood from lungs to the body tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs.
Trasnport of nutrients: Blood transports nutrients like glucose, amino acids, fatty acids obtained from the wall of alimentary canal to each cell of the body.
Transport of waste materials: Nitrogenous wastes like ammonia, urea and creatinine are released by tissues into blood, which carries these waste materials to the kidney for excretion.
Protection: Antibodies formed in the blood protect the body from microbes and other harmful particles.
Transport of enzymes and hormones: Enzymes and hormones are transported by blood from the site of their production to the target sites (organs/tissues) in the body.
Thermoregulation: It regualtes normal body temperature (37°C) by vasodilation (dilation of blood vessels) and vasoconstriction (narrow blood vessels).
Maintenance of concentration of minerals like Na, K, etc. in the body.
Platelets and fibrinogen protein present in the blood form a clot and seal the site of injury to prevent loss of blood by bleeding.
| Organ systems | Organs | Functions | |
| i. | Respiratory system | …………… | …………… |
| ii. | Circulatory system | …………… | …………… |
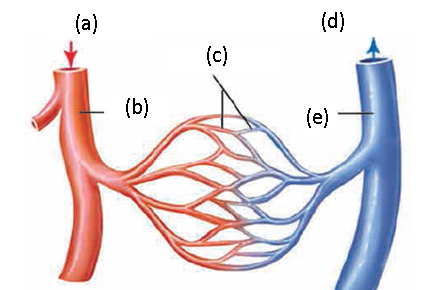
4. Label the given diagram and explain capillaries
Ans
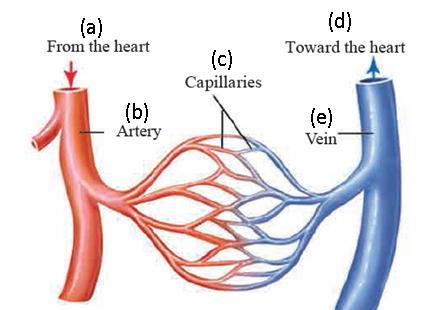
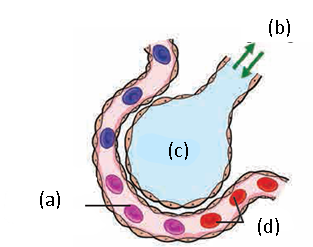
Capillaries : Arteries gradually branch out with a decrease in their diameter as they spread in the body and finally form fine hair-like vessels called as capillaries. Walls of capillaries are extremely thin and made up of a single layer of cells. Due to this, exchange of materials between capillaries and cells becomes easy. During the exchange, the oxygen, nutrients, hormones, vitamins, etc. are sent toward the cells and waste materials of the cells move into the blood. Capillaries unite together to form vessels of more diameter, called veins. A capillary network is present in each organ.
Q. 25. State True or False :
1. Simultaneous rising up of ribs and lowering of diaphragm causes the increase in pressure on lungs.
Ans False – Simultaneous rising up of ribs and lowering of diaphragm causes the decrease in pressure on lungs.
2. Wind pipe bifurcates in the abdomen.
Ans False – Wind pipe bifurcates in the thorax.
3. Both systolic and diastolic pressures are high in hypertension.
Ans True
4. Windpipe is swollen at the beginning due to sound box.
Ans True
5. WBCs participate in blood clotting process.
Ans False – Platelets participate in blood clotting process.
6. Specific organs carry out the specific steps. Ans : Ans : True
7. Diaphragam is present on either sides of heart in thoracic cavity.
Ans False – Lungs is present on either sides of heart in thoracic cavity.
8. Walls of capillaries are extremely thick.
Ans False – Walls of capillaries are extremely thick.
9. CO2 moves from blood into tissue fluid and Oxygen moves from tissue fluid into blood.
Ans False – Oxygen moves from blood into tissue fluid and CO2 moves from tissue fluid into blood.
10. Veins carry the blood towards the heart from various parts of the body.
Ans: True
11. WBCs are responsible for blood clotting process.
Ans False – Platelets are responsible for blood clotting process.
12. Blood plasma contains 55 % water.
Ans False – Blood plasma contains 90 -92 % water.
13. Human heart is a muscular organ, made up of voluntary cardiac muscles.
Ans False – Human heart is a muscular organ, made up of involuntary cardiac muscles.

