Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 12 Study of Sound Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 12 Study of Sound
Q.1. Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statements 39
1. Velocity of sound in air with an increase in temperature of air.
Ans Velocity of sound in air increases with an increase in temperature of air.
2.of a sound depends upon frequency of wave.
Ans Pitch of a sound depends upon frequency of wave.
3. Alternate compressions and rarefactions produce waves.
Ans Alternate compressions and rarefactions produce longitudinal waves.
4. is used to search underwater submarines, icebergs, etc.
Ans SONAR is used to search underwater submarines, icebergs, etc.
5. An is the repetition of the original sound because of reflection by some surface.
Ans An echo is the repetition of the original sound because of reflection by some surface.
6. Sound waves with frequency greater than 20KHz are called ……………
Ans Sound waves with frequency greater than 20KHz are called ultrasound.
7. technique can help to follow the growth and wellbeing of an unborn baby.
Ans Sonography technique can help to follow the growth and wellbeing of an unborn baby.
8. Sound cannot be heard in ……………
Ans Sound cannot be heard in vacuum.
9. The velocity of sound in air at 0°C is ……………
Ans The velocity of sound in air at 0°C is 332 m/s
10. Sound with frequency smaller than 20Hz is called …………….
Ans Sound with frequency smaller than 20Hz is called infrasound.
11. A is necessary for the propagation of source waves.
Ans A medium is necessary for the propagation of source waves.
12. sound can be heard by human beings.
Ans Sonic sound can be heard by human beings.
13. The velocity of sound in air is than that in a liquid.
Ans The velocity of sound in air is less than that in a liquid.
14. The velocity of sound in moist air is than that in dry air.
Ans The velocity of sound in moist air is greater than that in dry air.
15. Bats make use of to avoid collisions with obstacles when flying in the dark.
Ans Bats make use of ultrasonic sound to avoid collisions with obstacles when flying in the dark.
16. Sound requires a for its propagation.
Ans Sound requires a medium for its propagation.
17. The incidence of in daily life shows that the velocity of sound is less than the velocity of light.
Ans The incidence of lightening in daily life shows that the velocity of sound is less than the velocity of light.
18. The sound having high frequency is called sound.
Ans The sound having high frequency is called ultrasonic sound.
19. Sound is produced when an object is set into …………… .
Ans Sound is produced when an object is set into vibrations.
20. Sound waves give rise to a chain of …………… and in the medium.
Ans Sound waves give rise to a chain of compression and rarefaction in the medium.
21. A thin membrane in the cavity of the middle ear is called the ……………
Ans A thin membrane in the cavity of the middle ear is called the eardrum.
22. When sound is reflected from a plane surface, the angle of reflection is to the angle of incidence.
Ans When sound is reflected from a plane surface, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence.
23. The velocity of sound in air increases by 3 m/s when the temperature of air increases by °C.
Ans The velocity of sound in air increases by 3 m/s when the temperature of air increases by longitudinal °C.
24. An echo is heard only if the reflecting surface is at a minimum distance of …………… .
Ans An echo is heard only if the reflecting surface is at a minimum distance of 17 m.
25. The value of frequency determines the of the sound.
Ans The value of frequency determines the pitch of the sound.
26. The velocity of sound is highest in …………… and least in ……………
Ans The velocity of sound is highest in solids and least in gases.
27. Sound does not travel through ……………
Ans Sound does not travel through vacuum.
28. The audible range of human ear is between Hz to 20 kHz.
Ans The audible range of human ear is between 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
29. The velocity of sound in steel is than the velocity of sand in water.
Ans The velocity of sound in steel is greater than the velocity of sand in water.
30. The velocity of sound in air increases by m/s for a rise of 1°C in the temperature of air.
Ans The velocity of sound in air increases by 0.6 m/s for a rise of 1°C in the temperature of air.
31. The nerve connects the inner ear to the brain.
Ans The auditory nerve connects the inner ear to the brain.
32. is a form of energy which creates the sensation of hearing in our ears.
Ans Sound is a form of energy which creates the sensation of hearing in our ears.
33. The of sound wave determines its loudness.
Ans The amplitude of sound wave determines its loudness.
34. The velocity of sound is maximum in medium.
Ans The velocity of sound is maximum in solid medium.
35. Sound is a form of …………… .
Ans Sound is a form of energy.
36. Sound consists of waves.
Ans Sound consists of longitudinal waves.
37. The technique is used to measure the depth of the ocean.
Ans The SONAR technique is used to measure the depth of the ocean.
38. To discover a sunken ship or objects deep inside the sea, technology is used.
Ans To discover a sunken ship or objects deep inside the sea, SONAR technology is used.
39. If a person wants to hear an echo of his own voice, then he should stand at least at a distance of …………… from the reflecting surface.
Ans If a person wants to hear an echo of his own voice, then he should stand at least at a distance of 17m from the reflecting surface.
Q. 2. Find the odd one out 6
1. Cats, Mice, Bats, Dolphin
Ans Cats is the odd one out because cats cannot produce ultrasound but others can.
2. Sunken ships, Submarines, Fetal growth, Icebergs
Ans Fetal growth is the odd one out because this is done using Sonography technique while for others SONAR is used.
3. Density, Temperature, Pressure, Molecular weight.
Ans Pressure is the odd one out because the speed of the sound does not depend on the pressure of the gas but speed of the sound is affected by other factors.
4. Paper, Curtains, carpet, glass
Ans Glass is the odd one out because it is good reflector of sound while others are bad reflector of sound.
5. Dogs, human, Bat, Dolphin
Ans Human is the odd one out because other can hear ultrasound but human cannot.
Condition of heart, growth of appendix, growth of fetus, defects in brain
Ans Defect in brain is the odd one out because Sonography technique cannot be used here but the rest can be studied with the help of Sonography.
Q.3. Find co-related terms 5
1.Value of frequency : Pitch :: Value of amplitude : ……………
Ans Value of frequency : Pitch :: Value of amplitude : Loudness
2. Echocardiography : Heartbeats :: Sonography : ……………
Ans Echocardiography : Heartbeats :: Sonography : Fetal growth, Condition of heart
3. Mirror : Good reflector :: Bad reflector
Ans Mirror : Good reflector :: Curtains, Paper, Clothes, etc. : Bad reflector
4. Audible sound : 20 to 20,000Hz :: Infrasound : ……………
Ans Audible sound : 20 to 20,000Hz :: Infrasound : Below 20Hz
5. Eardrum : Middle ear :: Cochlea : ……………
Ans Eardrum : Middle ear :: Cochlea : Inner ear
Q. 4. Match the pair 7
1
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| i. Infrasound | a. Stationary waves |
| ii. Ultrasound | b. Frequency between 20 to 20,000Hz |
| c. Low frequency waves | |
| d. High frequency waves |
Ans
| i. Infrasound | Low frequency waves |
| ii. Ultrasound | High frequency waves |
2
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| i. Longitudinal Wave | a. Wave produced in a string |
| ii. Transverse Wave | b. High frequency wave |
| c. Wave produced in a slinky |
Ans
| i. Longitudinal Wave | Wave produced in a slinky |
| ii. Transverse Wave | Wave produced in a string |
3
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| i. Velocity of sound in air at 0°C | a. Echo |
| ii. Reflected sound | b. Ultrasonic sound |
| c. 332 m/s |
Ans
| i. Velocity of sound in air at 0°C | 332 m/s |
| ii. Reflected sound | Echo |
4
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| i. Pinna | a. Connects inner ear to the brain |
| ii. Auditory nerve | b. Middle ear |
| c. Collects sound |
Ans
| i. Pinna | Collects sound |
| ii. Auditory nerve | Connects inner ear to the brain |
5
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| i. Bats | a. Longitudinal waves |
| ii. Compression – Rarefaction | b. Ultrasonic sound |
| c. Echo |
Ans
| i. Bats | Ultrasonic sound |
| ii. Compression – Rarefaction | Longitudinal waves |
6
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| i. Amplitude | a. Reciprocal of frequency |
| ii. Frequency | b. Loudness of sound |
| c. Pitch of sound |
Ans
| i. Amplitude | Loudness of sound |
| ii. Frequency | Pitch of sound |
7
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| i. Cochlea | a. Connects inner ear to the brain |
| ii. Ear drum | b. Middle ear |
| c. Shell like structure |
Ans
| i. Cochlea | Shell like structure |
| ii. Ear drum | Middle ear |
Q. 5. State True or False 24
1. The speed of sound in air is greater than its speed in liquids.
Ans False – The speed of sound in air is lesser than its speed in liquids.
2. Other conditions remaining the same, if the temperature increases, then the velocity of sound increases.
Ans Other conditions remaining the same, if the temperature increases, then the velocity of sound increases. – True
3. The velocity of sound in air is 344m/s at 22°C.
Ans The velocity of sound in air is 344m/s at 22°C – True.
4. When the vacuum pump is stopped & air is allowed to enter bell jar, the sound is not heard at all.
Ans False – When the vacuum pump is stopped & air is allowed to enter bell jar, sound can be heard.
5. Velocity of sound in moist air is less than that in dry air.
Ans False – Velocity of sound in moist air is greater than that in dry air.
6. The velocity of sound is highest in liquids.
Ans The velocity of sound is highest in liquids – False.
7. The velocity of sound is lowest in liquids.
Ans The velocity of sound is lowest in liquids. – True
8. Female feticide is now a cognizable offence in India.
Ans Female feticide is now a cognizable offence in India – True.
9. SONAR is used to determine the speed of an underwater object.
Ans SONAR is used to determine the speed of an underwater object – True.
10. The velocity of sound is different in different media.
Ans The velocity of sound is different in different media.– True
11.The wavelength of sound waves is indicated by the Greek letter ‘µ’.
Ans The wavelength of sound waves is indicated by the Greek letter ‘λ’ – False.
12. Bats, mice can produce ultrasounds.
Ans Bats, mice can produce ultrasounds – True.
13. Echo can be heard only if the reflected sound reaches the ear at least 1/20th of a second after the direct sound is heard.
Ans False – Echo can be heard only if the reflected sound reaches the ear at least 1/10th of a second after the direct sound is heard.
14. The cochlea converts the vibrations coming from the membrane into electrical signals.
Ans The cochlea converts the vibrations coming from the membrane into electrical signals – True.
15. Sounds waves get reflected only from a solid surface.
Ans Sounds waves get reflected only from a solid surface – False.
16. The speed of sound in air at 0°C is about 280 m/s.
Ans False – The speed of sound in air at 0°C is about 332 m/s.
- Echo can be heard only if the reflecting surface is at a minimum distance of 34 meters.
Ans False – Echo can be heard only if the reflecting surface is at a minimum distance of 17 meters.
18. In winter, the velocity of sound at Nagpur is less than that at Mumbai.
Ans In winter, the velocity of sound at Nagpur is less than that at Mumbai. – True
19. Paper is a good reflector of sound.
Ans Paper is a good reflector of sound – False.
20. The velocity of sound is inversely proportional to the square root of molecular weight of the gas.
Ans The velocity of sound is inversely proportional to the square root of molecular weight of the gas – True.
21. Inner ear is also called as Pinna.
Ans Inner ear is also called as Pinna – False.
22 Crests and troughs are formed when sound propagates.
Ans False – Compressions and rarefactions are formed when sound propagates.
23. Human ear can hear sounds of frequencies in the range of 20 to 20,000Hz.
Ans Human ear can hear sounds of frequencies in the range of 20 to 20,000Hz – True.
24. The time taken for one oscillation at a point in the medium is called the time period.
Ans The time taken for one oscillation at a point in the medium is called the time period – True.
Q. 6. Name the following 17
1. Repetition of sound due to reflection.
Ans Echo
2. State what will happen in the following cases : A metallic object is dropped on the floor.
Ans If a metallic object is dropped on the floor, the object will start vibrating and sound is produced.
3. State what will happen in the following cases : A person standing at a distance of 20 m from a wall claps.
Ans If a person standing at a distance of 20 m from a wall claps, the sound will be reflected by the wall and an echo will be heard.
4. A form of energy that produces sensation in our ears.
Ans Sound
5. Three major parts of the human ear.
Ans Outer ear or Pinna, Middle ear and Inner ear
6.The medium in which the velocity of sound is highest.
Ans Solid medium
7. State the laws of reflection of sound.
Ans i. The direction of the incident sound wave and reflected sound wave make equal angles which is perpendicular to the surface.
ii. The incident sound, reflected sound and normal all three lie in the same plane.
8. Technique used to obtain images of internal organs of human body.
Ans Sonography
9. Sound that can be produced by elephants and whales.
Ans Infra sound
10. What is the minimum distance of the reflecting surface to hear an echo?
Ans For hearing a distinct echo, the minimum distance should be 17.2m from the reflecting surface.
11. Sound with frequency less than 20Hz.
Ans Infra sound
12. Any two animals that have the ability to hear ultrasound.
Ans Dog, mouse, bat, dolphin
13. The audible range of sound that humans can hear.
Ans 20 to 20,000Hz
14. State what will happen in the following cases :
One astronaut speaks with another astronaut on the moon.
Ans Since there is no atmosphere on the moon, the other astronaut will not be able to hear.
15. Distance between two consecutive compressions or two consecutive rarefactions.
Ans Wavelength
16. The main difference between the frequencies of the voice of a man and that of a woman.
Ans Voice of man is of low pitch while for women it is high pitch.
17. Any two bad reflectors of sound.
Ans Curtains, paper, carpet, furniture, etc.
Q. 7. Multiple Choice Questions 13
1. Sound cannot travel through ……………
a. solids b. gases c. liquids d. vacuum
Ans Option d.
2. Distant lightning flash is seen before thunder is heard.
a. Both sound and light have same speed in air.
b. Speed of light in air is more than speed of sound in air.
c. Speed of light in air is less than speed of sound in air.
d. None of the above.
Ans Option b.
3. Infra sound has frequency ……………
a. less than 20Hz b. between 20 to 20,000Hz
c. more than 20,000Hz d. None of these
Ans Option a.
4. Technology used by bats to detect their distant obstacles in dark and fly easily:
a. RADAR b. SONAR
c. X Ray d. Sonography
Ans Option b.
5. Sound gets transmitted through ……………
a. Solids b. Liquids c. Gases d. All of these
Ans Option d.
6. If person strikes at one end of a long iron tube and listener places his ear at a very far distance on the other end, he hears the sound twice.
a. Speed of sound in iron is more and less in air.
b. Speed of sound in air is more and less in iron.
c. Sound does not needs a material medium for propagation.
d. All of the above.
Ans Option a.
7. Waves created by dropping a stone in still water:
a. Longitudinal wave b. Transverse wave
c. Pulse d. None of the above
Ans Option b.
8. The velocity of sound in Iron is velocity of sound in Oxygen.
a. same as b. greater than c. less than d. almost equal to
Ans Option b.
9. Dogs, Mouse, Dolphin have a special ability to hear ……………
a. audible sound b. infrasound c. ultrasonic sound d. all of these
Ans Option c.
10. Which statement(s) hold true for sound waves:
a. Sound waves need a material medium for propagation.
b. Sound waves like light waves follow laws of reflection.
c. Both a and b.
d. None of the above.
Ans Option c.
11. Medical science uses ultrasound for:
a. X Ray b. Cataract
c. Plastic Surgery d. Sonography
Ans Option d.
12. The unit of frequency is ……………
a. m/s b. m/s2
Ans Option d.
c. meters d. Hertz
13. If a person is standing in front of a tall building 18m away from him. He would hear
a. Echo b. Reverberation
c. Noise d. None of the above
Ans Option a.
Q. 8. Solve Numerical problems 20
1. How long will it take for a sound wave of 25 cm wavelength and 1.5 KHz frequency to travel a distance of 1.5km?
Ans Given : Frequency (υ) = 1.5 kHz = 1.5 × 103Hz Wavelength (λ) = 25 cm =0.25m
Distance (s) = 1.5 km = 1.5 × 103 m
Find : Time (t) = ?
Formula : Velocity of sound = Frequency × Wavelength V= υ λ
Time = Distance / Velocity Solution : V = υ λ
= 1.5 × 103
× 0.25
= 0.375 × 103 = 375 m/s
Time = Distance / Velocity t = s / v = 1.5 x 103 / 375= 1500/375 =4s
Ans : The sound waves take 4s to travel the distance of 1.5 km.
2. Sound waves of wavelength 1cm have a velocity of 340 m/s in air. What is the frequency? Can this sound be heard by the human ear?
Ans Given : Wavelength (λ ) = 1cm = 1 × 10-2m Velocity of sound = v = 340m/s
Find : Frequency (υ ) = ?
Formula : = υ λ Solution : = υ λ
= v / λ
= 340/1 × 10-2
= 34000Hz
Ans: This frequency is higher than 20000Hz and therefore, this sound cannot be heard by the human ear.
2. Obtain a relation between Velocity, Frequency and Wavelength of a Wave. OR Derive an expression for speed of sound.
Ans i. Consider a wave travelling through a medium with a velocity ‘v’, frequency ‘f ’ and wavelength ‘λ’.
ii. Let ‘T’ be the period of the wave
iii. In T secs the wave covers a distance ‘λ’.
λ
Hence, in 1 sec, it would cover a distance = T
iv. But, the distance covered in 1 sec is called its velocity and 1 = f
T
... v = f λ
velocity = frequency x wavelength. Hence, Velocity = frequency x wavelength
2. Ultrasonic waves are transmitted downwards into the sea with the help of a SONAR. The reflected sound is received after 4s. What is the depth of the sea at that place? (Velocity of sound in sea water =1550 m/s)
Ans Given : Velocity of sound in sea water = 1550m/s
Find :
Depth of the sea at that place = ?
Formula : Velocity = Distance / Time
Solution : Time taken by sound waves to reach the bottom of the sea = 4/2 = 2s Velocity = Distance / Time
Distance = Velocity × Time
= 1550 × 2 = 3100m
Ans: Depth of the sea at that place = 3100m
3. The speed of sound in air at 0° C is 332 m/s. If it increases at the rate of 0.6 m/s per degree, what will be the temperature when the velocity has increased to 344 m/s?
Ans Data : Speed (v) at 0°C = 332 m/s. Increase in velocity of sound per degree = 0.6 m/s.
To find : Temperature (T) = ? Difference in velocity = 344 – 332 = 12 m/s.
For 1°C rise in temperature, velocity increases by 0.6 m/s. For x°C rise in temperature, velocity increases by 12 m/s.
1 0 . 6
=
x 12
12
x =
0 . 6
x = 20°C.
Result : Temperature at the velocity 344 m/s is 20oC.
4. Nita heard the sound of lightning after 4 seconds of seeing it. What was the distance of the lightning from her? (The velocity of sound in air is 340 m/s)
Ans Data : Velocity of sound in air (v) = 340 m/s. time (t) = 4 seconds.
To find : distance (λ) = ?
λ
v =
T .
λ = v x T.
λ = 340 m/s x 4 sec. λ = 1360 m.
Result : Therefore the distance of lightning from Nita is 1360 m
5. The molecular weight of oxygen gas is 32 while that of hydrogen gas is 2. Prove that under the same physical conditions, the velocity of sound in hydrogen is four times that in oxygen.
Ans Molecular weight (M1) of Oxygen gas (O2) = 32. Molecular weight (M2) of Hydrogen gas (H2) = 2.
1
Velocity of sound in a gas is inversely proportional to its molecular weight(M). v α
√M
Let ‘v1’ be the velocity of sound in O2 and ‘v2’ be the velocity of sound in H2.
Therefore, we get, v1 α
1 .
√M1 and v2 α
1 .
√M2
v1
i.e. =
v
2
i.e. v1
√M1
√M2
√2
= 32
v
2
i.e. v1 √1
v2 16
=
i.e. v1 √1
=
v2 4
v1 1
v = 4
2
Thus v2 = 4 v1. Hence, under the same physical conditions, the velocity of sound in hydrogen is four times that in oxygen.
6. A wave passes over a fixed point in space. Ten troughs and ten crests pass the point in 1 second. Find the frequency of the wave.
Ans Ten troughs and ten crests pass the given point in one second.
Therefore, 10 waves pass the point in 1 second.
No . of waves
Therefore, Frequency (f) =
=
Time period No . of waves
Time period
f = 10 hz.
Result : The frequency of the wave is 10 hz.
7. A wave has time period 20 seconds & is moving with a speed of 25 m/s. What is its wavelength? What is the distance between:
- two adjacent crests on wave 2) adjacent crest & trough?
Ans Data : Time period (T) = 20 seconds Velocity (v = 25 m/s.
To find : 1) Wavelength (λ) = ?
2) Half the Wavelength (λ/2) = ?
λ
v =
T
λ = v T
λ = 25 m/s x 20 sec. λ = 500 m.
Therefore, wavelength = 500 m.
The distance between two adjacent crests on the wave = λ = 500 m.
The distance between adjacent crest and trough on the wave =
λ 500m
2 = 2 = 250 m.
Hence, the distance between two adjacent crests is 500 m and the distance adjacent crest and trough on the wave is 250m.
8. A wave has wavelength 0.5 m and speed 50 m/s. Find the frequency of wave motion?
Data : Wavelength (λ) = 0.5 m Velocity (v) = 50 m/s.
To find : Frequency (f) = ?
Ans
v = f λ
v 50 m / s
f = λ = 0 . 5 m = 100 Hz.
Result : Hence, the frequency of the wavemotion is 100 Hz.
Q.9. Write Short Notes 6
1. Reverberation.
Ans i.. Reverberation is the phenomenon in which sound waves are reflected multiple times causing a single sound to be heard more than once.
ii. During reverberation, the time interval between the successive arrival of the same sound goes on decreasing.
iii. As a result, the reflected sound waves overlap and produce a prolongation of sound in the room which is at times difficult to understand.
iv. Some seats in public halls or auditoriums are considered acoustically poor because of reverberation.
2. Sonography
Ans i. Sonography technology uses ultrasonic sound waves to generate images of internal organs of the human body.
ii. This is useful in finding out the cause of swelling, infection, pain, condition of the heart, the state of the heart after a heart attack as well as the growth of foetus inside the womb of a pregnant woman are studied using this technique.
iii. This technique makes use of a probe and a gel. The gel is used to make proper contact between the skin and the probe so that the full capacity of the ultrasound can be utilized.
iv. The gel is applied to the skin outside the internal organ to be studied.
v. High-frequency ultrasound is transmitted inside the body with the help of the probe. The sound reflected from the internal organ is again collected by the probe and fed to a computer which generates the images of the internal organ.
vi. As this method is painless, it is increasingly used in medical practice for correct diagnosis.
3. SONAR
Ans i. SONAR is the short form for Sound Navigation and Ranging. It is used to determine the direction, distance and speed of an underwater object with the help of ultrasonic sound waves.
ii. SONAR has a transmitter and a receiver, which are fitted on ships or boats.
iii. The transmitter produces and transmits ultrasound waves. These waves travel through water, strike underwater objects and get reflected by them. The reflected waves are received by the receiver on the ship.
iv. The receiver converts the ultrasonic sound into electrical signals and these signals are properly interpreted.
v. The time difference between transmission and reception is noted. This time and the velocity of sound in water gives the distance from the ship, of the object which reflects the waves.
vi. SONAR is used to determine the depth of sea. SONAR is also used to search underwater hills, valleys, submarines, icebergs, sunken ships, etc.
Q.10. Attempt the following. 8
1. State the uses of echo.
Ans The uses of echo are as follows :
i. A bat produces ultrasonic waves and navigates itself by receiving the echo; thus avoiding the obstacles by hearing the echo from those obstacles.
ii. Principle of echo is used in the SONAR (Sound Navigation and Ranging)system. This method is used by ships to detect under water obstacles and also in measuring the depth of water.
iii. It is used to determine the position of an object in space.
2. Mention the uses of ultrasonic sound in the field of medicine.
Ans : Uses of ultrasonic sound in the field of medicine :
i. In the field of medicine, ultrasonic sound is used to observe the condition of unborn babies inside their mothers.
ii. Ultrasonic sound is used in the detection of some disease inside the stomach.
iii. Ultrasonic sound is used to study the heartbeats of a person by using the technique of Echocardiography.
3. State uses of SONAR.
Ans i. . SONAR is used to determine the direction, distance and speed of an underwater object with the help of ultrasonic sound waves.
ii. It is used to determine the depth of the sea.
iii. It is also used to search underwater hills, valleys, submarines, icebergs, sunken ships, etc.
4. State the uses of ultrasound.
Ans The uses of ultrasound are as follows :
i. For communication between ships at sea.
ii. To join plastic surfaces together.
iii. To sterilize liquids like milk by killing bacteria in it so that the milk stays for a longer duration.
iv. Echocardiography which studies heartbeats, is based on ultrasonic waves (Sonography technology)
v. To obtain images of internal organs in a human body.
vi. In industry, to clean intricate parts of machines where hands cannot reach.
vii. To locate the cracks and faults in metal blocks.
Q.11. Distinguish between : 8
1. Longitudinal Waves – Transverse Waves
Ans
| Longitudinal Waves | Transverse Waves | |
| i. | In a wave motion, if the particles of the medium vibrate in a direction parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave, then the wave is termed as longitudinal wave. | In a wave motion, if the particles of the medium vibrate in a direction perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave, then the wave is termed as transverse wave. |
| Longitudinal waves divide the medium into
alternate compressions and rarefactions. |
Transverse waves divide the medium into
alternate crests and troughs. |
|
| ii. | ||
| iii. | Longitudinal waves cannot be polarised. | Transverse waves can be polarised. |
| iv. | During wave motion, the density and pressure at any point vary between maximum and minimum values. | |
| During wave motion, there is no change in
density and pressure of the medium. |
||
| Longitudinal waves can be propagated through solids, liquids and gases. | Transverse waves can be propagated through solids but not through liquids and gases. | |
| v. | ||
| vi. | Example : Sound Waves. | Example : Light Waves. |
2. . Infra sound and Ultrasound waves.
Ans:
| Infrasound | Ultrasound | |
| Sound waves with frequency smaller than 20Hz is called infrasound. | Sound waves with frequency greater than 20KHz are called ultrasound. | |
| i. | ||
| ii. | Infrasonic sounds have frequency below the lower limit of human hearing. | Ultrasonic sounds have frequency above the higher limit of human hearing. |
| Whales, elephants produce sound in the infrasound range. | Bats, mice, dolphins, etc. can produce ultrasound. | |
| iii. |
3. Audible sound and Infra sound.
Ans
| Audible Sound | Infra Sound | |
| The frequency of these sounds ranges from 20 Hz to 20 KHz. | ||
| i. | The frequency of these sounds is below 20 Hz. | |
| ii. | These sounds are audible to humans. | These sounds are inaudible to humans. |
| Examples : Mass, volume, length, density, time, temperature, Energy. | Examples : Displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, momentum. | |
| iii. | ||
4. Compressions and Rarefactions.
Ans
| Compressions | Rere-factions |
| Compression is a region where the particles of the medium are crowded together, during the propagation of a longitudinal wave. | Rarefaction is a region where the particles of medium are well separated from each other during the propagation of a longitudinal wave |
| When a compression is formed at a point of the medium, the pressure is maximum. | When a rarefaction is formed at a point of the medium, the pressure is minimum. |
Q.12. Give scientific reasons 24
1. We cannot hear the explosions taking place on the sun.
Ans i. Sound requires a material medium for its propagation.
ii. There is vacuum between the sun and the earth for a considerable distance.
iii. Hence, the sound of the explosion on the sun cannot reach the earth.
iv. Therefore, we cannot hear the explosions taking place on the sun.
2. We cannot hear the echo produced in a classroom.
Ans i. Echo of sound depends upon the temperature of the surrounding and distance between source and reflecting surface.
ii. To hear distinct echo at 22 °C, the minimum distance required between the source of sound and obstacle should be 17.2 metre.
iii. In a classroom, the ceiling is not so high and the distance between the opposite walls is usually less than
17.2 m. Hence, we cannot hear echo produced in our classroom.
3. We cannot hear echo produced in our class room or in our house.
Ans i.Echo of sound depends upon the temperature of the surrounding and distance between source and reflecting surface.
ii.To hear distinct echo at 22°C, the minimum distance required between the source of sound and obstacle should be 17.2 metre.
iii. In a classroom, the ceiling is not so high and the distance between the opposite walls is usually less than
17.2 m.
iv.Hence, we cannot hear an echo in our class room or in our house.
4. Concave reflectors are built behind the preacher’s podium in old churches.
Ans i. The reflection of sound from a curved surface occurs in the same way as that of light.
ii. When a source of sound is kept at the focus of a concave reflector, the sound waves, on reflection, travel parallel to the principal axis of the reflector and reach the large audience.
iii. This was an effective method of magnifying the voice of the speaker in the absence of microphones.
iv. Hence, in the absence of microphones in old days, Concave reflectors are built behind the preacher’s podium in old churches.
5. Curved boards are placed behind a speaker in an auditorium.
Ans i. The reflection of sound from a curved surface occurs in the same way as that of light.
ii. When a source of sound is kept at the focus of a concave reflector, the sound waves, on reflection, travel parallel to the principal axis of the reflector.
iii. Hence, the curved boards are placed behind a speaker in an auditorium to increase the intensity of sound in the forward direction, towards the audience.
6 Sound waves travel faster in solids than in gases.
Ans i. Sound is a longitudinal wave and requires a material medium for its propagation.
ii. In solids, the particles of the medium are very close to the each other as compared to the particles in the gas.
iii. Denser is the medium, faster is the propagation of sound.
iv. Hence, sound travels faster on solids than in gases.
7. Bats can navigate in dark.
Ans i. For Bats, their ability to navigate in the dark depends on their ears and not eyes.
ii. The ultrasound produced by bats, gets reflected on hitting an obstacle.
iii. This reflected sound is received by their ears and they can locate the obstacle and estimate its distance even in the dark.
iv.Hence, bats can navigate in dark.
8. A microphone is used to speak in public in an open ground.
Ans i. In an open ground, the distance between the speaker and any sound reflecting surface is generally more than 17 metres.
ii. In such a condition, the reflected sound (i.e. echo) can be heard clearly.
iii. Moreover, to reach out to the audiences in an open ground, it is not possible without a mike.
iv. Hence, a microphone is used to speak in public in an open ground.
9. A bat can fly even in the dark night avoiding obstacles in its path.
Ans i. While flying, a bat produces sound of high frequency (ultrasonic sound).
ii. Ultrasonic sound is audible to a bat but not human beings.
iii. As the bat flies, it hears the sound reflected from the obstacles in its path.
iv. Thus, a bat can use echoes to detect the obstacles.
v. Hence, a bat can avoid collisions with obstacles and find its way even in the dark.
10. The intensity of reverberation is higher in a closed and empty house.
Ans i. In a closed house, the sound waves cannot escape and suffer multiple reflections from the wall of the house, resulting into reverberation.
ii. Also, a closed and empty house does not contain any sound absorbing materials like furniture.
iii. Hence, the intensity of reverberation is higher in a closed and empty house.
11. A person observes lightning first and then hears the thunder.
Ans i. The speed of light in air is 3 x 108 m/s while that of sound in air is about 332 m/s.
ii. Thunder and lightning occur at a short distance from the person standing nearby.
iii. Though they occur simultaneously, sound requires a few seconds more than light to cover the distance and reach the person as the speed of sound is far less than that of light.
iv. Hence, he hears the thunder some seconds after lightning is seen.
12. The roof of a movie theatre and a conference hall is curved.
Ans i. In a movie theatre or a conference hall, sound is produced at one place.
ii. These sound waves are usually reflected by the walls and ceilings.
iii. The acoustics of a movie theatre or conference hall should be such that the sound waves should reach everyone in the audience without any sound loss, echo production, reverberations after reflection.
iv. To make this possible, roof of a movie theatre and conference halls are curved so that sound reflected from the ceilings reaches all parts of the theatre or hall.
Q.13. Give examples 6
1. Give some examples where you encounter a) Transverse b) Longitudinal waves.
Ans i. Transverse waves: a. Waves produced in stringed musical instruments like sitar, violin etc.
b. Waves on the surface of water.
c. Light waves
ii. Longitudinal waves: a. Waves produced in a spring by pulling and pushing it.
b. Sound waves in air.
2. Name 4 Animals that have a special ability to hear ultrasonic sounds
Ans Dog, mouse, bat, dolphin
3. Give two examples of waves which are a mixture of transverse waves & longitudinal waves.
Ans The two examples of waves which are a mixture of transverse waves and longitudinal waves are :
i. Seismic waves. (Seismic waves are the waves which are produced due to an earthquake)
ii. Water waves on ocean.
Q.14. Give explanation using the given statement: 9
1. In a small hall, no distinct echo is heard – Justify.
Ans i. Distinct echo can be heard only if the reflecting surface is at a greater distance than 17 m.
ii. The sensation of sound formed on the ear–drum lasts only for 1/10th of a second.
iii. To hear a distinct echo, an echo should reach the ears after 1/10th of a second.
iv. In 1/10th of a second, the sound covers 340 m/s x 1 / 10
= 34 metres.
v. Hence, a distinct echo is heard only if the reflecting surface is at a distance greater than 17 m.
2. To hear the sound coming from a distant source, we hold the hollow of our hand at the back of our ear – Explain.
Ans i. We can hear sound only if sound waves enter our ear.
ii. The hollow of our hand acts as a concave sound reflecting surface.
iii. This would be helpful in directing the maximum number of sound waves into the ear.
iv. Hence, to hear the sound coming from a distant source, we hold the hollow of our hand at the back of our ear.
4. Explain “For echo to be heard clearly, the reflecting surface should be at a distance greater than 17 metres from the observer”.
Ans i. The repetition of sound, caused by its reflection from a distant surface, is called an echo.
ii. The effect of sound incident on human ears lasts for about 1/10th of a second.
iii. Hence, human brain cannot distinguish between two sounds if they are gathered by the ear within an interval of 1/10th of a second.
iv.Therefore, the echo can be heard clearly only if the reflected surface reaches the ear after an interval of 1/10th of a second.
v. The speed of sound in air at ordinary temperatures is about 340 m/s.
vi. Hence the reflected sound must travel at least 34 metre before reaching the human ear.
vii. Thus, for echo to be heard clearly, the reflecting surface should be at a distance greater than 17 metres from the observer.
Q.15. Suggest remedies / measures 6
1. How is sonography misused? What is the necessary step to prevent it?
Ans i. Sonography technology is used to follow the growth and well being of an unborn baby.
ii. Many people used this technique to find out the gender of an unborn baby which leads to the incidence of female foeticide.
iii. To prevent this, government has implied a law under PNDT Act in which female foecticide is considered as cognizable offence.
2. Measure that should be taken to prevent ear injury.
Ans 1. The ear is an important sensory organ.
- Sticks or other pointed objects should never be inserted into the ear for cleaning it.
-
Also, one should not hear very loud music using earphones.
-
It may cause grave injury to the eardrum.
Q.16. Attempt the following. 9
1. Explain why the whistle of a passing train is clearly heard on a quiet misty night.
Ans i. The velocity of sound in moist air is greater than that in dry air.
- Greater the humidity, greater is the velocity of sound in air.
- At night, the humidity is higher and the sound travels faster.
- Hence, the whistle of a passing train is clearly heard on a quiet misty night.
2. What should be the dimensions and the shape of classrooms so that no echo can be produced there?
Ans i. The major factors for production of echo are temperature of the surrounding and distance between the source and reflecting surface. At 22ºC, the minimum distance required for hearing a distinct echo is 17.2 m.
- Classrooms should be designed in such a manner that distance between two walls of the classrooms should be less than 17.2m.
- Classrooms are mostly designed in rectangular shape to avoid echo production.
-
- What do you mean by ultrasonic sound?
- Three different sounds of different frequencies 10 Hz, 500 Hz and 35,000 Hz are produced by different sources.
- Identify the sound produced by dolphins.
- Identify the sound that is audible to the human ear.
- Identify the sound produced by the pendulum?
Ans 1. i.Sound waves having frequency of more than 20 kilohertz are called ultrasonic sound.
ii. Ultrasonic sound is not audible to human beings
2. i.The sound with the frequency of 35,000Hz is produced by the dolphins.
- The sound with the frequency 500Hz is audible to the human ear.
- The sound with the frequency 10Hz is produced by pendulum.
Q.17. Solve Numerical problems 9
1. Helium gas is filled in two identical bottles A and B. The mass of the gas in the two bottles is 10 gm and 40 gm respectively. If the speed of sound is the same in both bottles, what conclusions will you draw?
Ans Mass of gas in bottle A = 10 gm Mass of gas in bottle B = 40 gm
Speed of sound in bottle A = Speed of sound in bottle B. i.e., VA = VB
As the gas in both the bottles is same, molecular weight is constant. Now, VA α √TA
VB α √TB
Also,
VA α
1
√ρA
, VB α
1
√ρB
where,
ρA = density of helium in bottle A,
ρB = density of helium in bottle B,
TA
∴ VA =
VB =
√ ρA
TB
√
ρB
But, VA = VB
TA TB
∴ ρA = ρB
√
√
TA ρA
√
√
TB = ρB
Taking squares on both sides
TA ρA
TB = ρB TA 10
TB = 40
TA 1
TB = 4
TB = 4TA
Temperature of B of 4 times the temperature of A.
2. Hydrogen gas is filled in two identical bottles, A and B at the same temperature. The mass of hydrogen in the two bottles is 12 gm and 48 gm respectively. In which bottles will the sound travel faster? How many times as fast as the other?
Ans Given : Mass of hydrogen in bottle A (m A ) = 12 gm Mass of hydrogen in bottle B (m B) = 48 gm
Find : Bottle in which the sound travels faster. Formula :Density = Mass / Volume
∴ ρ= m/v But, v 1/√p
√m
∴ v 𝖺 1/
√v
√v
So,v 𝖺 1/
√m
Solution : Since both the bottles are identical , the volume is the same.
√v
So, VA=
√mA
√v
VB =
√mB
….. 1
….. 2
Dividing 1 by 2
√mB
VA / VB=
√mA
= √48 / 12
= √4 = 2
So, VA= 2 VB
Ans : i. The velocity of sound will be more in bottle A.
ii. The velocity of sound in bottle A is twice that in bottle B.
3. Sunil is standing between two walls. The wall closest to him is at a distance of 360 m. If he shouts, he hears the first echo after 4 s and another after another 2 seconds
- What is the velocity of sound in air?
-
What is the distance between the two walls?
Ans Given : Distance of closest wall = 360 m
Time for first echo (T1) = 4 s Time for second echo (T2) = 2 s
To find : i. Velocity of sound in air.
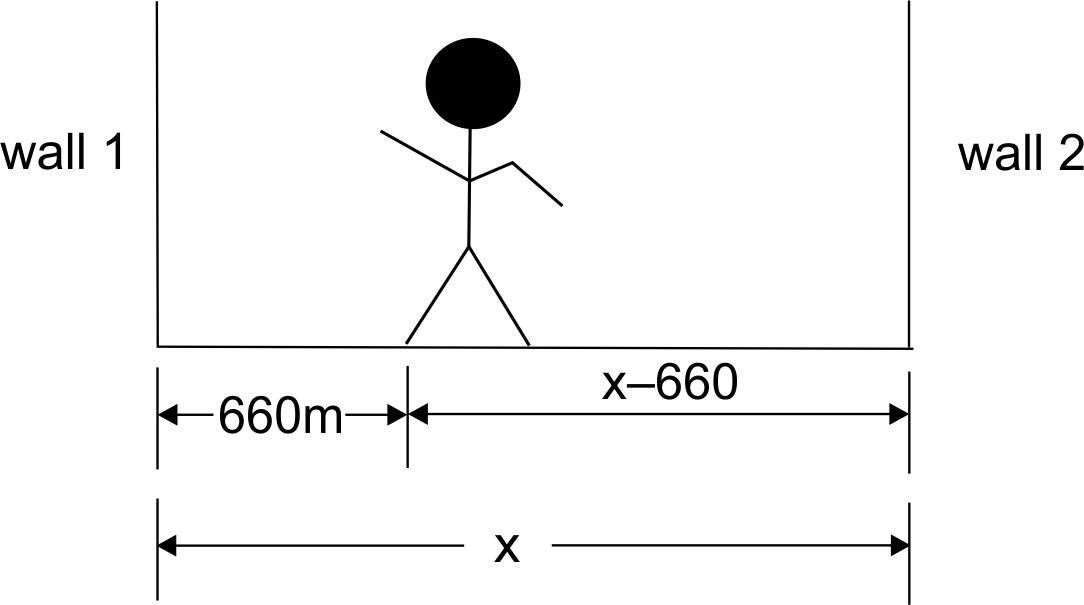 ii. Distance between two walls.
ii. Distance between two walls.
Calculation : i.
Disatance = 660 m
echo produced after time = 4 sec
∴ Time taken by sound to travel given distance = 2 sec
velocity = velocity =
Distance time
660
2
velocity = 330 m/s
ii. Let distance between two walls be x
∴ Distance of observer from wall 2 is (x – 660) m.
As, total time taken by sound to travel
4
(x – 660) m is 2 +
2
2 = 2 + 1 = 3s
x – 660
3
= 330
∴ x = 1650 m
- Velocity of sound in air is 330 m/s.
- Distance between two walls is 1650 m.
Q. 18. Complete the sentences in paragraph 9
1. Complete the paragraph.
(increases, brain, cavity, nerve, membrane, decrease, electrical, cochlea)
The outer ear collects the sound waves and passes them through a tube to a in the middle ear.
There is a thin membrane in the cavity of the middle ear called the eardrum. When a compression in a sound wave reaches the eardrum, the pressure outside it and it gets pushed inwards. The auditory nerve connects the inner ear to the brain. The inner ear has a structure resembling the shell of a snail. It is called the …………… . It receives the vibrations coming from the …………… and converts them into signals which are sent to the brain through the nerve. The analyses of these signals
Ans The outer ear collects the sound waves and passes them through a tube to a cavity in the middle ear. There is a thin membrane in the cavity of the middle ear called the eardrum. When a compression in a sound wave reaches the eardrum, the pressure outside it increases and it gets pushed inwards. The auditory nerve connects the inner ear to the brain. The inner ear has a structure resembling the shell of a snail. It is called the cochlea. It receives the vibrations coming from the membrane and converts them into electrical signals which are sent to the brain through the nerve. The brain analyses these signals
2. Complete the paragraph.
(same, parallel, Rarefactions, incident and reflected, longitudinal, Compressions, opposite, longitudinal)
…………… are regions where particles are crowded together. Here, density as well as pressure is high. are regions where particles are spread apart. Here, density as well as pressure is low. The direction in which a sound wave is , makes equal angles with the normal. The point of incidence, the normal, the incident wave and the reflected wave lie in the same plane. The incident and reflected sound waves are on the sides of the normal. During transmission of sound waves, the individual particles of the medium move in a direction to the direction of propagation of disturbance. Hence, sound waves are said to be waves.
Ans Compressions are regions where particles are crowded together. Here, density as well as pressure is high. Rarefactions are regions where particles are spread apart. Here, density as well as pressure is low. The direction in which a sound wave is incident and reflected, make equal angles with the normal. The point of incidence, the normal, the incident wave and the reflected wave lie in the same plane. The incident and reflected sound waves are on the opposite sides of the normal. During transmission of sound waves, the individual particles of the medium move in a direction parallel to direction of propagation of disturbance. Hence, sound waves are said to be longitudinal waves.
3. Complete the paragraph:
(audible, 20 Hz, infra-sound, greater, 20,000 Hz, electrical signals, less, pressure)
Range of frequencies of sound that can be heard by the human ears is called sound. The range of audible sound is between …………… to …………… . Sound of frequency less than 20 Hz is called …………… . Ultrasound has a frequency than 20,000 Hz. Human ear converts pressure variations in the air into ……………
Ans Range of frequencies of sound which can be heard by the human ears is called audible sound. The range of audible sound is between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Sound of frequency less than 20 Hz is called infra-sound. Ultrasound has a frequency greater than 20,000 Hz. Human ear converts pressure variations in air into electrical signals.
Q.19. Answer the following 33
1. What should be the dimensions and the shape of classrooms so that no echo can be produced there?
Ans i. For an echo to be heard, the minimum distance from the source should be 17.2m.
ii. Hence to avoid echo in the classroom , the distance between the two opposite walls should be less than 17.2m.
iii. Also dome shaped roof should be avoided in order to hear quality sound and no reverberations.
iv. Also sound absorbing materials like benches, furniture, boards, etc. should be used in order to prevent echoes in the classroom.
2. What is sonography? Explain the technique of sonography.
Ans i. Sonography technology uses ultrasonic sound waves to generate image of internal organs of the human body.
ii. Sonography is used to find swelling, infection pain etc.
iii. This technique uses a probe and a gel.
iv. The gel is used to make proper contact between the probe and the skin.
v. High-frequency ultrasound is transmitted inside the body with the help of the probe.
vi. The sound reflected from the internal organ is again collected by the probe and fed to the computer which generates the images of the internal organ.
3. Explain the factors on which velocity of sound in a gaseous medium depends.
Ans i. The velocity of sound in a gaseous medium depends on the physical conditions i.e. the temperature, density of the gas and its molecular weight.
ii. Temperature (T) : The velocity of sound is directly proportional to the square root of the temperature of the medium. This means that increasing the temperature four times doubles the velocity.
V 𝖺 √T
iii. Density (ρ) : The velocity of sound is inversely proportional to the square root of density. Thus, increasing the density four times, reduces the velocity to half its value.
1
V 𝖺
√ p
iv. Molecular Weight (M) : The velocity of sound is inversely proportional to the square root of molecular weight of the gas. Thus, increasing the molecular weight four times, reduces the velocity to half its value.
1
V 𝖺
√ M
4. Study the construction of the Golghumat at Vijapur and discuss the reasons for the multiple echoes produced there.
Ans i. Gol Gumbaz (or Goghumat) meaning circular dome at Bijapur is the mausoleum. It is also called whispering gallery.
ii. The sides of the chamber are semi-octagonal in shape with the diameter of the dome being 44m and height of 5m, thus meeting the condition of minimum distance for the echo i.e. 17.2 m.
iii.So, due to this larger distance and petal shaped domed structure, the sound is reflected multiple time and multiple echoes can be heard.
5. Where and why are sound absorbing materials used?
Ans i. Sound absorbing materials are used in auditorium and halls to reduce excessive reverberation.
ii. The roofs and walls of the auditorium are covered with sound absorbing materials like thermocol, fibre board, rough plaster etc.
iii.Seats are made of sound–absorbing materials so that excessive reverberation is reduced.
6. When is the reflection of sound harmful?
Ans i. Reflected sound of high intensity is disturbing and harmful.
ii. Reflected sound from poor quality infrastructure in concert halls, auditoriums, etc. can also be harmful.
iii. Apart from this, sound from loudspeakers, honking, supersonic jets, etc. can also be harmful to the human ear.
7. How do physical conditions affect velocity of sound in a gaseous medium?
Ans i. The velocity of sound in a gaseous medium depends on physical conditions like temperature, density of the gas and molecular weight.
ii. If temperature(T) of the medium increases then the velocity of sound in the medium also increases. The velocity of sound varies with temperature as v α √T
iii. If the density(ρ) and molecular weight (M) of the medium increases, then velocity of sound in the medium decreases. The velocity of sound varies with density(ρ) and molecular weight(M) as
1 1
v α and v α
√ρ √M
8. What is reflection of sound? Give any three practical applications of the phenomenon.
Ans i. When there is an obstacle in the path along which sound propagates in a medium, the sound strikes the obstacle and then propagates in a different direction. This phenomenon is known as reflection of sound.
ii. The practical applications of reflection of sound are as follows :
a. to determine the speed of sound in air.
b. to determine the depth of water.
c. to locate an object under water.
9. What is an echo? What factors are important to get a distinct echo?
Ans i. An echo is the repetition of the original sound because of reflection by some surface.
ii. At 22°C, the velocity of sound in air is 344 m/s. Our brain retains the sound for 0.1s.
iii. Thus for us to be able to hear a distinct echo, the sound should take more than 0.1s after starting from the source to get reflected and come back to us.
We know that,
iv. Distance = Speed x Time
= 344 m/s × 0.1s
= 34.4 m
v. Thus, to be able to hear a distinct echo, the reflecting surface should beat a minimum distance of half and above i.e. 17.2m
vi. As the velocity of sound depends on the temperature of air, this distance depends on the temperature.
10. What is infrasonic, sonic and ultrasonic sound?
OR How is ultrasound used in medical science?
Ans 1. Sound waves, on the basis of their frequency, are classified into :
i. Infrasonic sound : The frequency of Infrasonic sound is below 20 hertz.
ii.Sonic sound : Its frequency is between 20 – 20000 hertz which is audible to human ear.
iii.Ultrasonic sound : The frequency of ultrasonic sound is above 20000 hertz.
- Echocardiography : It technique which is used to study heart beats and is based on ultrasonic waves. Sonography : This technology uses ultrasound waves to generate images of internal organs of the human body. This technology is also used to follow the growth and well -being of an unborn baby.
11. Explain how the principle of echo is used in the SONAR systems to measure the depth of water.
Ans i. . The Principle of echo is used in the SONAR (Sound Navigation and Ranging) system. This method is used by ships to measure the depth of water.
ii. Sharp pulses are emitted from the transmitter in the ship.
iii. ` These pulses travel downward and are reflected from the sea bed.
iv. The reflected sound is detected by the receiver in the ship.
v. If ‘t’ is the time interval between the production of sound and its detection after reflection, and ‘V’ is the speed of sound in water, the total distance covered by the sound is Vt.
vi. These can be found as V and t are known.
vii. The depth of water is half the distance.
viii. Thus, the depth of water can be determined using the principle of echo.
Q.20. Extra data (Not to be Use) 15
1. What is SONAR system? State its uses?
Ans ii. SONAR is the short form for Sound Navigation and Ranging.
ii. SONAR is used to determine the direction, distance and speed of an underwater object with the help of ultrasonic sound waves.
iiii.I t is used to determine the depth of the sea.
iv.It is also used to search underwater hills, valleys, submarines, icebergs, sunken ships, etc.
2. What is an echo? Give the condition for it.
Ans ii. The repetition of sound, caused by its reflection from a distant surface, is called an echo.
ii. The echo can be heard if the distance between the reflecting surface and the observer is greater than 17 metres.
iii. Also, it depends upon the temperature of the surrounding.
3. Explain the working of the human ear.
Ans The ear is an important organ of the human body. We hear sounds because of our ear. When sound waves fall on the eardrum, it vibrates. These vibrations are converted into electrical signals which travel to the brain through nerves. The ear can be divided into three parts: 1. Outer ear, 2. Middle ear, 3. Inner ear
1. Outer ear or Pinna
i. The outer ear collects the sound waves and passes them through a tube to a cavity in the middle ear.
ii. Its peculiar funnel like shape helps to collect and pass sounds into the middle ear.
2. Middle ear
i. There is a thin membrane in the cavity of the middle ear called the eardrum.
ii. When a compression in a sound wave reaches the eardrum, the pressure outside it increases and it gets pushed inwards.
iii. The opposite happens when a rarefaction reaches there.
iv. The pressure outside decreases and the membrane gets pulled outwards. Thus, sound waves cause vibrations of the membrane.
2. Inner ear
i. The auditory nerve connects the inner ear to the brain.
ii. The inner ear has a structure resembling the shell of a snail. It is called the cochlea.
Iii .The cochlea receives the vibrations coming from the membrane and converts them into electrical signals which are sent to the brain through the nerve. The brain analyses these signals.
Q.21. Answer the following in detail 20
1. Explain why astronauts cannot communicate on the moon in a normal way?
Ans i. Sound requires a material medium for propagation.
ii. There is no atmosphere on the moon.
iii. Sound cannot propagate on the moon as it does on the earth.
iv. Thus, sound cannot be heard on the moon.
v. Hence, astronauts cannot communicate on the moon as it does on the earth.
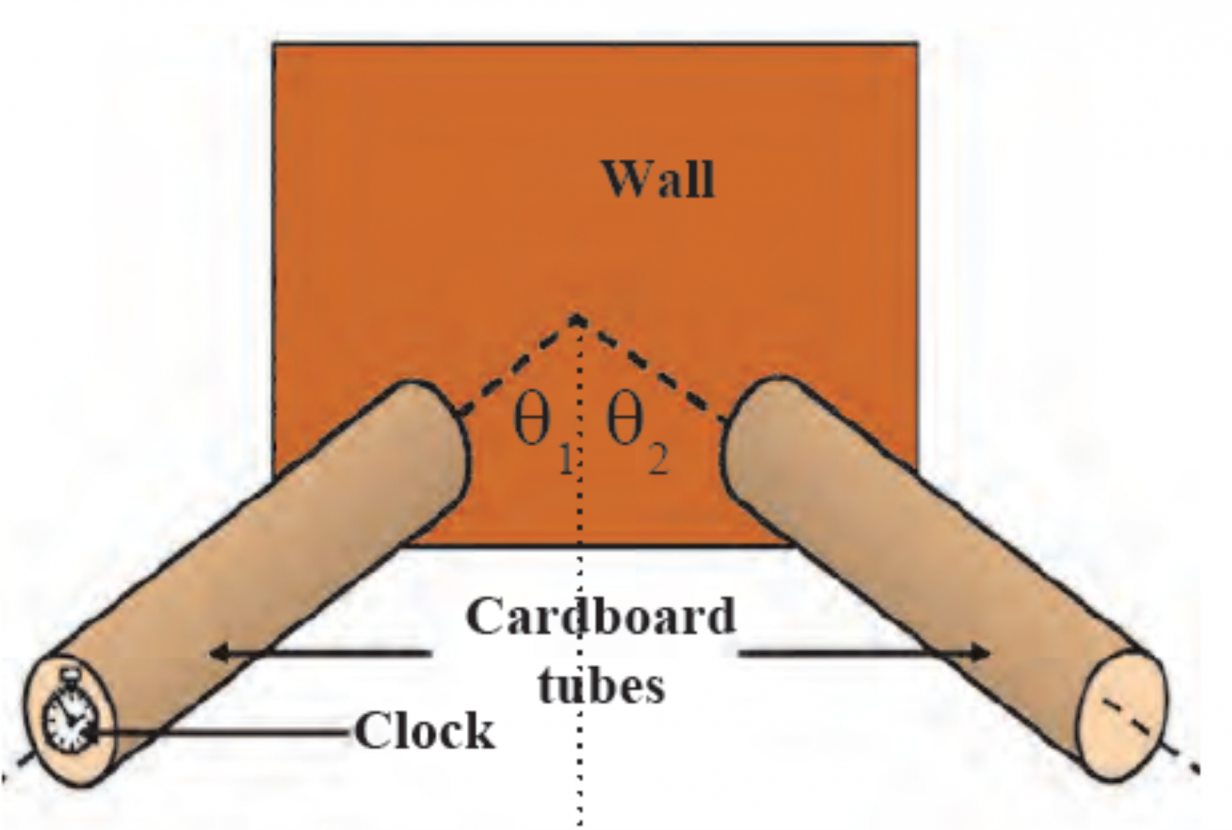
2.
i. What is the above activity based on?
ii. In the figure, name the angles θ1 and θ2.
iii. If θ1 is at 300, what will be the measure of θ2?
iv. In the above activity, what will happen if you lift one of the tubes to some height?
Ans i. . The above activity is based on Reflection of sound.
ii. θ1- angle of incidence and θ2- angle of reflection
iii. If θ1 is at 30o then θ2 will also be 30o because angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
iv. If one of the tubes is lifted to some height, then angle of incidence will not be equal to angle of reflection, so the reflected sound will not be clear.
3. How a tuning fork can produce longitudinal waves?
Ans i. Longitudinal waves consists of alternate compressions and rarefactions.
ii. When the prongs of a vibrating tuning fork bend outwards, a compression is formed because the layers of air adjacent to them are pressed together.
iii. When the prong of a vibrating tuning fork bend inwards, a rarefaction is formed because the layers of air adjacent to them are separated.
iv. As the prongs of the tuning fork vibrate very rapidly, the compressions and rarefactions are alternatively produced at a fast rate and they travel through air in the form of longitudinal waves.
v.Thus, a tuning fork can produce longitudinal waves.
4. Describe the human ear.
Ans i. Human beings hear sound through the ears.
ii. The ear converts vibrations which fall in it into electrical signals that travel to the brain via the nerves.
iii. There are three major parts of the ear :- a) outer b) middle c) inner.
iv. Outer ear (Pinna) : The outer part is called as Pinna. It has a funnel like shape which helps in collecting the sound waves. These sound waves are then carried by the auditory canal to the ear drum.
v. Middle ear : The middle ear consists of a thin membrane in the cavity called the ear drum. When a compression of a sound wave reaches the ear drum, the pressure outside the ear drum increases and forces the ear drum inwards. Similarly, when a rarefaction reaches it, the ear drum gets pulled outwards. In this way, sound waves cause the ear drum to vibrate. These vibrations are carried to the inner part of the ear.
Vi Inner ear : A part of the auditory nerve connects the part of inner ear to the brain. The inner ear has a snail’s shell shaped structure called the cochlea. In cochlea, the vibrations received from the ear drum are converted into nerve impulses or electrical signals, which are sent to the brain through the nerves.
The brain then analyses and interprets them as sound.