Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 13 Chemical Change and Chemical Bond Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Q.1. Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statements 1
1. New substances formed as a result of the reaction are called ……………
Ans New substances formed as a result of the reaction are called products.
Q. 2 . Find co-related terms 7
1. Boiling of water : Physical change : Softening of hard water:
Ans Chemical change
Boiling of water is a physical change while softening of hard water is a chemical change.
2. H2O: Covalent compound :: Cao:
Ans Ionic compound
H2O is a covalent compound while CaO is an ionic compound.
3. C + O2 →CO2: Chemical equation :: Carbon + Oxygen Carbon dioxide : Ans Word equation
The equation written using chemical formulae is called chemical equation while the equation written using names is known as word equation.
4. Magnesium : :: Chlorine : (2, 8, 7)
Ans (2, 8, 2)
The electronic configuration of chlorine is (2, 8, 7) while the electronic configuration of magnesium is (2, 8, 2).
4. NaCl : Ionic bond :: H2O : ?
Ans NaCl : Ionic bond :: H2O : Covalent bond
5. Formation of glucose : Photosynthesis :: Breaking of glucose : ?
Ans Formation of glucose : Photosynthesis :: Breaking of glucose : Respiration
6. Sodium atom : Valency 1 :: Oxygen atom : Ans Valency 2
Valency of sodium atom is 1 while valency of oxygen atom is 2.
Q.4. Extra data 2
1. Ionic compounds
Ans Potassium fluoride (KF) and calcium oxide (CaO).
2. Covalent compounds
Ans Water (H2O) and hydrogen (H2) molecule.
Q. 3 . Match the pair 4
1.
| Column – A | Column – B |
| i. Photosynthesis | a. Physical change |
| ii. Dissolution of salt in water | b. Covalent bond |
| c. Tendency to form ionic bond | |
| d. Chemical change |
Ans
| i. Photosynthesis | Chemical change |
| ii. Dissolution of salt in water | Physical change |
2.
| Column-A | Column-B |
| i. Carbon | a. Physical change |
| ii. Fluorine | b. Reactant in combustion process |
| c. Tendency to form ionic bond | |
| d. Tendency to form anion |
Ans
| i. Carbon | Reactant in combustion process |
| ii. Fluorine | Tendency to form anion |
3.
| Column – A | Column – B |
| i. Fluorine | a. Physical change |
| ii. Magnesium | b. Reactant in combustion process |
| c. Tendency to lose electrons | |
| d. Tendency to form anion |
Ans:
| i. Fluorine | Tendency to form anion |
| ii. Magnesium | Tendency to lose electrons |
4.
| Column – A | Column – B |
| i. Sodium chloride | a. Reactant in combustion process |
| ii. Water | b. Chemical change |
| c. Ionic bond | |
| d. Covalent bond |
Ans:
| i. Sodium chloride | Ionic bond |
| ii. Water | Covalent bond |
Q.4.State True or False 8
1. During a physical change the chemical composition of the original matter changes.
Ans False – During a chemical change the chemical composition of the original matter changes.
2. During a physical change the chemical composition of the original matter changes.
Ans False – During a chemical change the chemical composition of the original matter changes.
3. Respiration is a continuously occuring ecological process.
Ans False – Respiration is a continuously occuring biological process.
4. Combustion of fuel is a fast and irreversible chemical change.
Ans True
5. Respiration is a continuously occuring ecological process.
Ans False – Respiration is a continuously occuring biological process.
6. Combustion of fuel is a fast and irreversible chemical change.
Ans True
7. Substances written on the left side of the arrow are original substances that are formed in the reaction and are called products.
Ans False – Substances written on the left side of the arrow are original substances that take part in the reaction and are called reactants.
8. Substances written on the left side of the arrow are original substances that are formed in the reaction and are called products.
Ans False – Substances written on the left side of the arrow are original substances that take part in the reaction and are called reactants.
Q.5. Name the following 6
1. Name the two types of chemical bonds.
Ans Ionic and Covalent bond.
2. Name the two types of chemical changes.
Ans Manmade chemical changes and Natural chemical changes.
3. Name the two types of chemical changes.
Ans Manmade chemical changes and Natural chemical changes.
4. Name the two types of chemical bonds.
Ans Ionic and Covalent bond.
5. Name any two fuels.
Ans Wood, coal, petrol, cooking gas, etc.
6. Name any two fuels.
Ans Wood, coal, petrol, cooking gas, etc.
Q.6. Multiple Choice Questions (Activity) 8
1. Difference between H2 molecule and H2O molecule is ……………
a.H2 is monoatomic molecule while H2O is diatomic
b. Both show different type of bonding
c. Difference in ionic bonding
d. H2 molecule has incomplete duplet while H2O has complete octet.
Ans Option a.
2. On adding of which compound, Calcium hydroxide turns milky?
a.Carbon monoxide c. Carbon chloride
b Carbon dioxide d. Carbon citrate
Ans Option b.
3. Citric acid with sodium bicarbonate releases which gas ?
a.H2
b. O2
c. CO2
d. H2CO3
Ans Option c. CO2
4. Respiration takes place by intake of …………… .
a. H2
b. O2
c. CO2
d. H2CO3
Ans Option b. O2
5. Which of the following is not a man made chemical change?
a.Photosynthesis
b. Cleaning Shahabad tile with dilute hydrochloric acid.
c. Softening of hard water.
d. Combustion of fuels.
Ans Option a.
6. Acid with base undergo which reaction ?
Oxidation b. Respiration c. Photosynthesis d. Neutralization.
Ans Option d.
7. Positive and negative ions form ionic bond due to ……………
Repulsive forces c. Impulsive forces
Electrostatic forces d. Pressure applied
Ans Option b.
8. Which of the following is an irreversible chemical change?
Softening of water b. Boiling of water
c. Melting of ice d. Darkening of a cut potato.
Ans Option d.
Q.7. Multiple Choice Questions (Experiment) 5
1. Photosynthesis cannot take place without which of the following?
Oxygen b. Nitrogen c. Carbon dioxide d. Glucose
Ans Option c.
2. New substances formed as a result of the reaction of , are called products.
Reactants b. Pre-products c. Producers d. Precursors
Ans Option a.
3. Respiration takes place by intake of ……………
H2
Ans Option b.
O2
CO2
H2CO3
4. Which of the following is an irreversible chemical change?
Softening of water b. Boiling of water
c. Melting of ice d. Darkening of a cut potato.
Ans Option d.
5. Valence shell is ……………
a. the outermost shell b. shell containing highest number of electrons.
c. the innermost shell d. shell containing less than 2 electrons.
Ans Option a.
Q.8. Solve Numerical problems: 4
1. Photosynthesis.
Ans CO + H O
Sunlight
2 2 −−−−−−→ C6H12O6 + O2
Green plant
2. Combustion of fuels.
Ans C + O2 →CO2
Q.9. Write Short Notes 8
1. Ionic bond.
Ans i. The chemical bond formed due to an electrostatic force of attraction between the oppositely charged cation and anion is called an ionic bond or an electrovalent bond.
The compound formed by means of one or more ionic bonds is called ionic compound.
The valency of an ion is equal to the magnitude of positive or negative charge on it.
An ion forms the same number of ionic bonds as its valency.
2. Manmade chemical changes
Ans When the chemical composition of the original matter changes and new substances having different properties and different chemical composition are formed by means of human activities are called manmade chemical changes.
3. Softening of hard water.
Ans i. Some wells or tube wells have hard water. It is brackish to taste and does not form lather with soap.
This is because of hard water contains the chloride and sulphate salts of calcium and magnesium in dissolved state. To soften the hard water, a solution of washing soda is added to it.
This results in a chemical reaction to form a precipitate of insoluble carbonate salts of calcium and magnesium.
As the dissolved salts of calcium and magnesium go out in the form of precipitate of the carbonate salts, the water is softened.
4. Ionic compound.
Ans The chemical bond formed due to an electrostatic force of attraction between the oppositely charged cation and anion is called an ionic bond or an electrovalent bond. The compound formed by means of one or more ionic bonds is called ionic compound.
Q.10. Write equation 8
1. When baking soda is added to lemon juice
Ans Citric acid + Sodium bicarbonate → Carbon dioxide + Sodium citrate
Acid + Alkali →
2. Combustion of fuels.
CO2
+ Salt
Ans Combustion of fuels : Wood, coal, petrol or cooking gas are burnt for getting energy. The common substance that burns in all these fuels is ‘Carbon’. During the combustion process carbon combine with oxygen in air and the product carbon dioxide is formed. A common equation can be written for all these combustion processes as follows.
Word equation : Carbon + Oxygen →Carbon dioxide Chemical equation : C + O2 → CO2
Combustion of fuel is a fast and irreversible chemical change.
3. Respiration.
Ans Word equation :
Glucose + Oxygen respiration Carbon dioxide + Water Chemical equation :
−−−−−→
C6H12O6 + O2 respiration —-🡪 CO2 + H2O
4. Photosynthesis.
Ans You know that green plants perform photosynthesis in sunlight. A word equation and a chemical equation (unbalanced) can be written for this natural chemical change as follows.
Word equation : Carbon dioxide + Water
Sunlight
−−−−−−→
green plant
Glucose + Oxygen
Q.11. Complete the given flow chart / table / diagram 8
1
| Element symbol | Electronic configuration |
| 11Na | …………… |
| …………… | (2, 8, 7) |
| …………… | (2, 8, 2) |
| 9F | …………… |
Ans:
| Element symbol | Electronic configuration |
| 11Na | (2, 8, 1) |
| 17Cl | (2, 8, 7) |
| 12Mg | (2, 8, 2) |
| 9F | (2, 7) |
 2
2
 Ans
Ans
3.
| Compound | Type of chemical bonds |
| Cl2 | …………… |
| MgCl2 | …………… |
| HCl | …………… |
| CaO | …………… |
Ans
| Compound | Type of chemical bonds |
| Cl2 | Covalent |
| MgCl2 | Ionic |
| HCl | Covalent |
| CaO | Ionic |
4.
 Ans
Ans
Q.12. Distinguish between: 2
1. Ionic Bond & Covalent Bond (Minimum 4 points).
Ans
| Ionic bond | Covalent bond | ||
| i. | i. | The chemical bond formed by sharing of valence electrons of two atoms with each other is called a covalent bond. | |
| The chemical bond formed due to an electrostatic force of attraction between the oppositely charged cation and anion is called an ionic bond. | |||
| ii. | The ions are formed with positive and negative charges. | ii. | Partial charge is developed due electronegative difference of atoms. |
| It takes between heteronuclear as well as in homonuclear compounds. | |||
| iii. | It takes only between heteronuclear atoms. | iii. | |
| These compounds do not dissociate in water. | |||
| iv. | These compounds dissociate in water. | iv. | |
Q.13. Laws/define/principles: 2
1. ionic bond or an electrovalent bond.
Ans The chemical bond formed due to an elctrostatic force of attraction between the oppositely charged cation and anion is called an ionic bond or an electrovalent bond.
Q.14. Give scientific reasons 2
1. Noble gases do not form any chemical bond.
Ans i. Noble gases do not form any chemical bond as their electron octet/duplet is complete while the atoms with
incomplete electron octet/duplet form chemical bonds.
ii. Reason for this is that an atom uses its valence electrons during formation of a chemical bond. Moreover on forming chemical bonds equal to its valency the atom attains the electronic configuration of complete octet/duplet.
Q.15. Give examples 8
1. Formation of Covalent bond.
Ans . i.The chemical bond formed by sharing of valence electrons of two atoms with each other is called a covalent bond.
ii.One covalent bond is formed by sharing of two valence electron. The figure 13.5 shows formation of the H2 molecule from two hydrogen atoms, using diagramatic representation of electronic configuration.
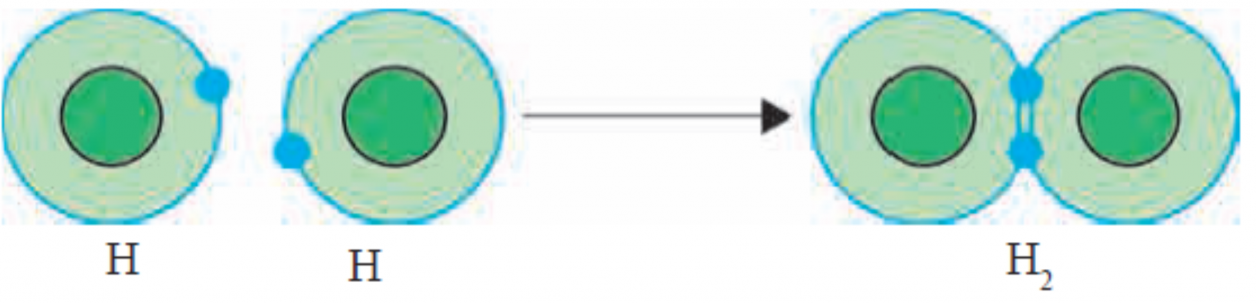 [Figure : Formation of Covalent bond in H2 molecule ]
[Figure : Formation of Covalent bond in H2 molecule ]
iii. A covalent bond between two atoms is also represented by dash joining their symbols.
2. Open ended questions. Such questions can be suggestion/ opinion based. How to write a chemical equation step by step?
Ans i. First step of writing a chemical equation is to write a word equation by using the names of the concerned substances.
ii. When the chemical formula is written in place of each of the names, it becomes a chemical equation.
iii. While writing a chemical equation, original substances are written on the left side and newly formed substances are written on right side and an arrow is drawn in between.
iv. Arrow head points towards the substances formed. Arrow indicates the direction of the reaction.
v. Substances written on the left side of the arrow are original substances that take part in the reaction. They are called reactants.
vi. New substances formed as a result of the reaction are called products. Place for the products of a reaction is on the right side of the arrow.
3. Manmade chemcal
Ans Four examples of manmade chemical changes are:
i. Preparation of soda-lemon cold drink
ii.Combustion of fuels
iii. Cleaning shahabad tile with dilute hydricholoric acid
iv.Softerning of hard water
4. Formation of Covalent bond.
Ans i. The chemical bond formed by sharing of valence electrons of two atoms with each other is called a covalent bond.
ii. One covalent bond is formed by sharing of two valence electron. The figure 13.5 shows formation of the H2 molecule from two hydrogen atoms, using diagrammatic representation of electronic configuration.
 [ Figure Formation of Covalent bond in H2 molecule ]
[ Figure Formation of Covalent bond in H2 molecule ]
iii.A covalent bond between two atoms is also represented by dash joining their symbols.
Q.16. Activity based question (3 mks) 9
1. Take the lemon juice in a clean glass. Take two drops of the lemon juice in a spoon and taste. Add a pinch of baking soda in the glass of lemon juice.
i. What is the observation of the following activity?
ii. Which component is acidic and which is basic in the reaction?
iii. What is the type of reaction taking place here?
Ans i. The rapid effervescence or bubbles of Carbon dioxide is seen.
ii. Lemon juice is acidic while baking soda is basic.
iii. Neutralization.
2. Classify the following into natural chemical changes and man made chemical changes.
[Respiration, Softening of hard water ,Cleaning Shahabad tile with dilute hydrochloric acid, Melting of ice, Combustion of fuels, Photosynthesis, Ripening of fruit, darkening of a cut potato]
Ans Natural chemical changes – Respiration, Melting of ice, Photosynthesis, Ripening of fruit, darkening of a cut potato. Man made chemical changes – Softening of hard water, Cleaning Shahabad tile with dilute hydrochloric acid, Combustion of fuels.
3. Classify the following into natural and man-made chemical changes.
[Respiration, Softening of hard water, Cleaning Shahabad tile with dilute hydrochloric acid, Melting of ice, Combustion of fuels, Photosynthesis, Ripening of fruit, darkening of a cut potato]
Ans Natural chemical changes – Respiration, Melting of ice, Photosynthesis, Ripening of fruit, darkening of a cut potato.
Man-made chemical changes – Softening of hard water, Cleaning Shahabad tile with dilute hydrochloric acid, Combustion of fuels.
Q.17. Explain the statement. 30
1. Covalent bond
Ans The chemical bond formed by sharing of valence electrons of two atoms with each other is called a covalent bond. One covalent bond is formed by sharing of two valence electron.
2. Bubbles are seen on adding lemon juice to baking soda.
Ans i. When baking soda is added to lemon juice, a chemical change takes place.
ii. Citric acid present in the lemon juice reacts with baking soda to form carbon dioxide gas and sodium citrate.
iii. The released carbon dioxide gas produces bubbles.
Hence, bubbles are seen on adding lemon juice to baking soda.
iv. The word equation is a follows:
Citric acid + Sodium bicarbonate → Carbon dioxide + Sodium citrate (Acid) (Alkali) (CO2) (Salt)
3.Ionic compound.
Ans The chemical bond formed due to an electrostatic force of attraction between the oppositely charged cation and anion is called an ionic bond or an electrovalent bond. The compound formed by means of one or more ionic bonds is called ionic compound.
4. Hard water gets softened on mixing with a solution of washing soda.
Ans i. Hard water is water that contains the chloride and sulphate salts of calcium and magnesium in dissolved form.
Ii. When washing soda (sodium carbonate) is added to hard water, a chemical reaction occurs.
iii. In this reaction, precipitate of insoluble carbonate salts of calcium and magnesium is formed.
iv.Since the dissolved salts of calcium and magnesium are removed in the form of insoluble carbonate salts as precipitate, the water gets softened. Hence, hard water gets softened on mixing with a solution of washing soda.
V The word equation for the removal of calcium from hard water is,
Calcium chloride +Sodium carbonate → Calcium carbonate + Sodium chloride
5. Natural chemical changes
Ans When the chemical composition of the original matter changes and new substances having different properties and different chemical composition are formed in nature spontaneously are called natural chemical changes.
6. Covalent bond.
Ans The chemical bond formed by sharing of valence electrons of two atoms with each other is called a covalent bond. One covalent bond is formed by sharing of two valence electron.
7. Lime stone powder disappears on adding to dilute hydrochloric acids.
Ans i. Lime stone powder is calcium carbonate.
ii.Lime stone powder reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid and three products are formed.
iii. The products are calcium chloride, carbon dioxide gas and water.
iv. The first product, calcium chloride is water soluble and mixes up air while the third product, water mixes up with water.
v. The second product, carbon dioxide forms bubbles and mixes up in air while the third product, water mixes up with water.
Hence, lime stone powder disappears on adding to dilute hydrochloric acids.
vi. The word equation is,
Calcium carbonate + dilute Hydrochloric acid → Calcium chloride + Carbon dioxide + Water
8. Natural chemical changes.
Ans When the chemical composition of the original matter changes and new substances having different properties and different chemical composition are formed in nature spontaneously are called natural chemical changes.
9. Manmade chemical changes.
Ans When the chemical composition of the original matter changes and new substances having different properties and different chemical composition are formed by means of human activities are called manmade chemical changes.
10. Respiration is a chemical change.
Ans i. Respiration is a biological process that occurs continuously.
ii. In this process, living organisms inhale air and exhale carbon dioxide.
iii. Through detailed study, it is learnt that glucose in the cells reacts with oxygen from the inhaled air to form carbon dioxide and water. Hence, respiration is a chemical change.
iv. The word equation for a chemical change occurring in respiration is as follows : Glucose + Oxygen −−−−−→ Carbon dioxide + Water
Respiration
Q.18. Suggest remedies / measures 3
1. How to write a chemical equation step by step?
Ans i. First step of writing a chemical equation is to write a word equation by using the names of the concerned substances.
ii. When the chemical formula is written in place of each of the names, it becomes a chemical equation.
iii. While writing a chemical equation, original substances are written on the left side and newly formed substances are written on right side and an arrow is drawn in between.
iv. Arrow head points towards the substances formed. Arrow indicates the direction of the reaction.
v. Substances written on the left side of the arrow are original substances that take part in the reaction. They are called reactants.
vi. New substances formed as a result of the reaction are called products. Place for the products of a reaction is on the right side of the arrow.
Q.19. Draw / Label the diagram 4
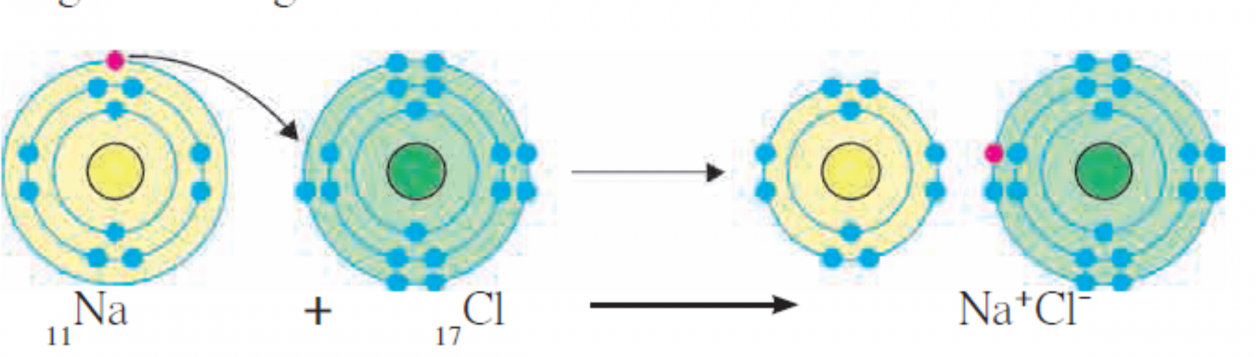
1. Formation of Ionic bond of NaCl
 Ans
Ans
Q. 20. Explain with the help of examples 6
1. Explain the formation of covalent bond.
Ans i. The chemical bond formed by sharing of valence electrons of two atoms with each other is called a covalent bond. One covalent bond is formed by sharing of two valence electron.
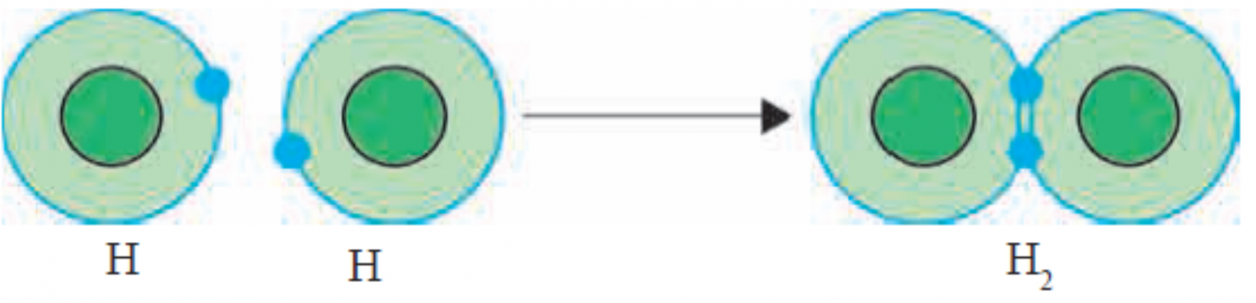 ii. Figure – Formation of Covalent bond in H2 molecule
ii. Figure – Formation of Covalent bond in H2 molecule
iii. The above figure shows formation of the H2 molecule from two hydrogen atoms, using diagramatic representation of electronic configuration.
iv. A covalent bond between two atoms is also represented by dash joining their symbols.
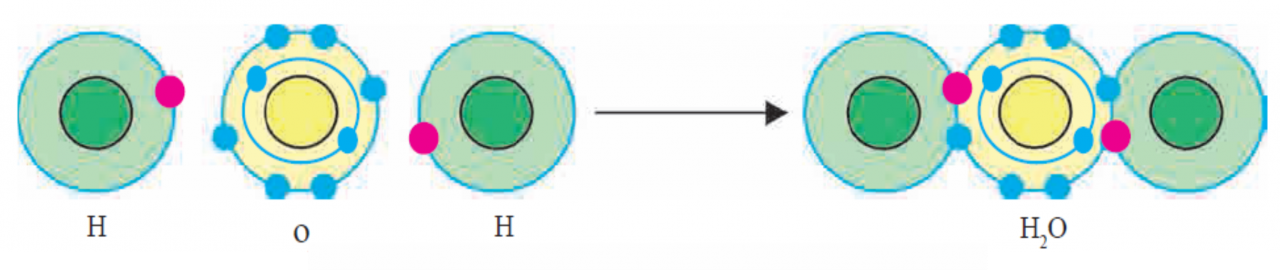 v. Figure – Formation of Covalent bond in H2O molecule
v. Figure – Formation of Covalent bond in H2O molecule
vi. Now let us see how an H2O molecule of a covalent compound is formed from hydrogen and oxygen atoms. (See figure at Serial No.v) There are six electrons in the valence shell of oxygen atom. It means that the electron octet in oxygen is short of two electrons and the valency of oxygen is ‘2’.
Vii In the H2O molecule the oxygen atom completes its octet by forming two covalent bonds, one each with the two hydrogen atoms. While this happens, the duplets of the two hydrogen atoms also are completed.
2. Explain the formation of Ionic bond.
Ans i. The chemical bond formed due to an electrostatic force of attraction between the oppositely charged cation and anion is called an ionic bond or an electrovalent bond.
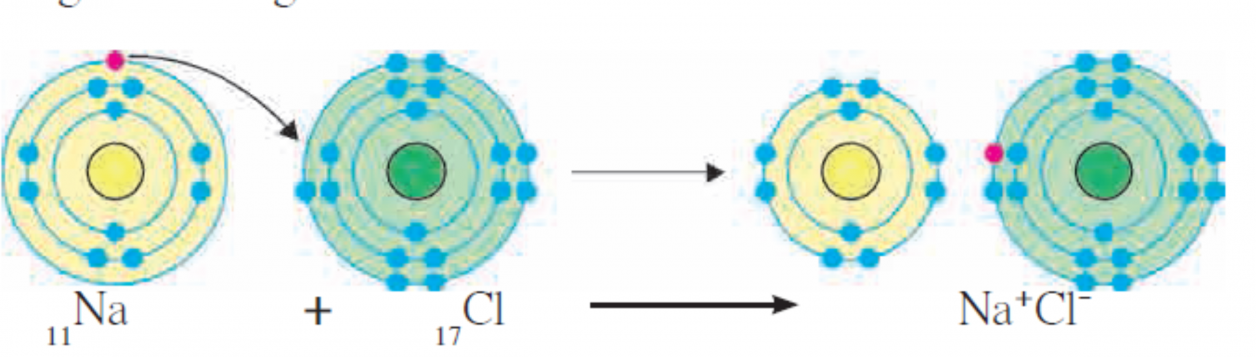 ii. The compound formed by means of one or more ionic bonds is called ionic compound.
ii. The compound formed by means of one or more ionic bonds is called ionic compound.
[Figure – Formation of Ionic bond of NaCl]
iii. Formation of an ionic compound sodium chloride from the elements sodium and chlorine is shown with the help of diagramatic representation of electronic configuration in the above figure.
iv. One ionic bond is formed due to the electrical charge +1 or -1 on an ion. The valency of an ion is equal to the magnitude of positive or negative charge on it.
v. An ion forms the same number of ionic bonds as its valency.
Q. 21. Complete the sentences in paragraph 6
1. Fill in the paragraph:
(soluble, calcium carbonate, carbon dioxide, water, calcium chloride, insoluble, hydrochloric acid)
The chemical composition of Shahabad tile is mainly ………………... During its cleaning with the
upper layer of the tile reacts with it and three products are formed. One of them is , which being
……………… in water, gets washed away with water. The second product is ; its bubbles mix up in air.
The third product, mixes with water.
Ans The chemical composition of Shahabad tile is mainly calcium carbonate. During its cleaning with hydrochloric acid the upper layer of the tile reacts with it and three products are formed. One of them is calcium chloride, which being soluble in water, gets washed away with water. The second product is carbon dioxide; its bubbles mix up in air. The third product, water mixes with water.
2. Complete the statement by filling the gaps using appropriate term from the terms given in the bracket.
(slow, coloured, arrow, fast, smell, milky, physical, product, chemical, reactant, covalent, ionic, octet, duplet, exchange, sharing, equality sign)
Complete the paragraph:
a. An is drawn in between the reactants and products while writing the equation for a chemical
reaction.
b. Rusting of iron is a chemical change.
c. .The spoiling of food is a chemical change which is recognized from the generation of certain due to
it.
d. A colourless solution of calcium hydroxide in a test tube turns on blowing in it through a blow tube for
some time.
E. The white particles of baking soda disappear when put in lemon juice. This means that it is a ……….
change.
F Oxygen is a in respiration.
g. Sodium chloride is ……….. compound while hydrogen chloride is compound.
H Electron is complete in each hydrogen in a hydrogen molecule.
i. Chlorine (Cl2) molecule is formed by of electrons between two chlorine atoms.
Ans a. An arrow is drawn in between the reactants and products while writing the equation for a chemical reaction.
- Rusting of iron is a slow chemical change.
- The spoiling of food is a chemical change which is recognized from the generation of certain smell due to it.
- A colourless solution of calcium hydroxide in a test tube turns milky on blowing in it through a blow tube for some time.
- The white particles of baking soda disappear when put in lemon juice. This means that it is a chemical
change.
- Oxygen is a reactant in respiration.
- Sodium chloride is ionic compound while hydrogen chloride is covalent compound.
- Electron duplet is complete in each hydrogen in a hydrogen molecule.
- Chlorine (Cl2) molecule is formed by sharing of electrons between two chlorine atoms.
Q. 22. Find the odd one out 3
1. Ripening of mango, Melting of ice, Boiling of water, Dissolution of salt in water.
Ans Ripening of mango – It is a chemical change while remaining are physical changes.
2. Combustion of fuels, Softening of hard water, Photosynthesis, Cleaning Shahabad tile with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Ans Photosynthesis – It is a natural chemical change while others are manmade chemical changes.
3. Ripening of banana, Fragrance on ripening fruit, Darkening of a cut potato, Bursting of an inflated balloon.
Ans Bursting of an inflated balloon – It is a physical change while remaining are chemical changes.
Q. 23. Draw a well labeled diagram and explain. 25
1. Show with the help of diagram of electronic configuration how the following compound are formed from the constituent atoms.
Sodium chloride
Ans i. Sodium chloride is formed from its constituent elements, sodium (11Na) and chlorine (17Cl).
ii. The electronic configuration of sodium is (2,8,1) and that of chlorine is (2, 8, 7).
iii. The valency of sodium is 1 as it has one electron in valence shell (M-shell). The valency of chlorine is 1 as it has 7 electrons in its valence shell (M-shell) and it just needs one electron to complete the octet.
iv. Sodium loses its valence electron form M-shell and hence, the penultimate L-shell becomes the o utermost shell which has 8 electrons in it. Thus, sodium attains a complete electron octet.
V .On loss of electron, the number of electrons in sodium becomes 10. Therefore, the total positive charge of +11 on sodium nucleus is imbalanced. Thus, a Na+ cation which carries net positive charge +1 is formed.
vi. Similarly, chlorine gains one electron to complete its octet in M-shell. However, the charge is imbalanced on chlorine nucleus. Thus, a Cl– anion which carries net negative charge–1 is formed.
- When elements of sodium and chlorine combine, a sodium atom gives its valence electron to a chlorine atom. In the process, Na+ cation and Cl– anion are formed.
- These oppositely charged cations and anions are attracted by electrostatic force of attraction resulting in the formation of chemical bond which is also called ionic bond or electrovalent bond.
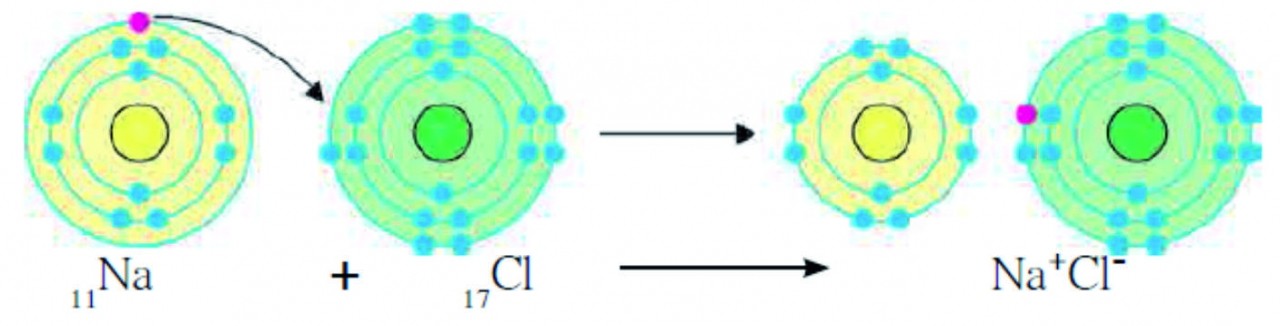
(2, 8, 1) (2, 8, 7) (2, 8) (2, 8, 8)
- Potassium fluoride
Ans i. Formation of K+F– from 19K and 9F:
-
- The electronic configuration of potassium is (2,8,8,1) and that of fluorine is (2,7).
- The valency of potassium is 1 as it has one electron in valence shell (N-shell). The valency of fluorine is 1 as it has 7 electrons in its valence shell (L-shell) and it just needs one electrons to complete the octet.
- Potassium loses its valence electron from N-shell and hence, the penultimate M-shell becomes the outermost shell which has 8 electrons in it. Thus, potassium attains a complete electron octet.
- On loss of electron, the number of electrons in potassium becomes 18. Therefore, the total positive charge of +19 on potassium nucleus is imbalanced. Thus, a K+ cation which carries net positive charge +1 is formed.
- Similarly, fluorine gains one electron to complete its octet in L-shell. However, the charge is imbalanced on fluorine nucleus. Thus, a F– anion which carries net negative charge –1 is formed.
- When elements of potassium and fluorine combine, a potassium atom gives its valence electron to a fluorine atom. In the process, K+ cation and F– anion are formed.
- These oppositely charged cations and anions are attracted by electrostatic force of attraction resulting in the formation of chemical bond which is also called ionic bond or electrovalent bond.
 The diagrammatic representation for the formation of K+F– from 19K and 9F is as follows:
The diagrammatic representation for the formation of K+F– from 19K and 9F is as follows:
- Explain bond formation in NaCl ? What is the type of the bond?
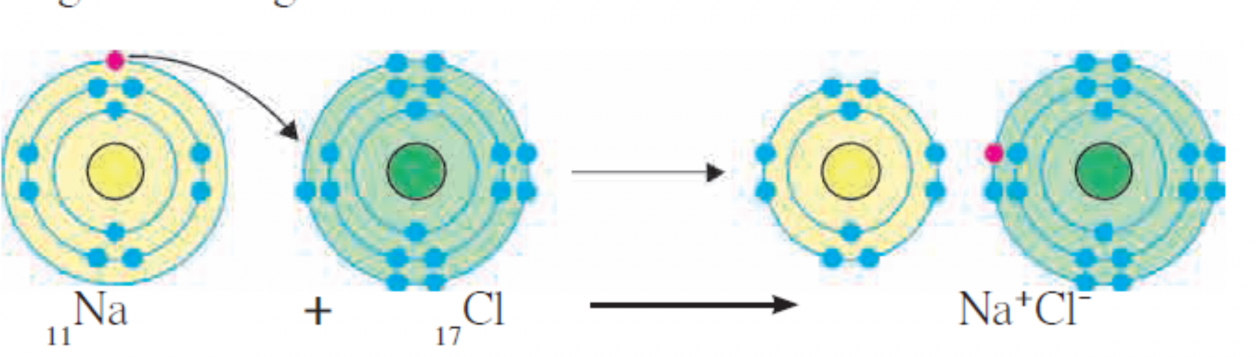 Ans
Ans
Figure of Formation of Ionic bond in NaCl molecule.
- Compound sodium chloride is formed from the atoms of the constituent elements sodium and chlorine.
- For this purpose, the electronic configuration of sodium and chlorine is given.
11Na 2,8,1
17Cl 2,8,7
- The valency of sodium is one as it has one electron in its valence shell and the valency of chlorine is one as its valence shell is short of one electron to have a complete octet.
- On loss of a valence electron from ‘M’ shell, the penultimate shell ‘L’ of sodium atom becomes outermost shell. It has eight electrons in it.
- Effectively, sodium attains an electron octet state. However, the electron number, becomes 10. Hence the positive charge +11 on the sodium nucleus is imbalanced and a Na+ cation, carrying net positive charge
+1 is formed.
- On the other hand, valence shell of chlorine atom contains an electron less to the octet state. On accepting an electron from outside, octet of chlorine is completed.
- However, the charge balance is disturbed due to addition of an electron to the neutral chlorine atom. This results in the formation of an anion Cl-, carrying a net negative charge -1.
- Hence, the bond formed is by transfer of electrons and electronic force.
- The chemical bond formed due to an electrostatic force of attraction between the oppositely charged
cation and anion is called an ionic bond or an electrovalent bond. The compound formed by means of one or more ionic bonds is called ionic compound.
- Water
Ans i. An atom of oxygen contains six electrons in its valence shell and it needs two electrons to complete the electrons octet. Therefore, valency of oxygen atom is two.
- An atom of hydrogen contains only one electron and it needs only one electron to complete its electron duplet. Therefore, valency of hydrogen atom is one.
- The oxygen atom completes its octet by sharing two electrons with two hydrogen atoms. Also, each of two hydrogen atoms completes its electron duplet.
- This result in the formation of two covalent bonds.
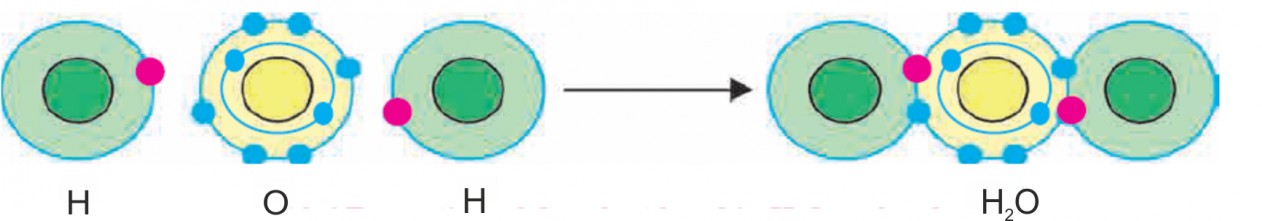 The diagrammatic representation for the formation of water molecule (H2O) is as follows:
The diagrammatic representation for the formation of water molecule (H2O) is as follows:- Hydrogen chloride
Ans Formation of HCl molecule:
- An atom of chlorine contains seven electrons in its valence shell and it needs one electron to complete the electron octet. Therefore, valency of chlorine atom is one.
- An atom of hydrogen contains only one electron and it needs only one electron to complete its electron duplet. Therefore, valency of hydrogen atom is one.
- The chlorine atom completes its octet by sharing its one valence electron with the hydrogen atom. The hydrogen atom also completes its electron duplet.
- This results in the formation of one covalent bond.
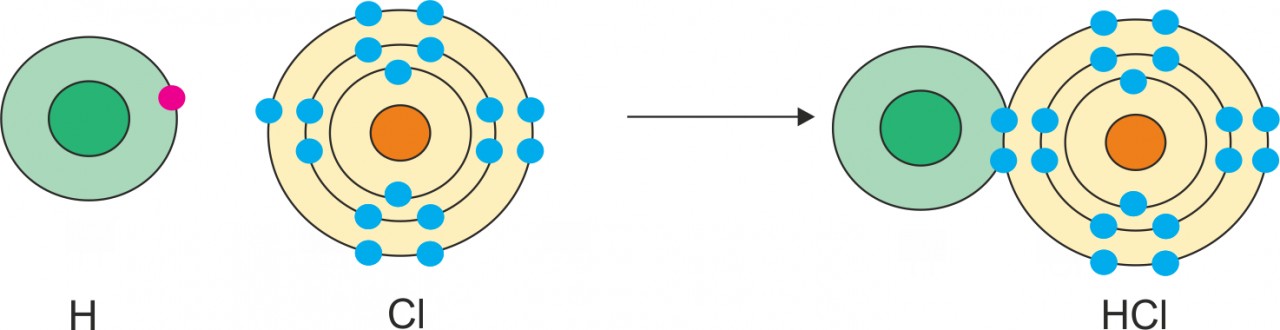 The diagrammatic representation for the formation of HCl is as follows:
The diagrammatic representation for the formation of HCl is as follows:
