Science Part ii Solutions Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Life Processes In Living Organisms Part 1 are provided here with simple step-by-step explanations. These solutions for Life Processes In Living Organisms Part 1 are extremely popular among class 10 students for Science Life Processes In Living Organisms Part 1 Solutions come handy for quickly completing your homework and preparing for exams. All questions and answers from the Science Part ii Solutions Book of class 10 Science Chapter 2 are provided here for you for free. You will also love the free experience on https://phdsciencegyan.com Part ii Solutions Solutions. All Science Part ii Solutions Solutions for class 10 Science are prepared by experts and are 100% accurate.
Q.1.Textbook activity question. 23
1. In terms of Chemistry what happens actually when a molecule is oxidized?
Ans When an ionic chemical reaction occurs on a metal’s surface while oxygen while oxygen is present, oxidation of metal takes place. There is a movement of electrons from the metal to the oxygen molecules during this process. The negative oxygen ions generated enter the metal & leads to the creation of an oxide surface. Thus, oxidation is a form of metal corrosion.
2. How are the various processes occurring in human body controlled? In how many ways?
Ans i. Various organ systems are continuously performing their functions in human body.
Along with the various systems like digestive, respiratory, circulatory, excretory and control systems, different external and internal organs are performing their functions independently but through a complete co-ordination.
This is controlled in two ways-Nervous control by nervous system and chemical control by the hormones secreted by the endocrine glands.
3. What is the importance of digestive juices in digestive system?
Ans i. Digestive juices create conditions requried for digestion of food.
Digestive juices contain enzymes which break down different components of food like carbohydrates proteins and fats, so that the essential nutrients are absorbed and properly utilized by the body.
4. Oral rehydration solution (Salt-sugar-water) is frequently given to persons experiencing loose motions.
Ans i. When loose motions occur, essential fluids and salts are lost from the body causing dehydration and must be quickly replaced.
ORS drink contains the main elements that are lost from the body during loose motions . Hence, ORS solution is frequently given to person experiencing loose motions.
5. How are the foodstuffs and their nutrient contents useful for body?
Ans Foodstuffs and their nutrients are required for normal functioning of our body. Food stuffs are broken down during digestion to convert them into soluble nutrients which are carried by the blood to various cells of the body. The nutrients are oxidized by cellular respiration to release energy.
Importance of some major nutrients is as follows :
Nutrients like carbohydrates and fats provide energy to perform various activities.
Proteins are the major structural components of cells. They are called body building nutrients, as they are responsible for building and repairing the body tissues. In our body, proteins are used to make amino acids, hormones and other body chemicals.
Vitamins and minerals act asthe protective and regulating nutrients in our body.
6. We sweat during summer and heavy exercise.
Ans i. Human beings are warm-blooded. We need to maintain a constant body temperature irrespective of the surrounding conditions.
In summer and during heavy exercise, lot of heat is generated which raises our body temperature.
Sweating leads to loss of excess body heat and brings down the body temperature to normal.
Therefore, we sweat during summer and heavy exercise.
7. Do the plants get injured when do we pluck the flowers? How are those wounds healed?
Ans Yes, plants get injured when we pluck flowers. Meristematic tissue present in plants gives rise to new cells at the site of injury and help plants to heal their wounds.
8. Which different functions are performed by muscles in body?
Ans Muscles are mainly responsible for the movements of // in the human body :
There are three main types of muscles :
Striated ( Voluntary ) muscles :
These muscles are attached to the bones ( hence also called as skeletal muscles) and bring about movement of arms, legs.
Non-Striated ( Involunary ) muslces:
These muscles bring about movement of eyelids, passage of food through alimentary canal, contracton and relaxation of blood vessels.
Cardiac muscles :
Cardiac muscles bring about contraction and relaxation of the heart.
9. Which types of chemical bonds are present between all these atoms?
Ans In glucose molecule, atomsof carbon, hydrogen and oxygen are held together by covalent bonds.
10. How does the growth of any living organism occur? Does the number of cells in their body increase? If yes, how?
Ans i. Growth of any living organism occurs due to cell division.
Yes, the number of cells in their bosy increase.
The number of cells increases by the process of mitosis.
11. Which type of cellular respiration performs complete oxidation of glucose?
Ans Complete oxidation of glucose occurs during aerobic respiration.
12. Which system is in action for removal of waste materials produced in human body?
Ans Excretory system is employed in discharging waste materials from the body.
13. Which cell organelle is necessary for complete oxidation of glucose?
Ans Mitochondria is necessary for complete oxidation of glucose.
14. What is the importance of balanced diet for body?
Ans A balanced diet supplies the nutrients your body needs to work effectively. Without balanced nutrition, your body is more prone to disease, infection, fatigue, and low performance. Children who don’t get enough healthy foods may face growth and developmental problems, poor academic performance, and frequent infections.
15. Whether the gametes are diploid or haploid? Why?
Ans The cells that give rise to gamtes are dipliod (2n). But by meisosis they give rise to gametes which are haploid (n.) Two haploid gametes undergo fertillization and the zygote formed becomes once again diploid (2n).
16. Whether new cells are formed during healing of wound?
Ans Yes, the injured cells are restored by the formation of new cells.
17.What is respiration? How does it occur?
Ans i. The process of release of energy by oxidation of food is called as respiration.
In living organisms, respiration occurs at two levels-body and cellular level.
In case of body level, oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the body and surrounding.
In case of cellular level, food is oxidized either with or without the help of oxygen to release energy.
18.Many times, we experience dryness in mouth.
Ans Dry mouth is also known as xerostomia. It’s a condition that happens when salivary glands in your mouth don’t produce enough saliva. It causes a parched, or dry, feeling in your mouth. It can also cause other symptoms, such as a rough tongue, mouth sores, and cracked lips.
19.How the new individual of a species is formed from existing one of same species?
Ans i. New individual of a species is formed from the existing one of the same species by the process of reproduction.
It involves cell division-mitosis and meiosis.
20.What happens to the cells of injured tissue?
Ans The cells of the injured tissue start dividing and increase in numbers to repair and heal the injured tissue.
21.What is the role of circulatory system in energy production?
Ans In the circulatory system, arteries carry oxygen rich blood from heart to the different parts of thebody. Along with oxygen, this blood also contains energy- rich nutrients such as glucose, fatty acids which are used by cells to produce energy.
22Why may be the players consuming these food stuffs?
Ans i. Players are in need of continuous energy during games.
Carbohydrates (glucose) are major and quick source of energy.
Hence, players are seen consuming food stuffs rich in carbohydrated during breaks of the game.
23.How many atoms of C, H and O are respectively present in a molecule of glucose?
Ans There are 6 atoms of C,12 atoms of H and 6 atoms of O present in a molecule of glucose (C6H12O6)
Q. 2. Multiple Choice Questions 17
1. In human beings, there are chromosomes.
a. 23 b. 46 c. 22 d. 47
Ans Option b.
2. We get energy from carbohydrates.
9 kcal / gm b. 9 cal / gm c. 4cal / gm d. 4 kcal / gm
Ans Option d.
3. The exchange of respiratory gases occur by the in the plants.
Air pores b. Stomata c. Lenticels d. Diffusion
Ans Option d.
4. Karyokinesis is the division of ……………
Cytoplasm b. Nucleus c. Cell wall d. Pollen grains
Ans Option b.
5. Duplicated chromosomes are joined at a point termed …………… .
Centrosome b. Centromere c. Centriole d. Chromatid
Ans Option b.
6. Which of the following vitamin is necessary for synthesis of NADH2?
Vitamin B2
Ans Option b.
Vitamin B5
Vitamin C d. Vitamin K
7. Cell division occurring in somatic cells is …………… .
mitosis b. meiosis c. diakinesis d. diplotene
Ans Option a.
8. The process of release of energy from the nutrients is called……………
Respiration b. Photosynthesis c. Nutrition d. Absorption
Ans Option a.
9. Cell organelle necessary for complete oxidation of glucose is ……………
mitochondria b. plastids c. ribosomes d. golgi body
Ans Option a.
10. The nuclear membrane disappears completely in …………… .
Prophase b. Anaphase c. Metaphase d. Telophase
Ans Option c.
11.Difficulty in night vision is due to the deficiency of vitamin …………… .
A b. B c. C d. D
Ans Option a.
12.The process of meiosis takes place to produce …………… .
cells of the body b. cells of the brain
c. sperms and ova d. testes and ovary
Ans Option c.
13.Meiosis is also known as …………… .
Equational division b. Reductional division
c. Meristematic cells d. None of the above
Ans Option b.
14.Oral rehydration solution(ORS) contains the following …………… .
salt+ water b. sugar+water c. salt+sugar+water d. distilled water
Ans Option c.
15. Cytokinesis is the division of …………… .
cell b. cytoplasm c. cell wall d. nucleus
Ans Option b.
16.The cellular respiration takes place in ……………
Lysosome b. Mitochondrion c. Chlorophyll d. Ribosome
Ans Option b.
17.Cell organelles involved in the cellular respiration are the …………… .
mitochondria b. plastids c. ribosomes d. lysosomes
Ans Option a.
Q. 3. Find the odd one out 4
1.Amitosis, Mitosis, Meiosis, Anaphase
Ans Anaphase is the odd one out as it one of stages of cell division while rest are types of cell division.
2.Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase-I, Telophase
Ans Anaphase-I is the odd one out as it one of the stages of Meiosis while rest are of mitosis.
3.Rickets, Night blindness, Beriberi , Anemia
Ans Anemia is the odd one out as it an iron deficiency while rest are deficiency related to Vitamins.
4. Riboflavin, Nicotinamide, Thiamine, Iron
Ans Iron is the odd one out as it is an element while rest are types of Vitamin B.
Q. 4. Find co-related terms 14
1. Get rid of waste : Excretion :: Assimilation of food for growth : ……………
Ans Get rid of waste : Excretion :: Assimilation of food for growth : Nutrition.
2. NADH2 : Nicotinamide Adenine dinucleotide :: FADH2 : …………….
Ans NADH2 : Nicotinamide Adenine dinucleotide :: FADH2 : Flavin adenine dinucleotide.
3. Cytokinesis : Division of cytoplasm :: Karyokinesis : ……………
Ans Cytokinesis : Division of cytoplasm :: Karyokinesis : Division of nucleus.
4. Protein : Amino acids :: Carbohydrates : ……………
Ans Protein : Amino acids :: Carbohydrates : Glucose.
5. Mitosis : Somatic cells :: Meiosis : …………… .
Ans Mitosis : Somatic cells :: Meiosis : Germ cells.
6. Vitamin B2 : riboflavin :: Vitamin B5 : …………… .
Ans Vitamin B2 : riboflavin :: Vitamin B5 : nicotinamide. 7 Bones : Ossein :: Skin : …………… .
Ans Bones : Ossein :: Skin : Melanin/Keratin.
8 Blood : Hemoglobin :: Pancreas : …………… .
Ans Blood : Hemoglobin :: Pancreas : Insulin. 9 Skin : Keratin :: Blood : ……………
Ans Skin : Keratin :: Blood : Hemoglobin.
10. Jaggary : Carbohydrates :: egg : …………… .
Ans Jaggary : Carbohydrates :: egg : Protein.
11. Mitosis : Growth of the body :: Meiosis : ……………
Ans Mitosis : Growth of the body :: Meiosis : gamete production.
12. NADH2 : 3 molecules of ATP :: FADH2 : ……………
Ans NADH2 : 3 molecules of ATP :: FADH2 : 2 molecules of ATP
13. Nicotinamide : NADH2 : : Riboflavin : ……………
Ans Nicotinamide : NADH2 : : Riboflavin : FADH2 14 Blood : : : Muscles : Myosin
Ans Blood : Hemoglobin : : Muscles : Myosin
Q. 5. Match the pair 3
| Column “A” | Column “B” | ||
| i. | Anaphase | a. | Chromosomes become arranged in a plane at the equator. |
| ii. | Prophase | b. | Daughter chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell |
| c. | Chromosomes become visible and centrioles moves to opposite poles of the cell. | ||
| Chromosomes lose their distinctiveness and gradually become transformed into chromatin network. | |||
| d. | |||
Ans
| i. | Anaphase | Daughter chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell. |
| ii. | Prophase | Chromosomes become visible and centrioles moves to opposite poles of the cell. |
| Column “A” | Column “B” | ||
| i. | Telophase | a. | Chromosomes become arranged in a plane at the equator. |
| ii. | Metaphase | b. | Daughter chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell |
| Chromosomes become visible and centrioles moves to opposite poles of the cell. | |||
| c. | |||
| d. | Chromosomes lose their distinctiveness and gradually become |
2.
transformed into chromatin network.
Ans
| i. | Telophase | Chromosomes lose their distinctiveness and gradually become transformed into chromatin network. |
| ii. | Metaphase | Chromosomes become arranged in a plane at the equator. |
3
| Column “A” | Column “B” |
| i. Proteins | a. Energy giving |
| ii. Vitamins and Minerals | b. Body building |
| c. Protective and regulating | |
| d. Biological catalysts |
Ans
| i. Proteins | Body building |
| ii. Vitamins and Minerals | Protective and regulating |
Q.6. State True or False 14
1. Excess of fats is stored in liver and muscles in the form of glycogen.
Ans False – Excess of carbohydrates is stored in liver and muscles in the form of glycogen.
2. Chromosomes are the thickest and shortest in telophase.
Ans False – Chromosomes are the thickest and shortest in anaphase.
3. Meiosis is called as a heterotypic division.
Ans True
4. Food and oxygen are transported up to the cell through the circulatory system in the body.
Ans True
5. Excess of proteins is converted into glucose through the process of gluconeogenesis.
Ans True
6. Proteins of animal origin are called as ‘first class’ proteins.
Ans Proteins of animal origin are called as ‘first class’ proteins.-True
7. Asexual reproduction is accomplished through mitosis.
Ans True
8. Germ cells divide by meiosis to produce gametes.
Ans True
9. Mitosis keeps the chromosome number constant through the generations.
Ans False – Meiosis keeps the chromosome number constant through the generations.
10. Prophase of meiosis-I has five sub-stages.
Ans True
11. Muscle cells in our body perform aerobic respiration while performing exercise.
Ans False – Muscle cells in our body perform anaerobic respiration while performing exercise.
12. Energy is required for the functioning of all the life processes.
Ans True
13. Mitosis results in four daughter cells.
Ans False – Meiosis results in four daughter cells.
14. Chromosomes are arranged in the form of chromatids at the equator in prophase.
Ans False – Chromosomes are arranged in the form of chromatids at the equator in metaphase.
Q.7. Name the following 28
1. Proteins present in skin.
Ans Keratin, Melanin
2. Name the stage of cell cycle at which the following event occur : Pairing between homologous chromosomes takes place.
Ans Zygotene of meiosis -I
3. The energy currency of the cell.
Ans ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)
4. The cells in which mitosis takes place.
Ans Somatic cells
5. The process by which the replacement of dead cells is accomplished.
Ans Mitosis
7 .Give the names of two co-enzymes that take part in the cellular respiration.
Ans NADH2 – Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide and FADH2 – Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide are the two co- enzymes that take part in the cellular respiration.
8. The result of uncontrolled cell division.
Ans Cancer
9. The two kinds of cell divisions found in living things.
Ans Mitosis, Meiosis
10. The process responsible for variations in organisms.
Ans Crossing-over
11. Process by which four haploid cells are formed from one diploid cell.
Ans Melosis
12. Acid formed at the end of glycolysis.
Ans Pyruvic acid
13. Name the stage of cell cycle at which the following event occur : Centromere splits and chromatids separate.
Ans Anaphase
14.The structure responsible for initiating cell division in animal cells.
Ans Centrioles
15. Most abundant protein found in nature.
Ans RUBISCO
16.The part of the nucleus cell associated with heredity.
Ans Chromosomes
17.The kind of division that takes place in reproductive cells.
Ans meiosis
18. Cell organelle responsible for harvesting cellular energy in human body.
Ans Mitochondria
19. The stage when chromosomes arrange at equator.
Ans Metpahse
20. Two enzymes formed in the cell and used in cellular respiration.
Ans NADH2 and FADH2 (Nicotinamide Adenine dinucleotide and Flavin adenine dinucleotide)
21. Hormones synthesised using fatty acids.
Ans Progesterone,estrogen, testosterone, aldosterone.
22. The stage in which the separation of sister chromatids takes place.
Ans Anaphase
23. Name the stage of cell cycle at which the following event occur : Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator.
Ans Metaphase
24. The type of cell division present in unicellular organisms.
Ans Mitosis/Amitosis
25. Name the stage of cell cycle at which the following event occur : Crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
Ans Pachytene of meiosis -I
26. The process by which gametes are produced.
Ans Meiosis
27. Flexible proteins in muscles.
Ans Actin, Myosin
28. Common step of aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Ans Glycolysis
29.The process by which the cell divides into two equal daughter cells.
Ans Mitosis
Q.9.Give scientific reasons: 12
1. Fibers are one of the important nutrients.
Ans i. Fiber is important for digestion and should be included in the diet.
ii. Fibers cannot be digested but they help in digestion of other substances and egestion of undigested waste. iii.Roughage in form of dietary fiber is useful for proper digestion and helps in bowel movement.
- Fibers can be obtained from leafy vegetables, fruits, cereals. Etc,
- Hence, fibers are one of the important nutrients.
2. Oxygen is necessary for complete oxidation of glucose.
Ans .i. Aerobic cellular respiration is the process by which cells use oxygen to help them convert glucose into energy.
ii. This type of respiration occurs in three steps: glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle and electron transfer chain reaction to produce carbon dioxide , water and 38ATP at the end of complete oxidation of glucose.
iii.Oxygen is not needed for glycolysis but is required for the rest of the chemical reactions to take place.
iv.In absence of oxygen, glucose is incompletely oxidized and less amount of energy is obtained.
Hence oxygen is necessary for complete oxidation of glucose.
3. Sometimes, higher plants and animals too perform anaerobic respiration.
Ans i. Anaerobic respiration is the respiration that takes place in absence of oxygen.
- Higher plants and animals perform aerobic respiration to produce energy.
- But sometimes, higher plants and animals too perform anaerobic respiration if there is depletion in oxygen level in the surroundings.
- For example. Seeds perform anaerobic respiration if the soil is submerged under water during germination. Our muscle cells perform anaerobic respiration while doing exercise.
4. Kreb’s cycle is also known as citric acid cycle.
Ans i. Acetyl-Co-A formed during glycolysis process enters the Kreb’s cycle and is converted to the first stable product called citric acid(citrate) in the presence of an enzyme called citrate synthase.
ii. Due to this, the Kreb’s cycle is called the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle because the structure of citric acid contains 3 carboxylic acid groups.
iii. Hence Kreb’s cycle is also called as citric acid cycle.
5. After doing physical activity, we feel hungry.
Ans i. During physical activity we need more energy.
Whenever a person needs extra energy, he/she breathes faster.
As a result, more oxygen is supplied to our cells. It speeds up the breakdown of food and more energy is released.
Due to rapid breakdown of food we feel hungry.
6. Cell division is one of the important properties of cell and organisms.
Ans i. Cell division is the process of formation of new or daughter cells from the pre-existing or parent cells.
ii. Cell division is one of the important properties of cell and organisms because due to this property, a new organism is formed from existing one, a multicellular organism grows up and
iii. emaciated body can be restored.
iv. Helps in repairing and replacing worm out cells.
Q. 9. Laws / Define / Principles 4
1. Gluconeogenesis
Ans i. Amino acids are obtained after digestion of proteins in the body.
ii. Excess of amino acids obtained from proteins are not stored in the body.
iii. They are broken down and the ammonia formed is eliminated out of the body.
iv. If necessary, excess of proteins are converted into other useful substances like glucose through the process of gluconeogenesis.
2.Explain respiration in yeast.
Ans i. Yeast is a single celled organism that respires anaerobically and during this process it yields alcohol.
ii. Yeast gets energy through anaerobic respiration, in the absence of oxygen, glucose breaks down to give carbon dioxide , alcohol along with production of energy.
iii. Glucose (in absence of oxygen) →Ethanol + CO2 + energy.
Q.10.Write properties/characteristics/uses/advantage/effects. 2
1. Advantage of mitosis :
Ans i. Essential for the growth of the body
ii. Necessary for restoration of emaciated body
iii. For wound healing
iv.For the formation of blood cells, etc.
Q.11. Write Short Notes 26
1. Write short note on Meiosis.
Ans i. Meiosis is completed through two stages. Those two stages are meiosis-I and meiosis-II.
ii. In meiosis-I recombination/crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes and thereafter those homologous chromosomes(not sister chromatids) are divided into two groups and thus two haploid cells
are formed.
iii. In meiosis-II, the two haploid daughter cells formed in meiosis-I undergo division by separation of recombined sister chromatids and four haploid daughter cells are formed.
iv. The process of gamete formation and spore formation occurs by meiosis.
v. During this cell division, crossing over occurs between the homologous chromosomes and thereby genetic recombination occurs.
vii. Due to this, all the four daughter cells are genetically different from parent cell and from each other too.
2. Write short note on Glycolysis.
Ans i. molecule of glucose is oxidized step by step in this process and two molecules of each i.e. pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water are formed.
ii.The process of glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm.
iii. The molecules of pyruvic acid formed in glycolysis Process are converted into molecules of Acetyl- Coenzyme-A.
iv. Two molecules of NADH2 and two molecules of CO2 are released during this process.
3.Write short note on Telophase of Mitosis.
Ans i. The chromosomes which have reached the opposite poles of the cell start to decondense due to which they again become thread-like thin and invisible.
ii. Nuclear membrane is formed around each set of chromosomes reached at poles. iii.Thus, two daughter nuclei are formed in a cell and spindle fibers completely disappear.
iv.Nucleolus also appears in each daughter nucleus.
4.Write short note on Energy production in microorganisms through Anaerobic Respiration.
Ans i. Some organisms cannot live in presence of oxygen. Example. Bacteria.
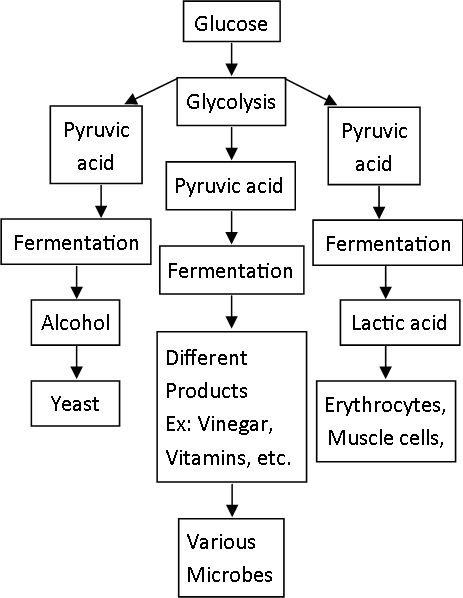
ii. Such living organisms have to perform anaerobic respiration for energy production. iii.Glycolysis and fermentation are two steps of anaerobic respiration.
Glucose is incompletely oxidized and less amount of energy is obtained in this type of respiration.
Pyruvic acid produced through glycolysis is converted into other organic acids (lactic acid) or alcohol with the help of some enzymes in this process. This is called as fermentation.
Some higher plants, animals and aerobic microorganisms also perform anaerobic respiration instead of vi.
aerobic respiration if there is depletion in oxygen level in the surroundings.
5.Write short note on Cytokinesis in Mitosis.
Ans i. The cytoplasm divides by cytokinesis and two new cells are formed which are called as daughter cells.
In cytokinesis, a notch is formed at the equatorial plane of cell which deepens gradually and thereby two new cells are formed.
However, in case of plant cells, instead of the notch, a cell plate is formed exactly along midline of the cell and thus cytokinesis is completed.
6.Write short note on prophase of mitosis.
Ans i. In prophase, condensation of basically thin thread-like chromosomes starts.
Due to this, chromosomes become short and thick and they start to appear along with their pairs of sister chromatids.
Centrioles duplicate and each centriole moves to opposite poles of the cells.
Nuclear membrane and nucleolus start to disappear.
7.Write short note on Anaphase of Mitosis.
Ans i. In anaphase, centromere spilts and thereby sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and they are pulled apart in opposite direction with the help of spindle fibres.
ii. Separated sister chromatids are called as daughter chromosomes. iii.Chromosomes being pulled appear like bunch of bananas.
iv.In this way, each set of chromosomes reach at two opposite poles of the cell.
8.Explain Kreb’s cycle with reaction.
Ans i. The cyclical reactions of tricarboxylic acid cycle were discovered by Sir Hans Kreb. Hence, this cyclical process is also called as Kreb’s cycle.
In tricarboxylic acid cycle, both the molecules of acetyl-CoA formed in glycolysis, enter the mitochondria.
Cyclic chain of reactions called as tricarboxylic acid cycle is operated on it in the mitochondria.
Acetyl part of acetyl-CoA is completely oxidized through this cyclical process and molecules CO2, H2O, NADH2, FADH2 are derived.
9.Write short note on Energy from Lipids.
Ans i. The substances formed by specific chemical bond between fatty acids and alcohol are called as lipids.
Digestion of lipids consumed is converted into fatty acids and alcohol.
Fatty acids are absorbed up and distributed everywhere in the body.
From those fatty acids, different cells produce various substances necessary to themselves.
For example. The molecules of phospho lipids which are essential for producing plasma membrane are formed from fatty acids.
Besides, fatty acids are used for producing hormones like progesterone, estrogen, testosterone etc. and the covering around the axons of nerve cells.
Excess of lipids are stored in adipose connective tissue in the body.
10.Write short note on Metaphase of Mitosis.
Ans i. Nuclear membrane completely disappears in metaphase.
ii. Chromosomes complete their condensation and become clearly visible along with their sister chromatids. iii.All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane of the cell.
iv.Special type of flexible protein fibers are formed between centromere of each chromosome and both centrioles.
11.Write short note on Tricarboxyclic acid cycle.
Ans i. Both the molecules of acetyl-CoA formed in glycolysis, enter the mitochondria.
Cyclic chain of reactions called as tricarboxylic acid cycle is operated on it in the mitochondria.
Acetyl part of acetyl-CoA is completely oxidized through this cyclical process and molecules CO2, H2O, NADH2, FADH2 are derived.
The cyclical reactions of tricarboxylic acid cycle were discovered by Sir Hans Kreb. Hence, this cyclical process is also called as Kreb’s cycle.
12.Write short note on Electron transfer chain reaction.
Ans i. Electron transfer chain reaction Occurs or takes place in mitochondria only.
Molecules of NADH2 and FADH2 formed in aerobic respiration process participate in electron transfer chain reaction.
Due to this 3 molecules of ATP are obtained from each NADH2 molecules and 2 molecule of ATP from each FADH2 molecule.
Besides ATP, water molecules are also formed in this reaction.
13.Write short note on Energy from Proteins.
Ans i. Proteins are the macromolecules formed by bonding together many amino acids.
ii. Proteins of animal origin are called as ‘first class’ proteins. iii.Amino acids are obtained after digestion of proteins.
Those amino acids are absorbed in the body and transported up to each organ and cell via blood.
From these amino acids, organs and cells produce various proteins necessary for themselves and the whole body.
Excess of amino acids obtained are not stored in the body. They are broken down and the ammonia formed vi.
is eliminated out of the body.
Q.. 12. Complete the given flow chart / table 6
- Complete the chart for anaerobic respiration in living organisms/ cells.
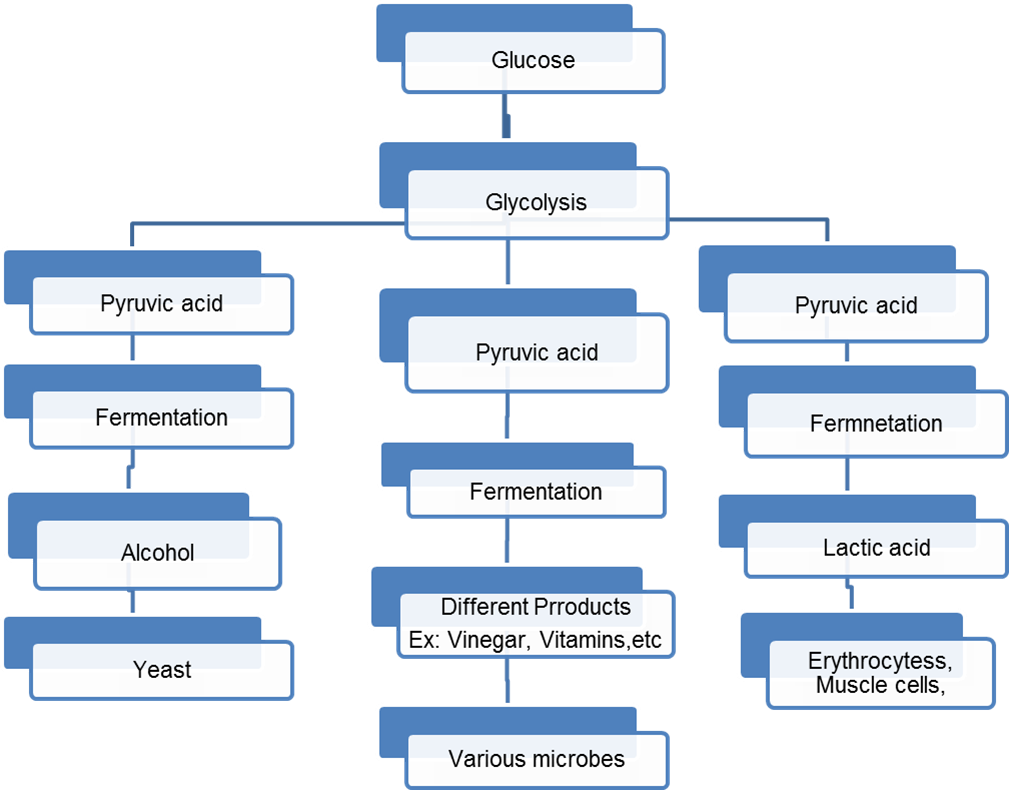 Ans
Ans
- 2. Complete the following chart and state which process of energy production it represents :
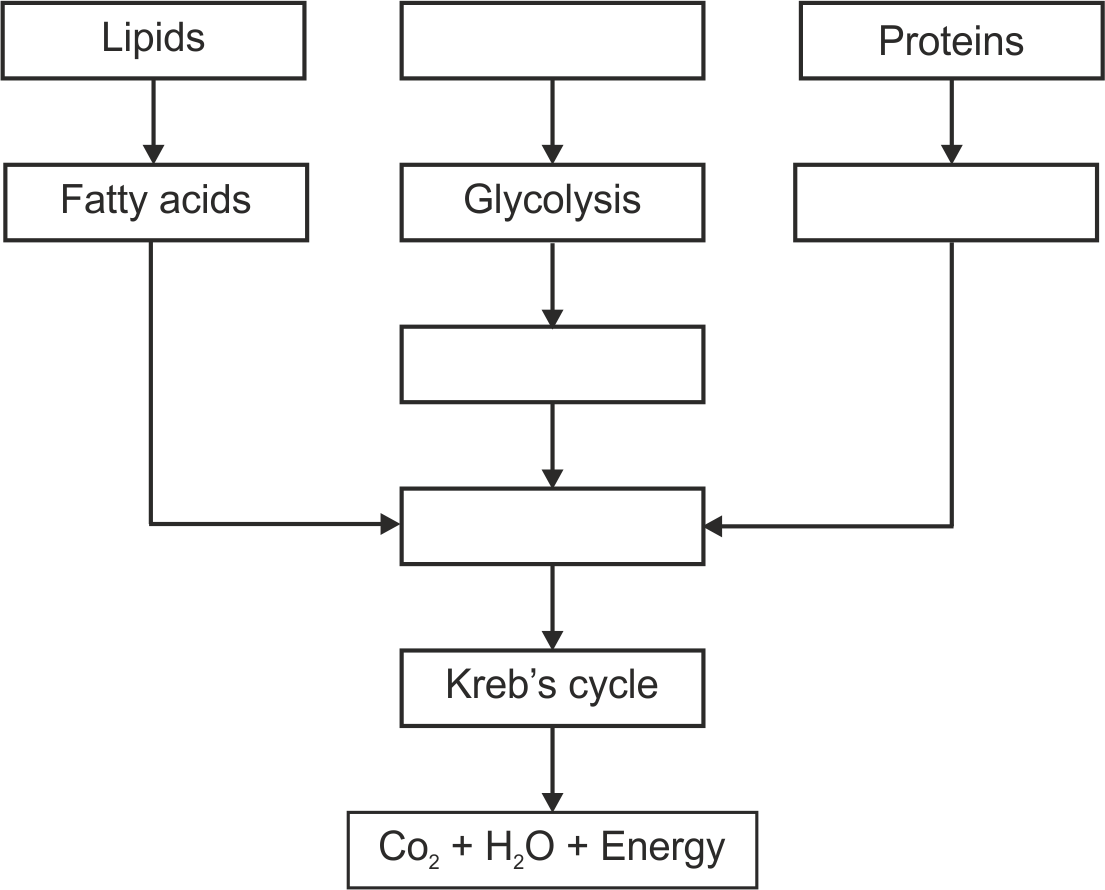
 Ans
Ans
 3.
3.
 Ans
Ans
Q. 13. Distinguish between 8
1. Aerobic and Anaerobic Respirationa
Ans
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration | |
| Aerobic respiration t akes place in the presence of oxygen. | Anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. | |
| i. | ||
| ii. | End products are carbon dioxide and water | End products may be alcohol or lactic acid. |
| iii. | Considerable amount of energy is released. – 38 ATP molecules | Less amount of energy is released. – 2 ATP molecules |
| It involves glycolysis, TCA cycle & election hamster chain reaction. | ||
| iv. | It involves only glycolysis & fermentation | |
2. Mitosis and Meiosis.
Ans
| Mitosis | Meiosis | |
| i. | Mitosis occurs in somatic cells. | Meiosis occurs in generative cells. |
| ii. | It involves a single division resulting into two diploid diploid daughter cells. | It involves two successive divisions resulting in the formation of four haploid daughter nuclei. |
| iii. | Number of chromosomes in daughter cells is equal to that of | Number of chromosomes in daughter cells is half to that of the mother cells. |
| parent cell. | ||
| iv. | It involves three stages glycolysis, TCA cycle & electron transfer reach on | Meiosis forms gametes and spores and maintains the chromosome number constant from generation to generation. |
3. Glycolysis and TCA cycle
Ans
| Glycolysis | TCA cycle | |
| i. | Glycolysis refers to the series of chemical reactions in which a glucose molecule is converted into pyruvic acid molecules | TCA cycle refers to the series of chemical reactions in which pyruvate is converted to acetyl-Co-A and is completely oxidized into CO2 and water. |
| ii. | It is the first step of the cellular respiration. | It is the second step of the cellular respiration. |
| iii. | It occurs in the cytoplasm | It occurs in the mitochondria |
| iv. | It occurs both in aerobic and anaerobic respiration. | It occurs in aerobic respiration. |
| v. | ||
| It consumes two ATP molecules. | It consumes no ATP molicules. |
4. Cytokinesis and Karyokinesis.
Ans
| Cytokinesis and Karyokinesis | Karyokinesis | |
| i. | Cytokinesis is the division of cytoplasm | Karyokinesis is the division of nucleus. |
| ii. | Karyokinesis is the division of nucleus. | It is the first division |
Q. 14. Give examples 6
1. Name scientists who discovered process of glycolysis :
Ans Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof and Jacob Parnas.
2.Name four proteins formed in body.
Ans Melanin, Keratin, Ossein, Hemoglobin
3.Name four Hormones synthesised from fatty acids.
Ans Progesterone, Estrogen, Testosterone, Aldosterone.
Q. 15. Give explanation using the given statements. 15
1. Fill in the blanks and explain the statements.
At the end of glycolysis, molecules are obtained.
Ans i. At the end of glycolysis, two molecules are obtained.
ii. These two molecules are each of pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water. iii.Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
iv.In this step, glucose is broken in a stepwise manner into two molecules of pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water.
2. Fill in the blanks and explain the statements.
For formation of plasma membrane, molecules are necessary.
Ans i. For formation of plasma membrane, Phospho lipids molecules are necessary.
ii. The lipids break down to form fatty acids and alcohol after digestion. iii.Fatty acids are absorbed up and distributed everywhere within the body.
From these fatty acids different cells produce various substances necessary for themselves.
For example: the molecules called as phosphor lipids which are essential for producing plasma membrane are formed from fatty acids.
3. Fill in the blanks and explain the statements.
Genetic recombination occurs in phase of prophase of meiosis-I.
Ans i. Genetic recombination occurs in crossing over phase of prophase of meiosis-I.
ii. It is the prophase-I of meiosis that chromosomes duplicate and produce homologues. iii.This homologous chromosomes then pair as bivalent.
Crossing over takes place in the prophase-I of meiosis-I.
This crossing over helps in bringing the recombination.
4. Fill in the blanks and explain the statements.
All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane of cell in phase of mitosis.
Ans i. All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane of cell in metaphase of mitosis.
In metaphase, the chromosome complete their condensation and become clearly visible along with their sister chromatids.
All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane of the cell.
5. Fill in the blanks and explain the statements.
After complete oxidation of a glucose molecule, number of ATP molecules are formed.
Ans i. After complete oxidation of a glucose molecule, 38 number of ATP molecules are formed.
Aerobic respiration is one in which molecular oxygen is used for the complete oxidation of glucose to yield CO2, H2O and 38 ATP molecules.
Aerobic respiration takes place in three stages-Glycolysis,
Kerb’s cycle and Electron transport system.
Q. 16. Label the diagram and explain. 3
1. Label the diagram: Human Respiratory System.
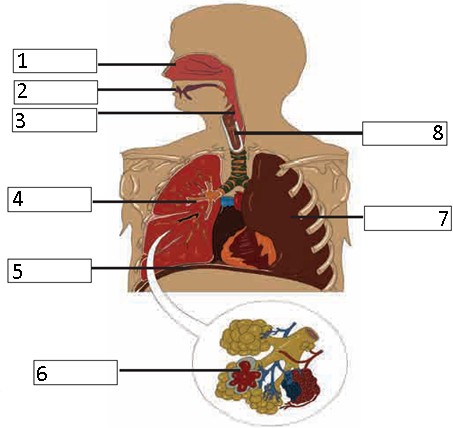
Ans i. Nasal cavity
- Mouth
- Larynx
- Bronchus
- Diaphragm
- Alveoli
- Left lung viii.Trachea
Q. 17. Complete the table/ web/ flow chart 6
1.Correct the following flow chart.
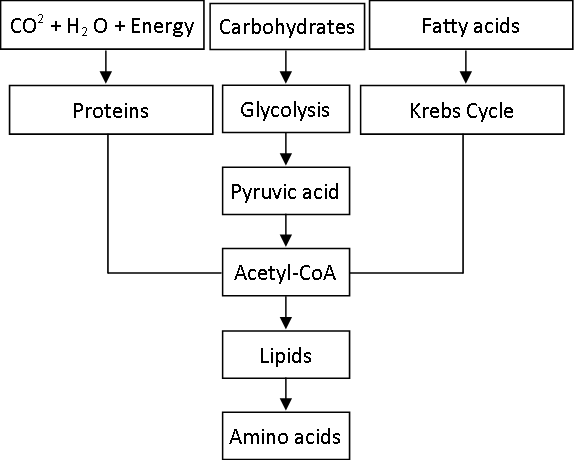
Ans
2.Complete the following table related to Proteins Amino Acids
| Name of Protein/ Amino acids | Where it is found |
| i. …………………………. | Skin |
| ii. Ossein | …………… |
| iii…………………… | Pancreas |
| iv. Actin and Myosin | …………… |
| v. ……………………… | Blood |
Ans
| Name of Protein/ Amino acids | Where it is found |
| i. Melanin, Keratin | Skin |
| ii. Ossein | Bones |
| iii. Insulin, Trypsin | Pancreas |
| iv. Actin and Myosin | Muscles |
| v. Hemoglobin | Blood |
Q.18. Complete the sentences in paragraph 9
1. Select the appropriate options and rewrite the following paragraph.
(Proteins, testosterone, 9 Kcal, epithelial, phospholipids, lipids, growth harmone, progesterone, 4 Keal, adipose connective)
Digestion of …………… results in formation of fatty acids and glycerol. Different cells use fatty acid to produce various substance necessary to themselves. For e.g. the molecules called …………… are required for production of plasma membrane. Fatty acids are required for production of hormones like …………… .estrogen, …………… , aldosterone, etc, and the covering around the axons of nerve cells. We get ofenergy per gram fo lipids. Excess lipids are stored in tissue in the body.
Ans: Digestion of lipids results in formation of fatty acids and glycerol. Different cells use fatty acid to produce various substance necessary to themselves. For e.g. the molecules called phospholipids are required for production of plasma membrane. Fatty acids are required for production of hormones like progesterone . estrogen, testosterone , aldosterone, etc, and the covering around the axons of nerve cells. We get 9 Kcal of energy per gram fo lipids. Excess lipids are stored in adipose connective tissue in the body.
2. Complete the paragraph.
(ATP, mitochondria, external, internal, inhalation, alveolar, breathing, respiration exhalation, Nitrogen) Release of energy from the assimilated food is called …………… . Inhalation and exhalation is called …………… . When …………… is done, air enters the lungs. The oxygen from this air enters the blood while carbon dioxide from the blood exits from the blood. Through exhalation, CO2 is given out. This gaseous exchange occurs through …………… membrane. This is called …………… respiration. The RBC’s carry oxygen to every cell. Here inside the …………… tissue respiration or respiration takes place.The oxygen is used for production of energy. By oxidation of food nutrients, energy is released in the form of……………. .
Ans Release of energy from the assimilated food is called respiration. Inhalation and exhalation is called breathing. When inhalation is done, air enters the lungs. The oxygen from this air enters the blood while carbon dioxide from the blood exits from the blood. Through exhalation, CO2 is given out. This gaseous exchange occurs through alveolar membrane. This is called external respiration. The RBC’s carry oxygen to every cell. Here inside the mitochondria tissue respiration or internal respiration takes place. The oxygen is used for production of energy. By oxidation of food nutrients, energy is released in the form of ATP.
3. Complete the paragraph.
(genetically, recombination, gamete, crossing over, haploid, diploid, Meiosis-II, meiosis-I, zygote)
…………… is just like mitosis. In this stage, the two haploid daughter cells formed in undergo
division by separation of recombined sister chromatids and four …………… daughter cells are formed. Process of …………… production and spore formation occurs by meiosis. In this type of cell division, four haploid (n) daughter cells are formed from one …………… cell. During this cell division, occurs between the
homologous chromosomes and thereby genetic …………… occurs. Due to this, all the four daughter cells are different from parent cell and from each other too.
Ans Meiosis-II is just like mitosis. In this stage, the two haploid daughter cells formed in meiosis-I undergo division by separation of recombined sister chromatids and four haploid daughter cells are formed. Process of gamete production and spore formation occurs by meiosis. In this type of cell division, four haploid (n) daughter cells are formed from one diploid cell. During this cell division, crossing over occurs between the homologous chromosomes and thereby genetic recombination occurs. Due to this, all the four daughter cells are genetically different from parent cell and from each other too.
Q.19. Write answers based on given diagram/ figure 6
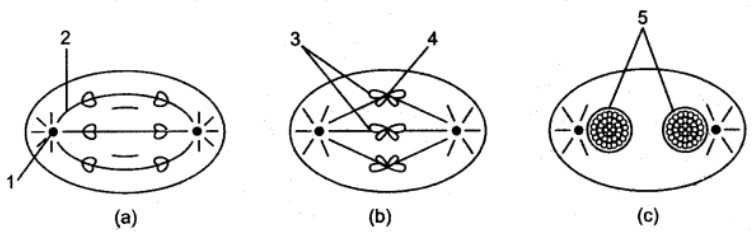 1. Identify the stages of mitosis given below and label the figure from the alternatives provided. (Spindle fibers, Centrioles, Daughter nuclei, Chromosomes, Centromere)
1. Identify the stages of mitosis given below and label the figure from the alternatives provided. (Spindle fibers, Centrioles, Daughter nuclei, Chromosomes, Centromere)
Ans i. Stages :
a. Anaphase b. Metaphase c. Telophase
Label :
a. Centriole b. Spindle fibers c. Chromosomes d. Centromere e. Daughter nuclei
22.
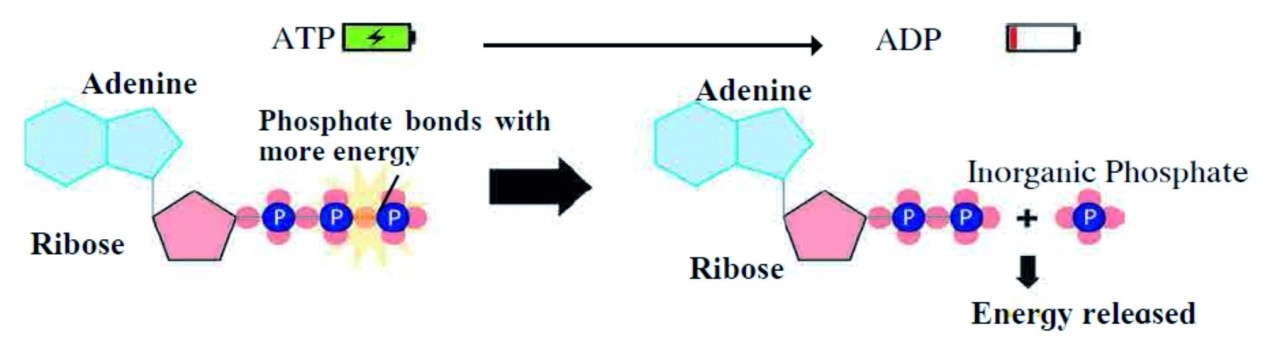
i. What is ATP composed of ?
ii. Explain why ‘ATP is called as energy currency of the cell”.
Ans . i. ATP is composed of a nitrogenous compound (adenine), pentose sugar (ribose) and three phosphate groups.
ii. ATP is called on energy currency of the cell because;
a. ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) is an energy-rich molecule.
b. Energy is stored in the bonds that join phosphate groups in ATP.
c. ATP is stored in a cell as per the energy requirements of the cell.
d. As per the energy need, phosphate bonds of ATP are broken and energy is derived.
Q..20. Answer the following 21
1. i. What do you mean by diploid (2n)cell ?
ii. What do you mean by haploid (n) cell ?
iii. What do you mean by homologous chromosomes ?
Ans i. A diploid cell is a cell that contains two sets of chromosomes.
A haploid cell is a cell that contains a single set of chromosomes.The cell that has two sets of each chromosomes, one pair is derived from its mother and the other derived from its father.
2. 1. What is Meiosis?
2.What is the significance of meiosis? (any 2)
3.Why is meiosis called a reductional division?
Ans i. i. Meiosis is the process involving the reduction in the amount of genetic material.
ii. Significance of meiosis are :
Meiosis maintains the chromosomes number from generation to generation. It reduces the chromosome number to half so that the process of fertilization restores the original number in the zygote.
Variations are caused by the cross-over and the random distribution of homologous chromosomes between daughter cells. Variations play an important role in evolution.
Chromosomal mutations are brought about by the introduction of certain abnormalities. These chromosomal mutations may be advantageous for an individual.
iii. Meiosis is called as reductional cell division since the four daughter cells formed have half the number of chromosomes than the mother cell.
3. How all the life processes contribute to the growth and development of the body ?
Ans i. The process which maintains the body functions and are necessary for survival are called life processes.
Different life processes of an organism, like growth and maintenance require energy which is obtained from food by a process called nutrition.
Nutrients are substances that give nourishment, which provides energy to an organism. Cells obtain
nutrients from the food taken by the organism. Nutrition promotes growth of the body and meets the energy requirement of the body.
Food is broken down into simpler forms by a stepwise process called as respiration. During this process,
oxygen is commonly required by organisms to release energy from food for carrying out various life processes.
In multicellular organisms all the cells are not in contact with the environment. The exchange of gases and
the uptake of food occur in specialized tissues. So food and oxygen have to be transported to all the parts of the body by the transportation system.
Living things produce new individuals similar to themselves by a process called reproduction.
All these life processes is coordinated by the control system of the body.
Thus, each life process contributes in its own way in the process of growth, development and energy production of the body.
4. i. How are the haploid cells formed ?
ii.What is the importance of haploid cells ?
Ans: Gametes contain half the chromosomes contained in the normal diploid cells of the body which are known
as somatic cells. Haploid gametes are produced during meiosis, which is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in a parent diploid cell by half.
Haploid cells are usually the gamete cells of any organism and hence the gametes unite during fertilization and thus help in restoring the diploid number.
5. i. What is cell division ?
ii. Which type of cell division occurs in somatic cells of the body ? iii.Where does meiosis occur in the body ?
Ans i. Cell division is the process of formation of new cells or daughter cells from the pre-existing cells or parent cells.
Mitotic cell division occurs in somatic cells of the body.In our body, meiosis occurs in germ cells.
6.i. Why some living organisms have to perform anaerobic respiration?
ii. Give examples of such living organisms.
iii. What are the two steps of anaerobic respiration?
Ans i. Some organisms cannot live in presence of oxygen, hence they have to perform anaerobic respiration for energy production.
ii. Yeast, seeds submerged in water, our muscle cells while exercising. iii.Glycolysis and fermentation are two steps of anaerobic respiration.
7. Why is ATP called as ‘energy currency’ of the cell ?
Ans ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) is energy-rich molecule and the energy is stored in the bonds by which phosphate groups are attached to each other.
These molecules are stored in the cells as per need.
Chemically, ATP is triphosphate molecule formed from adenosine ribonucleoside.
It contains a nitrogenous compound-adenine, pentose sugar-ribose and three phosphate groups.
As per the need, energy is derived by breaking the phosphate bond of ATP, hence ATP is called as ‘energy currency’ of the cell.
Q.. 21. Answer the following in detail 30
1. i. What do you mean by cell-cycle ?
ii. Why gametes have a haploid number of chromosomes ? iii.What is cytokinesis ?
iv.What is the importance of meiosis in creating variations ?
Ans i.Every cell capable of cell division process through different stages or phase in a cyclic manner. It is called the cell-cycle.
ii. The gametes are produced as a result of meiosis hence they have haploid number of chromosomes and after fertilization a diploid zygote can be obtained.
During cell division karyokinesis is followed by the division of cytoplasm. It is called cytokinesis. Cytokinesis is the division of cytoplasm.
iii. During meiosis, the exchange of chromosomal material takes place between the non-sister chromatids forming new combinations
These new combinations give rise to variations which result in the evolution of species and even in the origin of new species.
2.The diagram below represents a stage during cell division. Study the same and answer the questions.
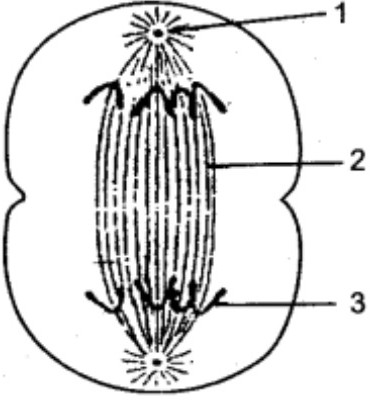
i.Name the labelled parts 1,2 and 3 ?
ii.Identify the above stage and give a reason to support your answer ? iii.Give an example of this type of cell division in the body ?
iv.Name the stage prior to this stage ?
Ans i. 1. Centriole 2. Spindle fibers 3. Chromatids
ii. Anaphase. The daughter chromosomes are reaching to the opposite poles of the cell. iii.It is Mitosis and this type of cell division is seen in the somatic cells of the body.
iv.Metaphase is the phase prior to this stage.
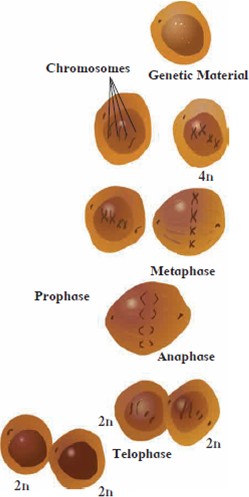
3. Explain in detail the process mentioned in the diagram.
Ans Somatic cells and stem cells divide by mitosis. Mitosis is completed through two main steps. Those steps are Karyokinesis and Cytokinesis.
Karyokinesis is completed through four steps: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
i. Prophase of Mitosis :
In prophase, condensation of basically thin thread-like chromosomes starts.
Due to this, chromosomes become short and thick and they start to appear along with their pairs of sister chromatids.
Centrioles duplicate and each centriole moves to opposite poles of the cells.
Nuclear membrane and nucleolus start to disappear.
ii. Metaphase of Mitosis :Nuclear membrane completely disappears in metaphase.
Chromosomes complete their condensation and become clearly visible along with their sister chromatids.
All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane of the cell.
Special type of flexible protein fibers are formed between centromere of each chromosome and both centrioles.
iii. Anaphase of Mitosis :
In anaphase, centromere spilt and thereby sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and they are pulled apart in opposite direction with the help of spindle fibers.
Separated sister chromatids are called as daughter chromosomes.
Chromosomes being pulled appear like bunch of bananas.
In this way, each set of chromosomes reach at two opposite poles of the cell.
iv. Telophase of Mitosis :
- i.The chromosomes which have reached the opposite poles of the cell start to decondense due to which they again become thread-like thin and invisible.
ii.Nuclear membrane is formed around each set of chromosomes reached poles.
Iii.Thus, two daughter nuclei are formed in a cell and spindle fibers completely disappear.
Iv.Nucleolus also appears in each daughter nucleus.
v. Cytokinesis in Mitosis :
a. The cytoplasm divides by cytokinesis and two new cells are formed which are called as daughter cells.
b .In cytokinesis, a notch is formed at the equatorial plane of cell which deepens gradually and thereby two new cells are formed.
c. However, in case of plant cells, instead of the notch, a cell plate is formed exactly along midline of the cell and thus cytokinesis is completed.
4. Arrange the following in the given Anaerobic respiration in living organisms/cells chart.
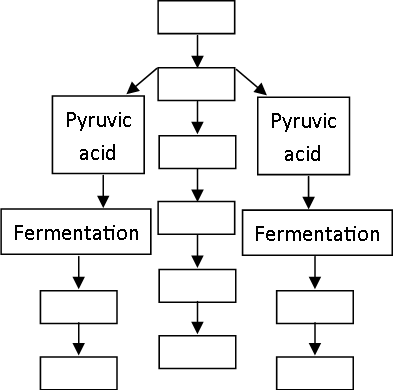 (Various Microbes, Erythrocytes, Muscle cells, Yeast, Different Products Ex: Vinegar, Vitamins, etc., Lactic acid, Alcohol, Pyruvic acid, Glycolysis, Glucose)
(Various Microbes, Erythrocytes, Muscle cells, Yeast, Different Products Ex: Vinegar, Vitamins, etc., Lactic acid, Alcohol, Pyruvic acid, Glycolysis, Glucose)
Ans
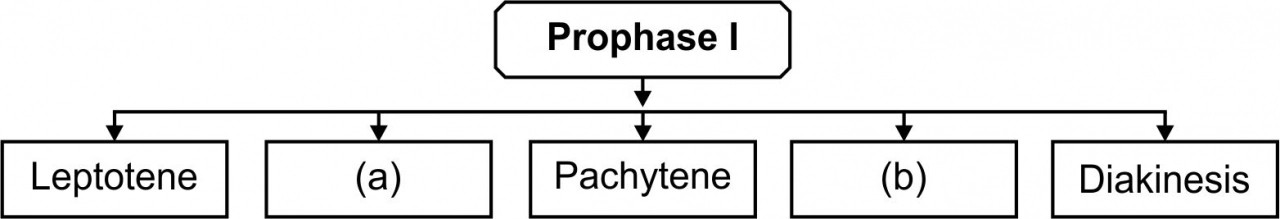
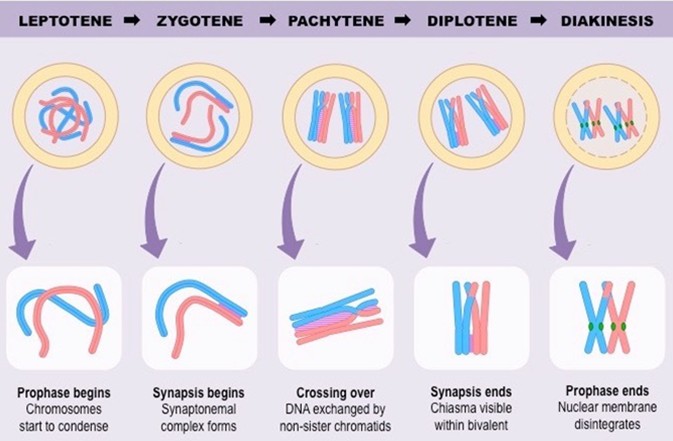 5.Explain the five stages of prophase-I of meiosis given in the diagram.
5.Explain the five stages of prophase-I of meiosis given in the diagram.
Ans The Prophase of the first meiotic division is typically longer and more complex when compared to prophase of mitosis.
It is further subdivided into the following five phases based on chromosomal behavior.i.e. Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene and Diakinesis.
i. Leptotene :
The chromosomes gradually become visible. This compaction of chromosomes continues throughout
leptotene.
Ii. Zygotene :
a. Chromosomes start pairing together and this process of association is called synapsis.
b. Such paired chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes.
Iii. Pachytene :
a. During this stage bivalent chromosomes clearly appears as tetrads.
b. This stage is characterized by the appearance of recombination nodules, the sites at which crossing over occurs between non sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
c. Crossing over leads to recombination of genetic material on the two chromosomes.
Iv. Diplotene :
The recombined homologous chromosomes of the bivalent tend to separate from each other except at the site of crossover.
These X shaped structures are called as chiasmata.
V. Diakinesis :
a. The final stage of meiotic prophase-I is diakinesis.
b. During this phase, the chromosomes are fully condensed and the meiotic spindle is assembled to prepare the homologous chromosomes for separation.
c. By the end of diakinesis, the nucleus disappears and the nuclear envelope also breaks down.
d. Diakinesis represents transition to metaphase.
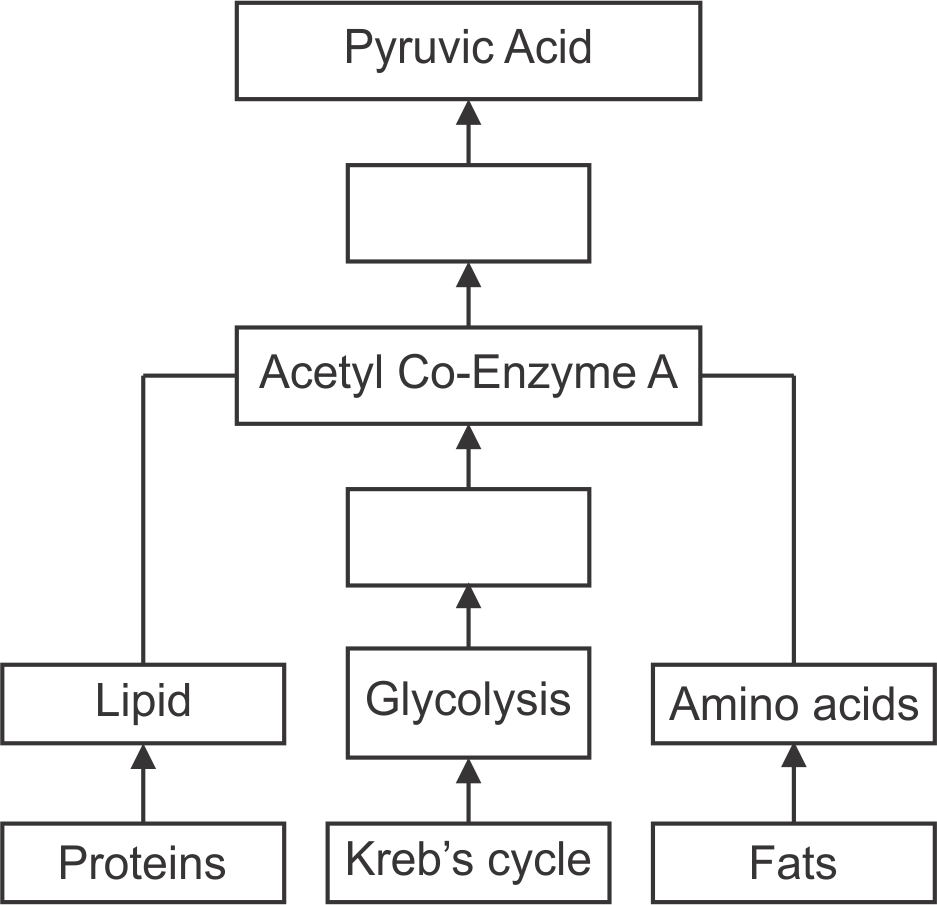 6. Redraw the flow-chart with corrections. Explain in brief the process of obtaining energy through oxidation of carbohydrates, lipids & proteins.
6. Redraw the flow-chart with corrections. Explain in brief the process of obtaining energy through oxidation of carbohydrates, lipids & proteins.

Ans Corrected flow-chart-
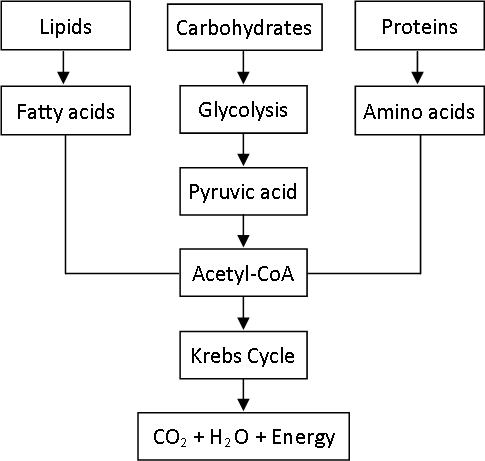
Process of obtaining the energy
Carbohydrates–Carbohydrates like glucose are oxidized to pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid is converted to acetyl- co-enzyme-A which is oxidized through Kreb’s cycle. The molecules of NADH2 produced during this are oxidized through electron transfer chain reaction and finally energy is obtained.
Proteins- Proteins are digested to amino acids and amino acids are converted into acetyl-co-enzyme-
A. Acetyl-co-enzyme-A is oxidized through Kreb’s cycle. The molecules of NADH2 produced during this are oxidized through electron transfer chain reaction and finally energy is obtained.
Lipids- Lipids are converted to fatty acids and fatty acids to acetyl-coenzyme- A. Acetyl-co-enzyme- A is oxidized through Kreb’s cycle. The molecules of NADH2 produced during this are oxidized through electron transfer chain reaction and finally energy is obtained.
Q.22. Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statements 8
1. The nuclear membrane completely disappears in of mitosis.
Ans The nuclear membrane completely disappears in metphase of mitosis.
2. Meiosis-II produces …………… cells, each of which is ……………. .
Ans Meiosis-II produces four cells, each of which is haploid.
3. Excess of is stored in adipose connective tissue in the body.
Ans Excess of lipids is stored in adipose connective tissue in the body.
4. When the cytoplasm divides in telophase, the two new cells formed are called as cells.
Ans When the cytoplasm divides in telophase, the two new cells formed are called as daughter cells.
5. ………..and cells divide by mitosis.
Ans Somatic and stem cells divide by mitosis.
6. The process of gamete production and spore formation occurs by …………… .
Ans The process of gamete production and spore formation occurs by meiosis.
7. ……is called as the energy currency of the cell.
Ans ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) is called as the energy currency of the cell.
8. Our muscle cells perform type of respiration during exercise.
Ans Our muscle cells perform anaerobic type of respiration during exercise