Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 18 Observing Space: Telescopes Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 18 Observing Space: Telescopes
Q.1. Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statements 31
- The Newtonian and Cassegrain telescopes use to reflect the light coming from the space.
Ans The Newtonian and Cassegrain telescopes use concave mirror to reflect the light coming from the space.
- The wavelength of rays is shorter than 3 pm.
Ans The wavelength of Gamma rays is shorter than 3 pm.
- The wavelength of Visible light rays is between …………… and …………… .
Ans The wavelength of Visible light rays is between 400 nm and 800 nm.
- The …………… series of satellite is used for monitoring and management of natural resources as well as disaster management.
Ans The IRS series of satellite is used for monitoring and management of natural resources as well as disaster management.
- A certain X-ray telescope is named after scientist …………… .
Ans A certain X-ray telescope is named after scientist Subramanian Chandrashekhar. 6. Light is an wave.
Ans Light is an electromagnetic wave.
- The biggest optical telescope in India is situated at …………… .
Ans The biggest optical telescope in India is situated at Nainital.
- The wavelength of waves is between 800 nm and 0.3 mm.
Ans The wavelength of Infrared waves is between 800 nm and 0.3 mm.
- Hubble telescope has a diameter of inches.
Ans Hubble telescope has a diameter of 94 inches.
- The only light radiation that our eyes are capable to sense is radiation.
Ans The only light radiation that our eyes are capable to sense is visible radiation.
- The GMRT gives data equivalent to a telescope having a dish with diameter ………….. .
Ans The GMRT gives data equivalent to a telescope having a dish with diameter 25km.
- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration launched an X-ray telescope in space called …………… .
Ans The National Aeronautics and Space Administration launched an X-ray telescope in space called Chandra.
- Using his telescope Galileo discovered the moons of ……………. .
Ans Using his telescope Galileo discovered the moons of Jupiter.
- The wavelength of Ultraviolet rays is between …………… and …………… .
Ans The wavelength of Ultraviolet rays is between 300 pm and 400 nm.
- The first scientist to use a telescope for space observation was …………… .
Ans The first scientist to use a telescope for space observation was Galileo.
- Hubble satellite is orbiting at a height of km from earth.
Ans Hubble satellite is orbiting at a height of 589 km from earth.
- The wavelength of rays is between 300 pm and 400 nm.
Ans The wavelength of Ultraviolet rays is between 300 pm and 400 nm.
- The wavelength of X-rays is between …………… and …………… .
Ans The wavelength of X-rays is between 3 pm and 300 pm.
- The wavelength of light rays is between 400 nm and 800 nm.
Ans The wavelength of Visible light rays is between 400 nm and 800 nm.
- The wavelength of Micro waves is between …………… and …………… .
Ans The wavelength of Micro waves is between 0.3 mm and 20 cm.
- GMRT is used for waves.
Ans GMRT is used for Radio waves.
- Using his telescope Galileo discovered on the sun.
Ans Using his telescope Galileo discovered black spots on the sun.
23 The largest telescope in Asia that is situated at Nainital, has a mirror with diameter …………… .
Ans The largest telescope in Asia that is situated at Nainital, has a mirror with diameter 3.6m.
- The wavelength of is between 3pm and 300 pm.
Ans The wavelength of X-rays is between 3pm and 300 pm.
- The wavelength of Infrared waves is between …………… and …………… .
Ans The wavelength of Infrared waves is between 800 nm and 0.3 mm.
- The wavelength of waves is longer than about 20 cm.
Ans The wavelength of Radio waves is longer than about 20 cm.
- The wavelength of Radio waves is longer than about …………… .
Ans The wavelength of Radio waves is longer than about 20 cm.
- A telescope is used to observe …………… .
Ans A telescope is used to observe space.
- The wavelength of waves is between 0.3 mm and 20 cm.
Ans The wavelength of Micro waves is between 0.3 mm and 20 cm.
- The satellite series is used for education.
Ans The EDUSAT satellite series is used for education.
- The wavelength of Gamma rays is shorter than …………… .
Ans The wavelength of Gamma rays is shorter than 3 pm.
Q.2. Find the odd one out : 3
- Chandra, INSAT, GSAT, Astrosat are satellites.
Ans Chandra is a telescope while others are satellites
- GMRT, Hubble, Chandra, Astrosat
Ans Astrosat is an artificial satellite with multiple telescopes and detectors while others are telescopes that can sense only one type of radiation.
- INSAT, EDUSAT, GMRT, IRS
Ans GMRT is a telescope on earth while others are satellite in space.
Q.3. Match the pair 3
1
| Group A | Group B |
| i. Ultraviolet rays | a. 400 nm and 800 nm |
| ii. X-rays | b. 300 pm and 400 nm |
| iii. Visible light rays | c. 3 pm and 300 pm |
| iv. Gamma rays | e. 0.3 mm and 20 cm |
| f. Shorter than about 3pm | |
| g. Longer than about 20 cm |
Ans
| i. Ultraviolet rays | 300 pm and 400 nm |
| ii. X-rays | 3 pm and 300 pm |
| iii. Visible light rays | 400 nm and 800 nm |
| iv. Gamma rays | Shorter than about 3pm |
2
| Group A | Group B |
| i. Micro waves | a. 300 pm and 400 nm |
| ii. Infrared waves | b. 400 nm and 800 nm |
| iii. Radio waves | c. 3 pm and 300 pm |
| iv. Visible light rays | d. 0.3 mm and 20 cm |
| e. 800 nm and 0.3 mm | |
| f. longer than about 20 cm |
Ans
| i. Micro waves | 0.3 mm and 20 cm |
| ii. Infrared waves | 800 nm and 0.3 mm |
| iii. Radio waves | longer than about 20 cm |
| iv. Visible light rays | 400 nm and 800 nm |
3
| Group A | Group B |
| i. X – rays | a. GMRT |
| ii. Optical telescope | b. ISRO |
| iii. Indian radio telescope | c. Hubble |
| iv. Launching artificial satellites | d. Chandra |
Ans
| i. X – rays | Chandra |
| ii. Optical telescope | Hubble |
| iii. Indian radio telescope | GMRT |
| iv. Launching artificial satellites | ISRO |
Q.4.State True or False 24
- EDUSAT is a satellite used exclusively for education.
Ans EDUSAT is a satellite used exclusively for education – True.
- The IRS series of satellites are used for the monitoring and management of natural resources as well as disaster management.
Ans The IRS series of satellites are used for the monitoring and management of natural resources as well as disaster management –True
- The IRS series of satellites are used for telecommunications network, television broadcasting and meteorological services.
Ans False – The IRS series of satellites are used for the monitoring and management of natural resources as well as disaster management.
- INSAT and GSAT series of satellites are used for telecommunications network, television broadcasting and meteorological services.
Ans INSAT and GSAT series of satellites are used for telecommunications network, television broadcasting and meteorological services – True
- INSAT and GSAT series of satellites are used for the monitoring and management of natural resources as well as disaster management.
Ans False – INSAT and GSAT series of satellites are used for telecommunications network, television broadcasting and meteorological services.
- The biggest optical telescope in India has a diameter of 3.6 km.
Ans False – The biggest optical telescope in India has a diameter of 3.6 m.
- Newtonian telescope uses a combination of concave mirror and convex mirror to reflect the light.
Ans False – Newtonian telescope uses a combination of concave mirror and plane mirror to reflect the light.
- Newtonian and Cassegrain are refracting telescopes.
Ans False – Newtonian and Cassegrain are reflecting telescopes.
- Newtonian and Cassegrain are reflecting telescopes.
Ans Newtonian and Cassegrain are reflecting telescopes – True
- Newtonian telescope uses a combination of concave mirror and plane mirror to reflect the light.
Ans Newtonian telescope uses a combination of concave mirror and plane mirror to reflect the light. – True
- Refracting telescopes are made by using Convex lens.
Ans Refracting telescopes are made by using Convex lens – True
- Cassegrain telescope uses a combination of concave mirror and plane mirror to reflect the light.
Ans False – Cassegrain telescope uses a combination of concave mirror and convex mirror to reflect the light.
- Hubble and Chandra telescope are launched by NASA in space.
Ans Hubble and Chandra telescope are launched by NASA in space – True
- Galileo made the first telescope.
Ans False – Hans Lippershey made the first telescope.
- Astrosat satellite has ultraviolet and X-ray telescopes and detectors.
Ans Astrosat satellite has ultraviolet and X-ray telescopes and detectors – True
- The biggest optical telescope in India is situated in Nainital.
Ans The biggest optical telescope in India is situated in Nainital – True
- Cassegrain telescope uses a combination of concave mirror and convex mirror to reflect the light.
Ans Cassegrain telescope uses a combination of concave mirror and convex mirror to reflect the light – True
- Light is an electromagnetic wave.
Ans Light is an electromagnetic wave – True
- GMRT uses radio waves.
Ans GMRT uses radio waves – True
- GMRT uses Micro waves.
Ans false. GMRT uses radio waves.
- A concave mirror is used in a refracting telescope
Ans False – A convex lens is used in a refracting telescope.
- Hans Lippershey made the first telescope.
Ans Hans Lippershey made the first telescope. – True
- INSAT, GSAT and EDUSAT are satellites launched by ISRO.
Ans INSAT, GSAT and EDUSAT are satellites launched by ISRO – True.
- The biggest optical telescope in India is situated in Narayangaon.
Ans False – The biggest optical telescope in India is situated in Nainital.
Q.5. Name the following 4
1. Name Reflecting telescopes
Ans Newtonian telescope, Cassegrain telescope, GMRT, Hubble and Chandra
2. Name Satellites launched by ISRO
Ans INSAT, GSAT, EDUSAT, IRS and Astrosat
3. Name Indian Telescopes in space
Ans Hubble and Chandra
4. Name Artificial satellites
Ans INSAT, GSAT, EDUSAT, IRS and Astrosat
Q.6. Multiple Choice Questions 9
1. The images formed by as lenses had error in colors known as.
a. Dispersion b. Distortion
c. Chromatic aberration d. None of the above
Ans Option c.
2. Giant Meter wave Radio Telescope has been elected at Narayangaon Near Pune. Scientists from all over the world come here to study.
a. Solar system and solar words
b. Super Nova
c. Interstellar hydrogen clouds
d. All of the above
Ans Option d.
3. A model of a telescope is shown to students It has two or more lenses This is.
a. reflecting telescope b. Refracting telescope
c. Principal telescope d. Radio telescope
Ans Option b.
4. A light wave has a wave length of 500nm this wave is
a. Visible radiation b. Invisible radiation
c. Complete radiation d. Incomplete radiation
Ans Option a.
5. Two telescope launched into space are.
a. Indus, Rave b. Jupiter, Saturn
c. Hubble, Chandra d. Ganga, Gomti
Ans Option c.
6. Two microscope are bought ‘A’ has concave mirror and Plane mirror where as ‘B’ has concave mirror and convex mirror. Which one is Newt onion telescope.
a. Microscope A b. Microscope B
c. Bath A and B d. Neither A Nor B
Ans Option a.
7. It was required to Place telescope in space
a. Optical telescopes could not be used during day because of sunlight
b. In Night city lights and cloudy skies caused difficulties in observing the heavenly bodies
c .Telescope kept in space could give very bright and clean image
d. All of the above
Ans Option d.
8. INSAT, GSAT, MOON, ASTROSAT which statement is correct in regard to the above list:
a. All are as artificial satellite
b. All are natural satellite
c. Moon is the natural satellite and rest all are artificial satellite
d. None of the above
Ans Option c.
9. My friend saw largest optical telescope in Asia, where did he go
A .Aryabhatt Research Institute of Experimental sciences Nainital
b. Nehru science centre Mumbai
c. Indian museum Kolkata
d. Narayan gaon near Pune
Ans Option a.
Q.8. Write Short Notes 14
1. GMRT
Ans i. Giant Meterwave Radio Telescope (GMRT) is situated at Narayangaon near Pune. It uses radio waves having a wavelengths of about a metre, coming from heavenly bodies to study them.
ii. The telescope is actually a collection of 30 dishes, each having diameter 45 m arranged over an area of 25 km.
iii. All the 30 dishes together function as a single dish of diameter 25 km.
iv. GMRT is used to study solar system, solar winds, pulsars, supernova etc.
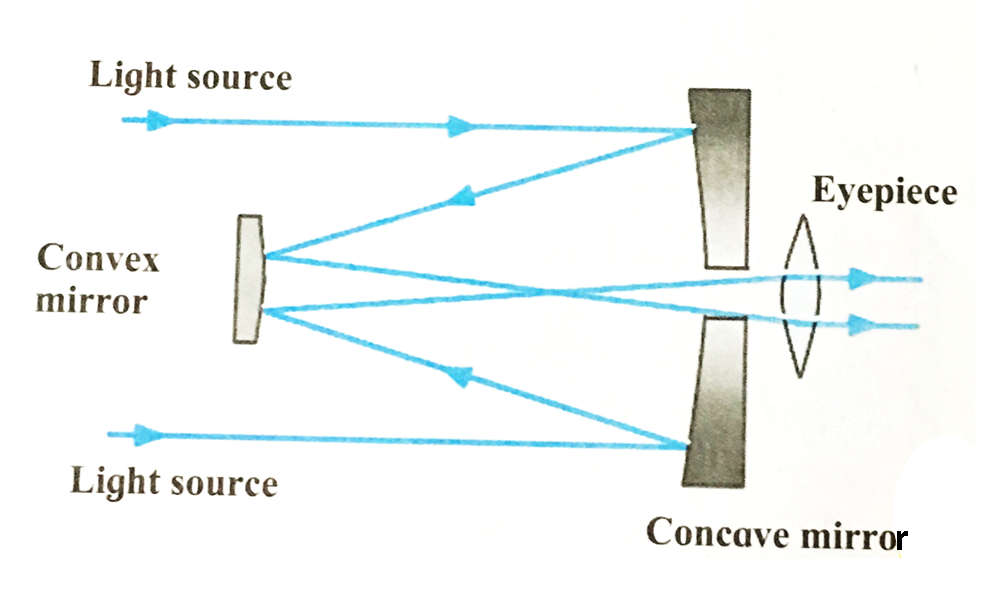
2. Cassegrain telescope
Ans i. The Cassegrain telescopes is a reflecting telescope made with a concave mirrors, convex mirror and an eyepiece.
ii. The light rays coming from the space are reflected by the concave mirror. The light rays after reflection from the concave mirror are reflected back towards a small convex mirror.
iii. After reflection from the convex mirror they diverge and pass through a hole at the centre of the concave mirror and fall on eyepiece.
iv. The eyepiece situated at the back of the concave mirror gives us the magnified image of the source.
3. Chandra
Ans i. The X-ray telescope Chandra was launched by National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in the year 1999.
ii. This telescope is named after the famous Indian scientist Subramanian Chandrashekhar.
iii. This telescope is used to study the X-rays coming from heavenly bodies.
iv. Spherical mirrors that can reflect X-rays are used in this telescope.
v.Chandra gives very useful information about stars and galaxies.
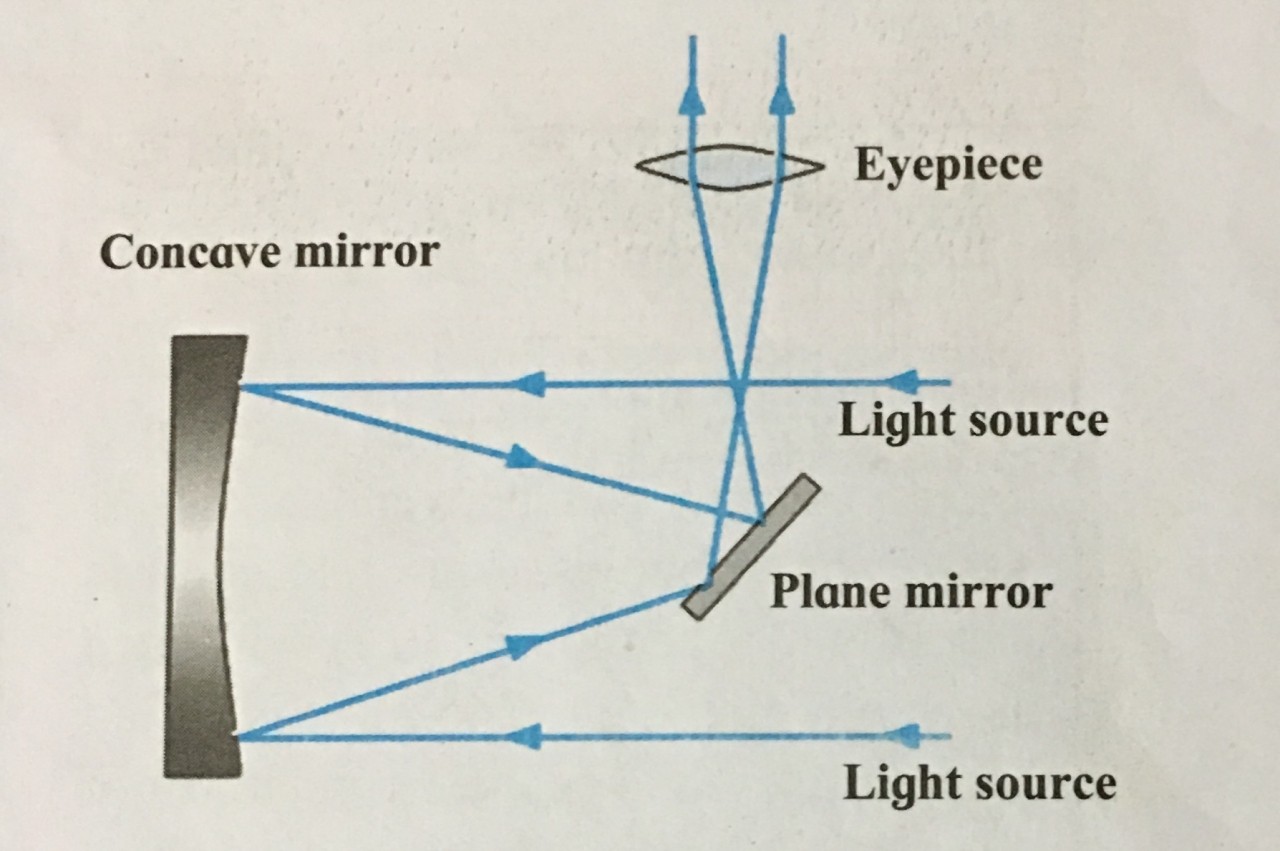
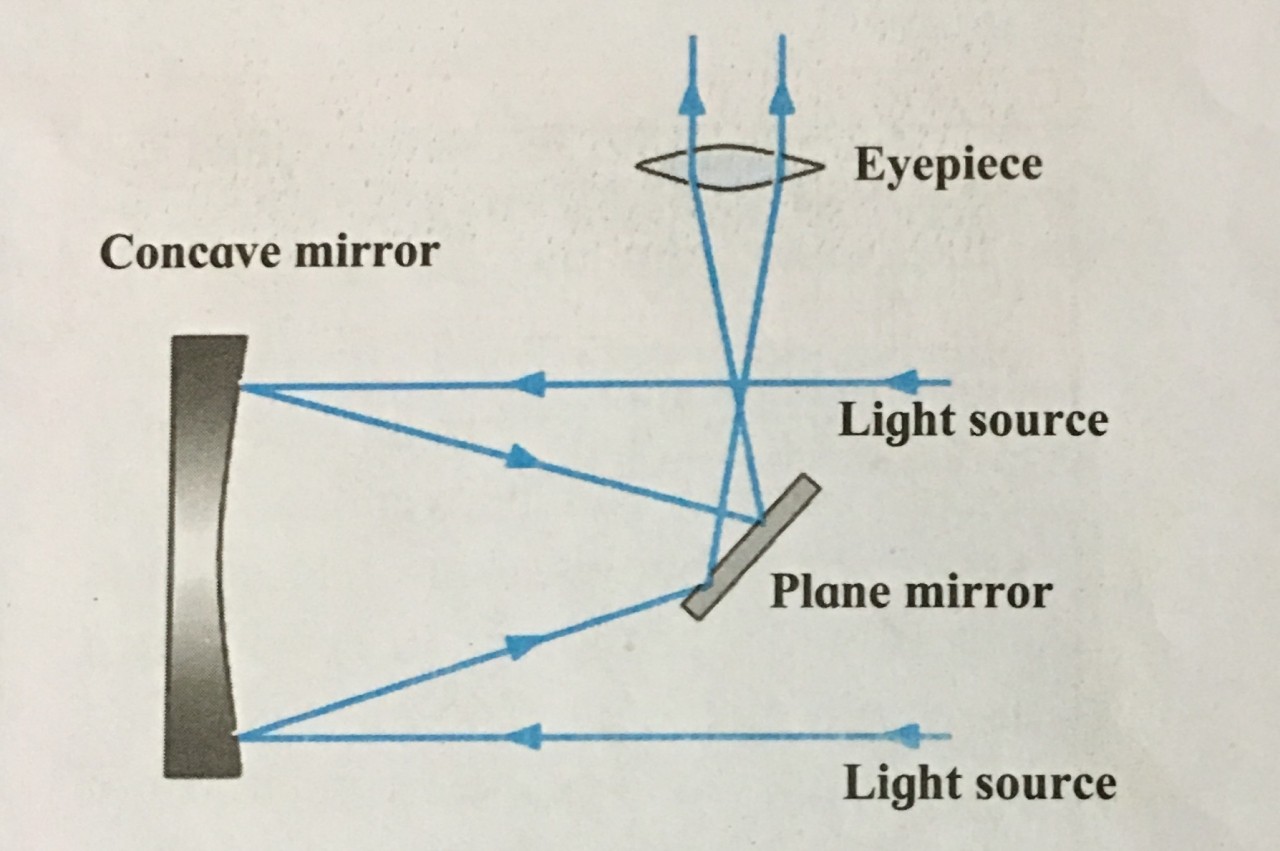
4. Newtonian telescope
Ans i. The Newtonian telescopes is a reflecting telescope made with a concave mirrors, plane mirror and an eyepiece.
ii. The light rays coming from the space are reflected by the concave mirror.
iii. Before these rays converge at the focus, they are deflected again by a small plane mirror.
iv. As a result, they get focused at a point lying on the perpendicular to the axis of the telescope cylinder. They pass through eyepiece and we get a magnified image of the source.
4. Refracting telescopes
Ans i. The telescopes made with two or more lenses are called refracting telescopes.
ii. These telescopes consists of an objective lens and an eyepiece.
iii. iTo collect maximum light coming from a heavenly object, the objective lens of refracting telescopes should be made as large as possible.
iv. Using the light collected by the objective lens the smaller lens called eyepiece, produces a large image of the source.
5. Radio telescope
Ans i. Many heavenly objects emit radio waves in addition to visible radiation. We cannot see this radiation with our eyes.
ii. A radio telescope is used to receive these rays.
iii. It is made up of one or more dishes of a particular parabolic shape.
iv. The radio waves incident on the dish are reflected and converged at the focus. A radio receiver is placed at the focus .
v. The information gathered by the receiver is passed on to a computer which analyses it and constructs an image of the source.
6. Write note on the following figure.
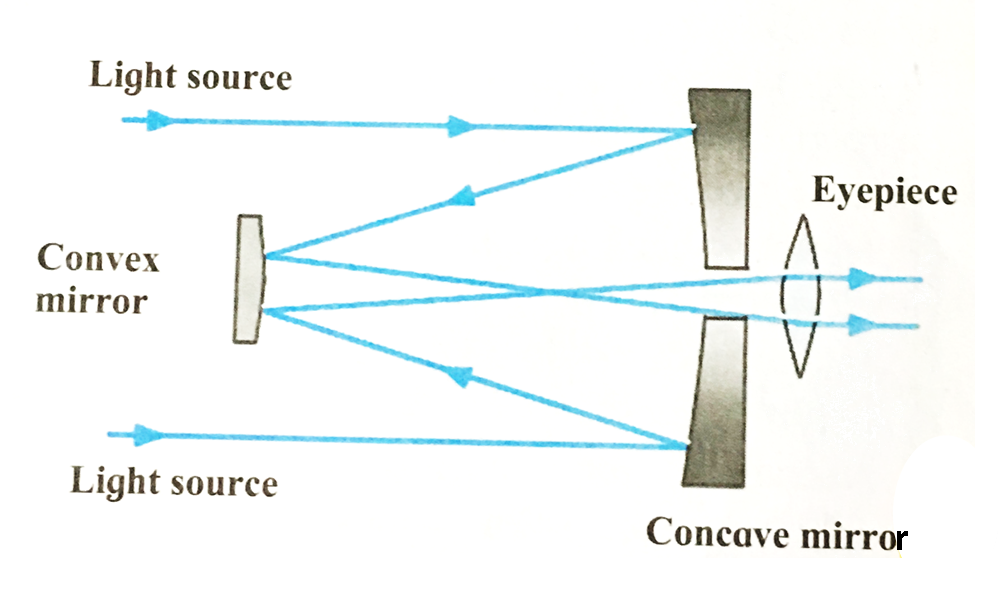
Ans Cassegrain telescopes
i.The light rays coming from the space are reflected by the concave mirror. The light rays after reflection from the concave mirror are reflected back towards a small convex mirror.
ii. After reflection from the convex mirror they diverge and pass through a hole at the centre of the concave mirror and fall on eyepiece.
iii. The eyepiece situated at the back of the concave mirror gives us the magnified image of the source.
Q.9. Attempt the following. 6
1. Complete the table.

Ans:
2
| Type of radiation | Wavelength |
| Radio waves | …………… |
| Visible light rays | …………… |
| X-rays | …………… |
| Gamma rays | …………… |
Ans
| Type of radiation | Wavelength |
| Radio waves | Longer than about 20 cm |
| Visible light rays | 400 nm – 800 nm |
| X-rays | 3 pm – 300 pm |
| Gamma rays | Shorter than 3pm |
3 Explain the construction of Galileo’s telescope.
Ans i. Galileo made the telescope using spectacle makers glass.
ii. He placed two such lenses on the either end of a hollow cylindrical tube. He used trial and error method to achieve the proper placement of the lenses.
Q. 9. Distinguish between 4
1. Newtonian telescope and Cassegrain telescope.
Ans:
| Newtonian telescope | Cassegrain telescope | |
| i. | The Newtonian telescopes is a reflecting telescope made with a concave mirrors, plane mirror and an eyepiece. | The Cassegrain telescopes is a reflecting telescope made with a concave mirrors, convex mirror and an eyepiece. |
| ii. | The eyepiece is placed perpendicular to the axis of the telescope cylinder. | The eyepiece is placed just behind the hole of the concave mirror. |
2. Refracting telescopes and Reflecting telescopes.
Ans
| Refracting telescopes | Reflecting telescopes | |
| i. | Refracting telescopes the telescopes made with two or more lenses. | Reflecting telescope made with two or more mirrors and an eyepiece. |
| ii. | The image formed by refracting telescopes have more chromatic aberration as compared to reflecting telescopes | The image formed by refracting telescopes have less chromatic aberration as compared to refracting telescopes. |
Q.10. Give scientific reasons 6
1. Astrosat satellite plays an important role for Indian scientists to study Universe.
Ans i. Astrosat is an artificial satellite launched by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in 2015.
ii. This satellite has ultraviolet and X-ray telescope and detectors.
iii. It is a unique system having different kinds of telescopes on a single satellite.
iv. Hence, Astrosat satellite plays an important role for Indian scientists to study various aspects of the Universe using the data obtained with these telescopes.
2. X-ray telescope are not based on earth.
Ans i. X-ray telescopes are used detect the X-rays coming from a heavenly body.
ii. The earth’s atmosphere blocks almost all the X-rays coming towards the surface of the earth.
iii. Due to this reason an X-ray telescope not based on earth.
3. Optical telescopes are located in uninhabited places on mountains.
Ans i. The visible light coming from the heavenly body has to pass through the earth’s atmosphere to reach the earth surface.
ii. During this journey, some light is absorbed by the atmosphere and intensity of light decreases.
iii. The changes in atmospheric pressure and temperatures cause turbulence due to which the direction of light rays changes thereby changing the position of image.
iv. Due to theses reasons optical telescopes located in uninhibited places on mountains.
Q.11. Write properties / characteristics / uses / advantages / effects: 4
1. What are the demerits of refracting telescopes
Ans i. In order to obtain a bright image by collecting maximum light, the lens should be as large as possible. However, it is very difficult to make very large lenses. Also large lenses are very heavy and tend to get distorted.
ii. As objective and eyepiece are at the opposite ends of the telescope, the length of the telescope also increases due to this it becomes difficult to manage the telescope.
iii. The images formed by lenses have errors of colours. This is called chromatic aberration.
2. What are the merits of reflecting telescopes.
Ans i. In order to obtain a bright image by collecting maximum light, the mirror should be as large as possible. It is easier to make very large mirrors compared to making large lenses.
ii. Also a big mirror can be made by combining several smaller pieces.
iii. The weight of large mirror is too less than that of a lens of the same size.
iv. The images formed by mirrors do not have errors of colour. Only by using these large telescopes, can we see far away stars and galaxies, which we could never have seen using our naked eyes.
Q.12. Attempt the following. 6
 1. Identify the telescope and label its parts.
1. Identify the telescope and label its parts.
Ans: The given diagram is of Newtonian telescope
2. Identify the telescope and label its parts.
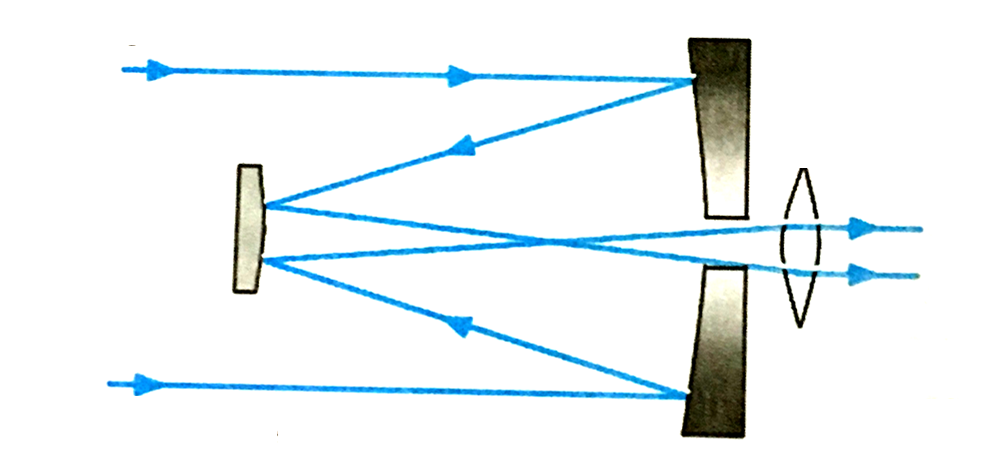
Ans:
The given diagram is of Cassegrain telescope.
Q.13. Label and explain the diagram 6
1. Explain with the help of neat labelled diagram Newtonian telescope.
Ans:
Newtonian telescopes
i. The light rays coming from the space are reflected by the concave mirror.
ii. Before these rays converge at the focus, they are deflected again by a small plane mirror.
iii. As a result, they get focused at a point lying on the perpendicular to the axis of the telescope cylinder.
iv. They pass through eyepiece and we get a magnified image of the source.
2. Explain with the help of neat labelled diagram Refracting telescope.
Ans:
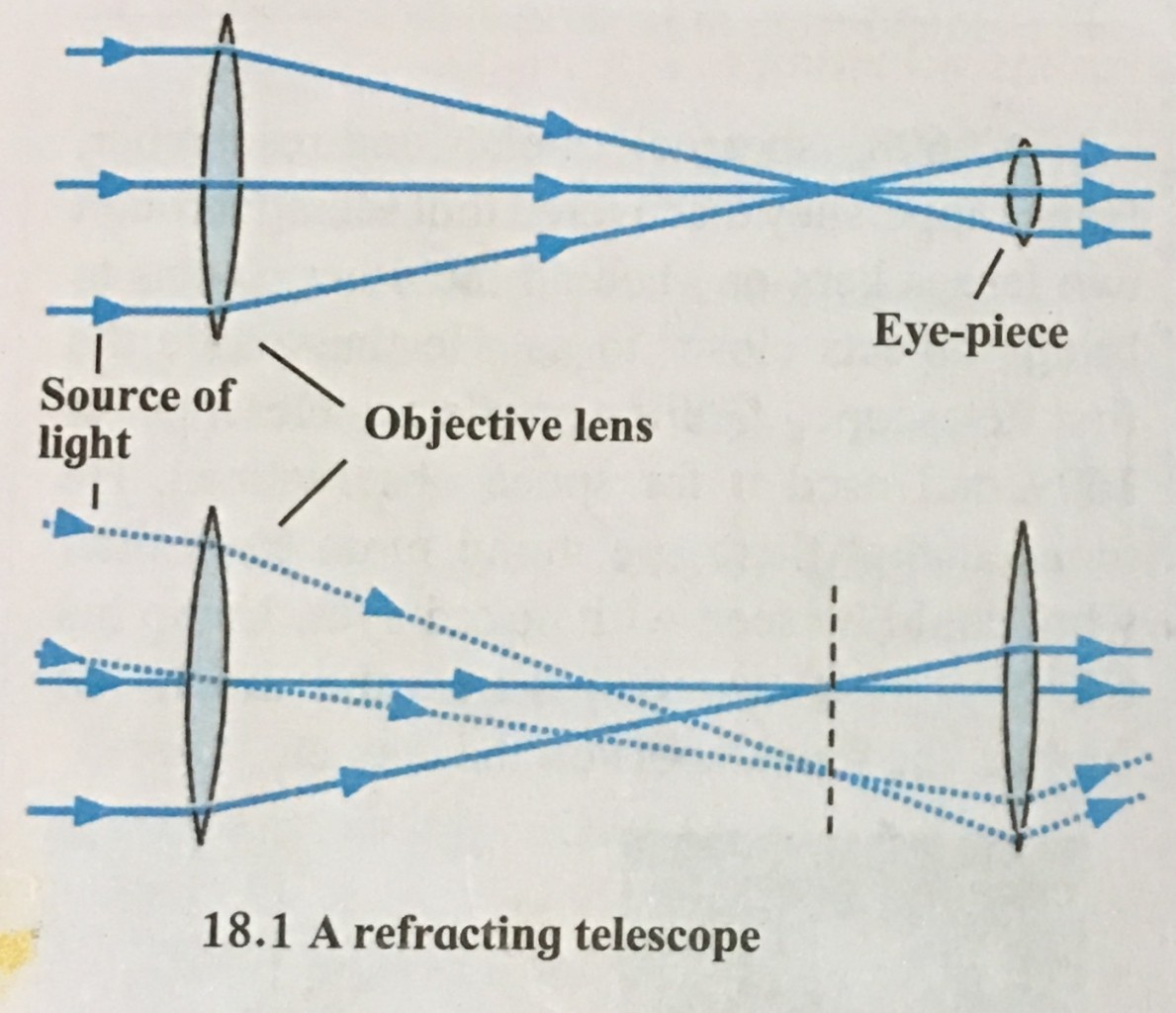
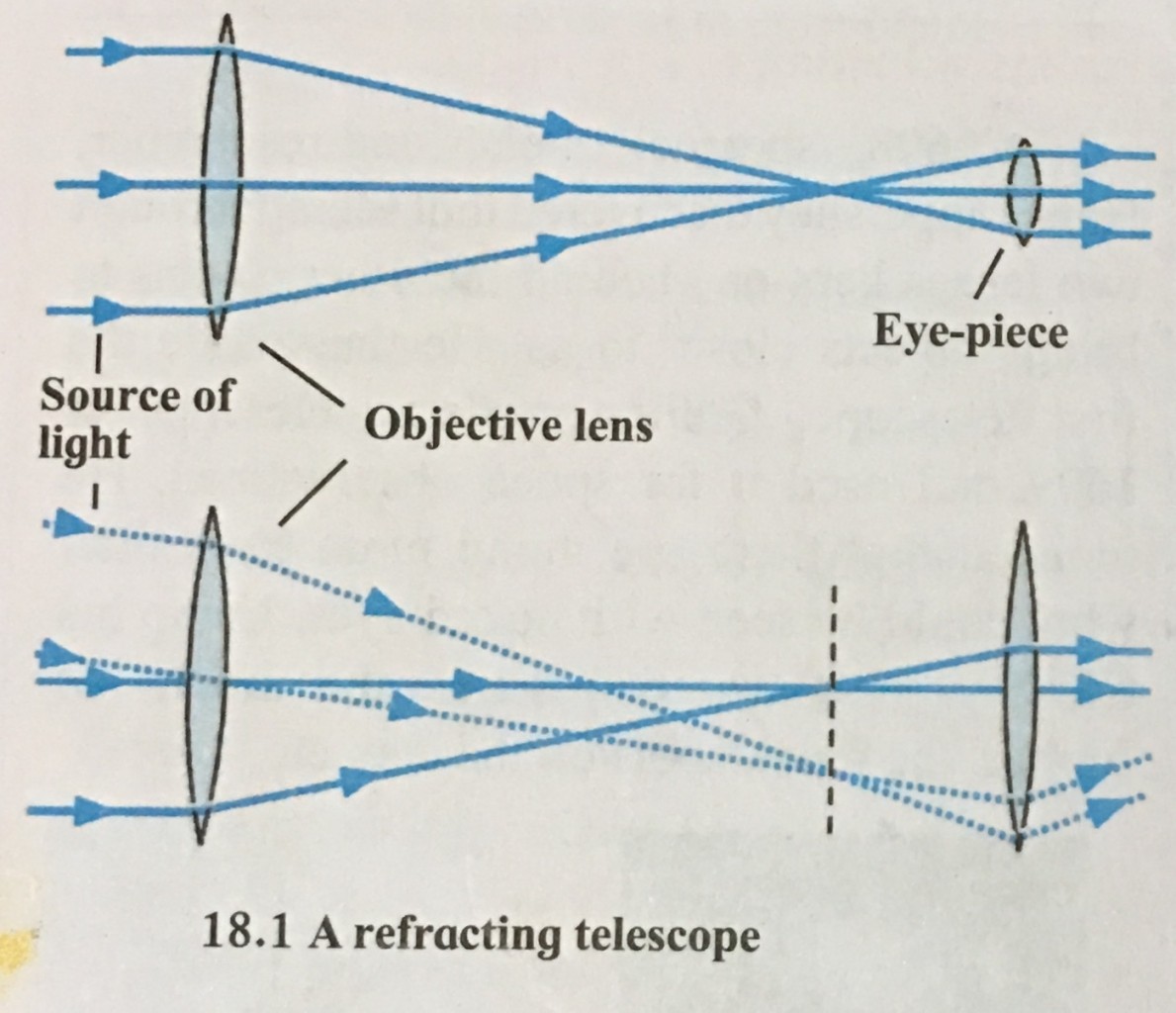
Refracting telescope.
i.The telescopes made with two or more lenses are called refracting telescopes.
ii. These telescopes consists of an objective lens and an eyepiece.
iii. To collect maximum light coming from a heavenly object, the objective lens of refracting telescopes should be made as large as possible.
iv. Using the light collected by the objective lens the smaller lens called eyepiece, produces a large image of the source.
Q.14. Complete the sentences in paragraph 12
1. Complete the paragraph.
(EDUSAT, GSAT, natural disaster, meteorological, INSAT, internet, natural resources, IRS)
The …………… and …………… series of satellites support our telecommunication network, television broadcasting and services. It is because of them that telephone, television and internet services are
available everywhere in the country. The satellite in this series is used exclusively for education.
The …………… satellite series is used for the monitoring and management of as well as disaster
management.
Ans : The INSAT and GSAT series of satellites support our telecommunication network, television broadcasting and meteorological services. It is because of them that telephone, television and internet services are available everywhere in the country. The EDUSAT satellite in this series is used exclusively for education. The IRS satellite series is used for the monitoring and management of natural resources as well as disaster management.
2. Complete the paragraph.
(INSAT, 25 km, 54 km, 1 metre, Narayangoan, 45 m, giant, 25 km, GMRT)
…………… is a radio telescope which uses radio waves having wavelength of about coming from
heavenly bodies. GMRT is located at …………… near Pune. It is a collection of 30 dishes each having a diameter of This collection of 30 dishes is spread across an area measuring upto 25 km. It is
designed in such a way that it works as a single dish of …………… diameter. Thus, it is called as ……………
telescope. GMRT is used for the study of solar system, solar winds, pulsars, supernova, interstellar hydrogen clouds, etc.
Ans GMRT is a radio telescope which uses radio waves having wavelength of about 1 metre coming from heavenly bodies. GMRT is located at Narayangoan near Pune. It is a collection of 30 dishes each having a diameter of 45 m. This collection of 30 dishes is spread across an area measuring upto 25 km. It is designed in such a way that it works as a single dish of 25 km diameter. Thus, it is called as giant telescope. GMRT is used for the study of solar system, solar winds, pulsars, supernova, interstellar hydrogen clouds, etc.
3. Complete the paragraph.
(eyepiece, convex, hole, concave, virtual, Cassegrain, magnified, space, object)
…………… telescope consists of a convex mirror, concave mirror and a lens. Light rays coming from ,
after reflection from the concave mirror, are reflected back towards it by a small mirror. These
reflected rays pass through a hole at the centre of the mirror and then through the eyepiece placed
at the back of the concave mirror. In this way, a …………… image of the source is obtained through …………… .
Ans Cassegrain telescope consists of a convex mirror, concave mirror and a lens. Light rays coming from space, after reflection from the concave mirror, are reflected back towards it by a small convex mirror. These reflected rays pass through a hole at the centre of the concave mirror and then through the eyepiece placed at the back of the concave mirror. In this way, a magnified image of the source is obtained through eyepiece.
4. Complete the paragraph:
(optical, X-ray, artificial, 1990, 1999, 2015, radio, 1969)
Hubble telescope is an …………… telescope which was launched into space in Chandra telescope
is an …………… telescope which was launched into space in ……………. Astrosat is an satellite which
was launched into space in …………… .
Ans Hubble telescope is an optical telescope which was launched into space in 1990. Chandra telescope is an X- ray telescope which was launched into space in 1999. Astrosat is an artificial satellite which was launched into space in 2015.
Q.15. Answer the following 24
1. Explain the working of Hubble.
Ans i. The optical telescope Hubble was launched by National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in the year 1990.
ii. It has mirror of diameter 94 inches and is orbiting the earth at a height of 589 km from it.
iii. This telescope has helped to make important discoveries.
2. What is GMRT? Explain its construction and uses.
Ans i. Giant Meterwave Radio Telescope (GMRT) is situated at Narayangaon near Pune. It uses radio waves having a wavelengths of about a metre, coming from heavenly bodies to study them.
ii. The telescope is actually a collection of 30 dishes, each having diameter 45 m arranged over an area of 25 km. All the 30 dishes together function as a single dish of diameter 25 km.
iii. GMRT is used to study solar system, solar winds, pulsars, supernova etc.
3. Explain the construction of a radio telescope.
Ans i. Many heavenly objects emit radio waves in addition to visible radiation. We cannot see this radiation with our eyes.
ii. A radio telescope is used to receive these rays.
iii. It is made up of one or more dishes of a particular parabolic shape.
iv. The radio waves incident on the dish are reflected and converged at the focus. A radio receiver is placed at the focus.
v. The information gathered by the receiver is passed on to a computer which analyses it and constructs an image of the source.
4. Explain the construction and working of Newtonian telescope.
Ans i. The Newtonian telescopes is a reflecting telescope made with a concave mirrors, plane mirror and an eyepiece.
ii. The light rays coming from the space are reflected by the concave mirror.
iii. Before these rays converge at the focus, they are deflected again by a small plane mirror.
iv. As a result, they get focused at a point lying on the perpendicular to the axis of the telescope cylinder.
v. They pass through eyepiece and we get a magnified image of the source.
4. Explain the working of Chandra
Ans i. The X-ray telescope Chandra was launched by National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in the year 1999.
ii. This telescope is named after the famous Indian scientist Subramanian Chandrashekhar.
iii. This telescope is used to study the X-rays coming from heavenly bodies.
Iv Spherical mirrors that can reflect X-rays are used in this telescope.
v. Chandra gives very useful information about stars and galaxies.
5. Explain the construction and working of Cassegrain telescope.
Ans i. The Cassegrain telescopes is a reflecting telescope made with a concave mirrors, convex mirror and an eyepiece.
ii. The light rays coming from the space are reflected by the concave mirror. The light rays after reflection from the concave mirror are reflected back towards a small convex mirror.
Iii .After reflection from the convex mirror they diverge and pass through a hole at the centre of the concave mirror and fall on eyepiece.
iv. The eyepiece situated at the back of the concave mirror gives us the magnified image of the source.
6. What is Radio telescope? Explain it’s working.
Ans i. . Many heavenly objects emit radio waves in addition to visible radiation. We cannot see this radiation with our eyes.
ii. A radio telescope is used to receive these rays.
iii. It is made up of one or more dishes of a particular parabolic shape.
iv. The radio waves incident on the dish are reflected and converged at the focus. A radio receiver is placed at the focus .
v. The information gathered by the receiver is passed on to a computer which analyses it and constructs an image of the source.
7. What are Refracting telescopes?
Ans i. The telescopes made with two or more lenses are called refracting telescopes.
ii.These telescopes consists of an objective lens and an eyepiece.
iii. To collect maximum light coming from a heavenly object, the objective lens of refracting telescopes should be made as large as possible.
iv. Using the light collected by the objective lens the smaller lens called eyepiece, produces a large image of the source.
Q.15. Extra data 10
1. Hubble
Ans i. The optical telescope Hubble was launched by National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in the year 1990.
ii. It has mirror of diameter 94 inches and is orbiting the earth at a height of 589 km from it.
iii. This telescope has helped to make important discoveries.
2. Astrosat
Ans i. Astrosat is an artificial satellite launched by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in 2015.
ii. This satellite has ultraviolet and X-ray telescope and detectors.
iii. Most of the parts used in the satellite are made in India.
iv. It is a unique system having different kinds of telescopes on a single satellite.
V .Indian scientist are studying various aspects of the Universe using the data obtained with these telescopes.
Q.16. Answer the following in detail 15
1. What are the difficulties in using ground based optical telescopes? How are they overcome?
Ans i. The radiations coming from the heavenly body has to pass through the earth’s atmosphere to reach the earth surface.
ii. During this journey, some radiations are absorbed by the atmosphere and intensity of light decreases.
iii. The changes in atmospheric pressure and temperatures cause turbulence due to which the direction of light rays changes thereby changing the position of image.
iv. During day due to sunlight and during night due to city lights we cannot use the telescope efficiently.
v. Changes in seasons or cloudy atmosphere also affects the image formed by the telescope. These difficulties are overcome by the following ways:
a. The optical telescopes should be located in uninhabited places on mountains.
b. The best way to overcome all the above difficulties is to place the telescope in space.
2. Which type of telescope can be made using a concave mirror, convex mirror, plane mirror and a lens? Draw diagrams of these telescopes.
Ans We can make Refracting telescopes and Reflecting telescopes by using a concave mirror, convex mirror, plane mirror and a lens.
 Refracting telescopes: The telescopes made with two or more lenses are called refracting telescopes. These telescopes consists of an objective lens and an eyepiece (lens).
Refracting telescopes: The telescopes made with two or more lenses are called refracting telescopes. These telescopes consists of an objective lens and an eyepiece (lens).
Reflecting telescopes: These telescopes are of two types.
i. Newtonian telescope: The Newtonian telescopes is a reflecting telescope made with a concave mirrors, plane mirror and an eyepiece(lens).

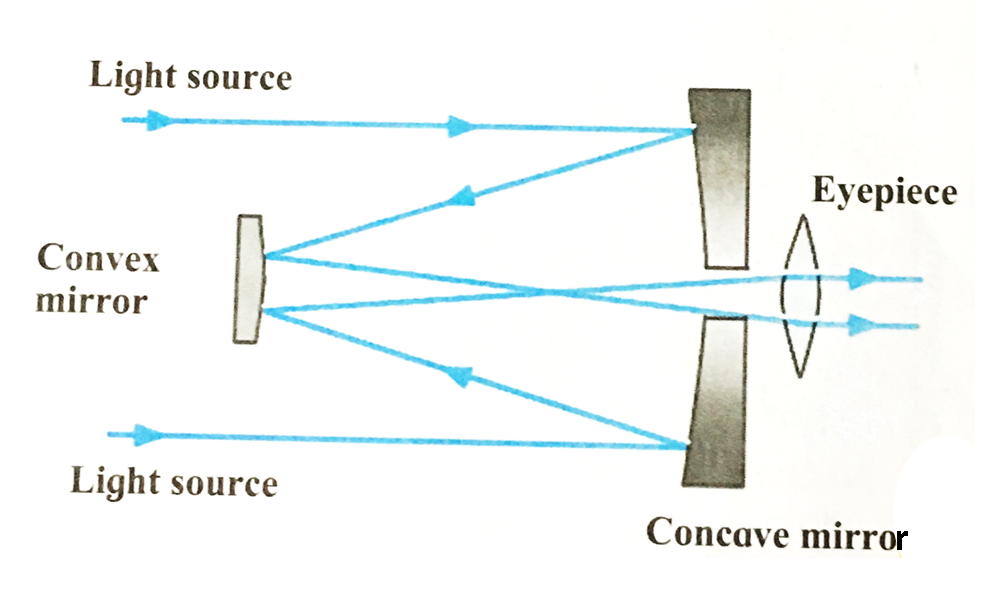 ii. Cassegrain telescope: The Cassegrain telescopes is a reflecting telescope made with a concave mirrors, convex mirror and an eyepiece(lens).
ii. Cassegrain telescope: The Cassegrain telescopes is a reflecting telescope made with a concave mirrors, convex mirror and an eyepiece(lens).
3. Study the figure and answer the following questions.
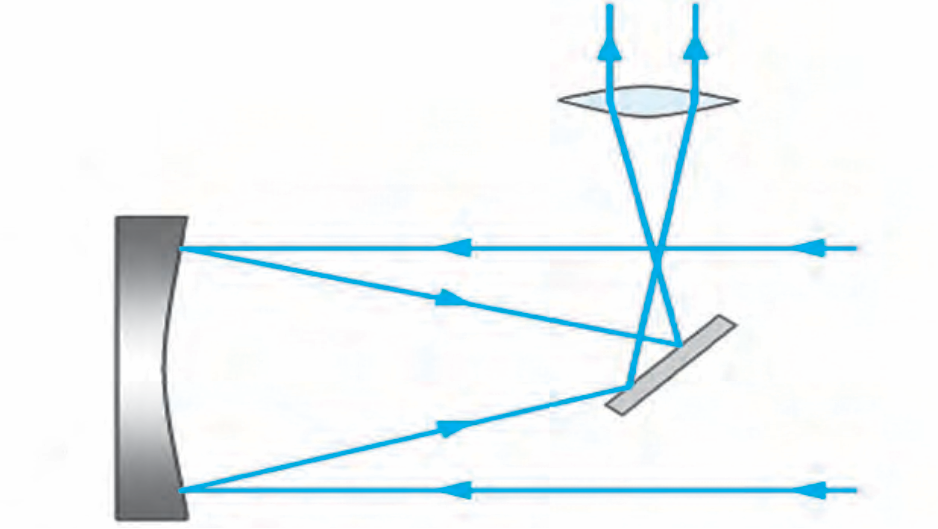
i. What type of telescope is shown in the figure?
ii. What other type of telescope uses a curved mirror?
iii. Label the main parts of the telescope.
iv. Which type of mirror does the telescope use?
Ans i. The figure shows a Newtonian telescope.
ii. Newtonian and Cassegrain telescope also uses curved mirrors. iii.
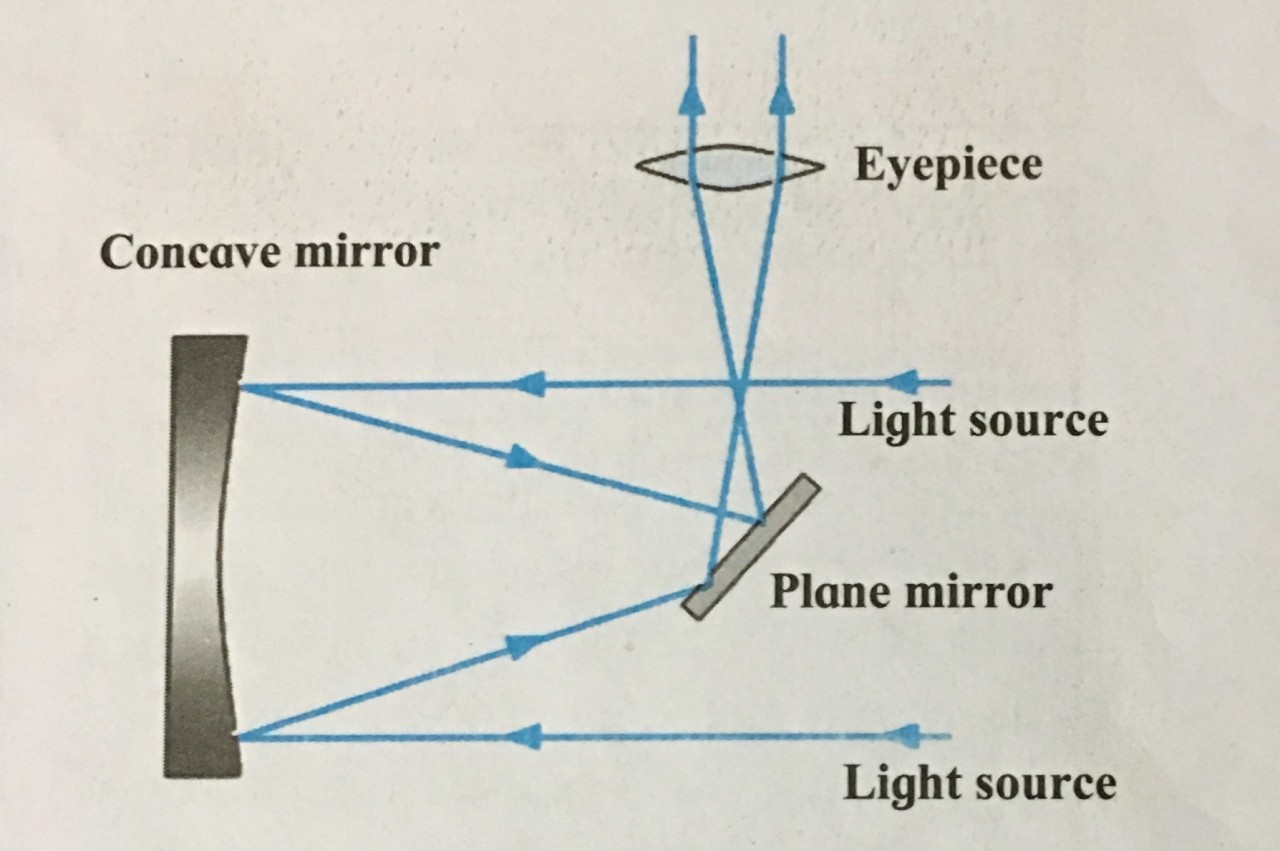
iv.. The telescope uses a Concave mirror and a plane mirror.